Chapter 15: The Milky Way Galaxy
... Where is our solar system located in the Milky Way Galaxy? The solar system is between the Sagittarius and Perseus spiral arms about 26,000 ly from the center of the Galaxy. Is the Sun moving through the Milky Way Galaxy and, if so, how fast? The Sun orbits the center of the Milky Way Galaxy at a sp ...
... Where is our solar system located in the Milky Way Galaxy? The solar system is between the Sagittarius and Perseus spiral arms about 26,000 ly from the center of the Galaxy. Is the Sun moving through the Milky Way Galaxy and, if so, how fast? The Sun orbits the center of the Milky Way Galaxy at a sp ...
Formation and Dynamical Evolution of the Neptune Trojans – the
... Current models of Solar system formation suggest that the four giant planets accreted as a significantly more compact system than we observe today. In this work, we investigate the dynamical stability of pre-formed Neptune Trojans under the gravitational influence of the four giant planets in compac ...
... Current models of Solar system formation suggest that the four giant planets accreted as a significantly more compact system than we observe today. In this work, we investigate the dynamical stability of pre-formed Neptune Trojans under the gravitational influence of the four giant planets in compac ...
CVs
... – Amount of accretion necessary depends on mass of WD – Short time scale (~100yrs) could occur for stars near the ...
... – Amount of accretion necessary depends on mass of WD – Short time scale (~100yrs) could occur for stars near the ...
Jovian Planet Systems
... • How do other jovian ring systems compare to Saturn's? – The other jovian planets have much fainter ring systems with smaller, darker, less numerous particles. • Why do the jovian planets have rings? – Ring particles are probably debris from moons. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • How do other jovian ring systems compare to Saturn's? – The other jovian planets have much fainter ring systems with smaller, darker, less numerous particles. • Why do the jovian planets have rings? – Ring particles are probably debris from moons. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
The Cosmic Perspective Jovian Planet Systems
... • How do other jovian ring systems compare to Saturn's? – The other jovian planets have much fainter ring systems with smaller, darker, less numerous particles. • Why do the jovian planets have rings? – Ring particles are probably debris from moons. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • How do other jovian ring systems compare to Saturn's? – The other jovian planets have much fainter ring systems with smaller, darker, less numerous particles. • Why do the jovian planets have rings? – Ring particles are probably debris from moons. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the fourth largest (by
... about Neptune comes from this single encounter. But fortunately, recent ground-based and HST observations have added a great deal, too. Because Pluto's orbit is so eccentric, it sometimes crosses the orbit of Neptune making Neptune the most distant planet from the Sun for a few years. Neptune's comp ...
... about Neptune comes from this single encounter. But fortunately, recent ground-based and HST observations have added a great deal, too. Because Pluto's orbit is so eccentric, it sometimes crosses the orbit of Neptune making Neptune the most distant planet from the Sun for a few years. Neptune's comp ...
Life on Our Evolving Planet slides
... The National Academy of Sciences says that it is the role of science to provide plausible natural explanations of natural phenomena. The ultimate question for Earth System History is: How did a giant cloud of cold dilute gas and dust evolve into astronauts in a spacecraft orbiting a planet orbiting ...
... The National Academy of Sciences says that it is the role of science to provide plausible natural explanations of natural phenomena. The ultimate question for Earth System History is: How did a giant cloud of cold dilute gas and dust evolve into astronauts in a spacecraft orbiting a planet orbiting ...
Document
... • A protostar forms with a surrounding disk of material (b) • Stellar wind breaks out along the poles of the star (c) • The solar wind sweeps away the cloud material and halts the accumulation of more material and a newly formed star is visible surrounded by a disk (d) ...
... • A protostar forms with a surrounding disk of material (b) • Stellar wind breaks out along the poles of the star (c) • The solar wind sweeps away the cloud material and halts the accumulation of more material and a newly formed star is visible surrounded by a disk (d) ...
Did Saturn`s Rings Form During The Late Heavy Bombardment?
... Triton’s craters or present day ecliptic comets are assumed. With these assumptions, Zahnle et al. derive a cratering rate on Iapetus that is between 2x10-16 km-2year-1 and 8x10-15 km-2year-1 (for craters with diameter D> 10 km). Integrated over the age of the Solar System, these rates would imply a ...
... Triton’s craters or present day ecliptic comets are assumed. With these assumptions, Zahnle et al. derive a cratering rate on Iapetus that is between 2x10-16 km-2year-1 and 8x10-15 km-2year-1 (for craters with diameter D> 10 km). Integrated over the age of the Solar System, these rates would imply a ...
1 Today Kepler`s Laws Question Kepler`s 2nd Law of Planetary Motion
... • Millions of small, rocky bodies • Includes one dwarf planet: Ceres • Most reside in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter • May consist of material that was never able to consolidate into a planet ...
... • Millions of small, rocky bodies • Includes one dwarf planet: Ceres • Most reside in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter • May consist of material that was never able to consolidate into a planet ...
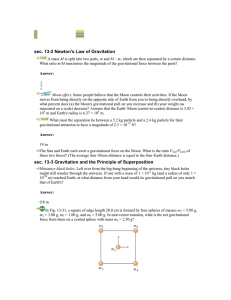
Halliday 9th chapter 13
... Certain neutron stars (extremely dense stars) are believed to be rotating at about 1 rev/s. If such a star has a radius of 20 km, what must be its minimum mass so that material on its surface remains in place during the rapid rotation? Answer: 5 × 1024 kg ••22The radius Rh and mass Mh of a black hol ...
