PDF format
... • How do other jovian ring systems compare to Saturn's? – The other jovian planets have much fainter ring systems with smaller, darker, less numerous particles. • Why do the jovian planets have rings? – Ring particles are probably debris from moons. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • How do other jovian ring systems compare to Saturn's? – The other jovian planets have much fainter ring systems with smaller, darker, less numerous particles. • Why do the jovian planets have rings? – Ring particles are probably debris from moons. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
printer-friendly version of benchmark
... 3. Students incorrectly think that our Sun will end as a supernova explosion. All stars that are about 8 MSun or greater will end as a supernova, leaving some kind of stellar remnant (e.g., a neutron star or black hole). Specifically, these massive stars will end as a Type II supernova. In massive ...
... 3. Students incorrectly think that our Sun will end as a supernova explosion. All stars that are about 8 MSun or greater will end as a supernova, leaving some kind of stellar remnant (e.g., a neutron star or black hole). Specifically, these massive stars will end as a Type II supernova. In massive ...
Investigation of evolution of orbits similar to that of (4179) Toutatis
... and 1:1, concentrations of asteroids are observed. These values of semimajor axis have been shown to be stable for small eccentricities by Yoshikawa (1989). On shorter timescales, mean motion resonances can be stable by protecting the asteroid from close approaches: for example, a resonance state w ...
... and 1:1, concentrations of asteroids are observed. These values of semimajor axis have been shown to be stable for small eccentricities by Yoshikawa (