... Certain neutron stars (extremely dense stars) are believed to be rotating at about 1 rev/s. If such a star has a radius of 20 km, what must be its minimum mass so that material on its surface remains in place during the rapid rotation? Answer: 5 × 1024 kg ••22The radius Rh and mass Mh of a black hol ...
Celestial Motions
... shadow, and its appearance to us is determined by the relative positions of Sun, Moon, and Earth. • What causes eclipses? – Lunar eclipse: Earth’s shadow on the Moon – Solar eclipse: Moon’s shadow on Earth – Tilt of Moon’s orbit means eclipses occur during two periods each year. © 2010 Pearson Educa ...
... shadow, and its appearance to us is determined by the relative positions of Sun, Moon, and Earth. • What causes eclipses? – Lunar eclipse: Earth’s shadow on the Moon – Solar eclipse: Moon’s shadow on Earth – Tilt of Moon’s orbit means eclipses occur during two periods each year. © 2010 Pearson Educa ...
File - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... TEK 8.7A – the student knows the effects resulting from cyclical movements of the Sun, Earth, and Moon. The student is expected to model and illustrate how the tilted Earth rotates on its axis, causing day and night, and revolves around the sun causing changes in seasons. ...
... TEK 8.7A – the student knows the effects resulting from cyclical movements of the Sun, Earth, and Moon. The student is expected to model and illustrate how the tilted Earth rotates on its axis, causing day and night, and revolves around the sun causing changes in seasons. ...
1 We finished our last lecture by examining the “Jovian planets” of
... – and remember, they have many such moons – suffer from frequent collisions with free-floating debris attracted by their planet’s immense gravity. These collisions can kick up enough dust and rocks to keep small rings like those around Jupiter, Uranus, and Neptune populated with particles for billio ...
... – and remember, they have many such moons – suffer from frequent collisions with free-floating debris attracted by their planet’s immense gravity. These collisions can kick up enough dust and rocks to keep small rings like those around Jupiter, Uranus, and Neptune populated with particles for billio ...
– 1 – 1. Historical Notes for Ay 123 1.1.
... Self gravitating sphere (or almost sphere) of gas with a finite definable radius, not easily deformed, not like a cloud in the Earth’s atmosphere Nuclear reactions occur at least to the point where 3 He is produced. radiates energy into the surrounding medium. Jupiter also does this, some internal h ...
... Self gravitating sphere (or almost sphere) of gas with a finite definable radius, not easily deformed, not like a cloud in the Earth’s atmosphere Nuclear reactions occur at least to the point where 3 He is produced. radiates energy into the surrounding medium. Jupiter also does this, some internal h ...
13 The Family of Stars
... The Hertzsprung–Russell Diagram Once many stars are plotted on an H–R diagram, a pattern begins to form: These are the 80 closest stars to us; note the dashed lines of constant radius. The darkened curve is called the main sequence because this is where most stars are. The white dwarf region ...
... The Hertzsprung–Russell Diagram Once many stars are plotted on an H–R diagram, a pattern begins to form: These are the 80 closest stars to us; note the dashed lines of constant radius. The darkened curve is called the main sequence because this is where most stars are. The white dwarf region ...
Safety criteria for flying E
... Mars or Venus [6]. By rendezvous we mean that the spacecraft’s heliocentric orbit coincides with the heliocentric orbit of the planet, so that in the planet’s frame of reference the orbit is parabolic. It is possible to use E-sail propulsion to change the parabolic orbit into a bound elliptic or ci ...
... Mars or Venus [6]. By rendezvous we mean that the spacecraft’s heliocentric orbit coincides with the heliocentric orbit of the planet, so that in the planet’s frame of reference the orbit is parabolic. It is possible to use E-sail propulsion to change the parabolic orbit into a bound elliptic or ci ...
PDF format
... • How do other jovian ring systems compare to Saturn's? – The other jovian planets have much fainter ring systems with smaller, darker, less numerous particles. • Why do the jovian planets have rings? – Ring particles are probably debris from moons. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • How do other jovian ring systems compare to Saturn's? – The other jovian planets have much fainter ring systems with smaller, darker, less numerous particles. • Why do the jovian planets have rings? – Ring particles are probably debris from moons. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Neptune Mission Concept
... terms of the magnetic field by flying by Neptune at a different latitude / longitude than Voyager, preferably over the south polar region ...
... terms of the magnetic field by flying by Neptune at a different latitude / longitude than Voyager, preferably over the south polar region ...
Formation and evolution of the Solar System

The formation of the Solar System began 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed.This widely accepted model, known as the nebular hypothesis, was first developed in the 18th century by Emanuel Swedenborg, Immanuel Kant, and Pierre-Simon Laplace. Its subsequent development has interwoven a variety of scientific disciplines including astronomy, physics, geology, and planetary science. Since the dawn of the space age in the 1950s and the discovery of extrasolar planets in the 1990s, the model has been both challenged and refined to account for new observations.The Solar System has evolved considerably since its initial formation. Many moons have formed from circling discs of gas and dust around their parent planets, while other moons are thought to have formed independently and later been captured by their planets. Still others, such as the Moon, may be the result of giant collisions. Collisions between bodies have occurred continually up to the present day and have been central to the evolution of the Solar System. The positions of the planets often shifted due to gravitational interactions. This planetary migration is now thought to have been responsible for much of the Solar System's early evolution.In roughly 5 billion years, the Sun will cool and expand outward many times its current diameter (becoming a red giant), before casting off its outer layers as a planetary nebula and leaving behind a stellar remnant known as a white dwarf. In the far distant future, the gravity of passing stars will gradually reduce the Sun's retinue of planets. Some planets will be destroyed, others ejected into interstellar space. Ultimately, over the course of tens of billions of years, it is likely that the Sun will be left with none of the original bodies in orbit around it.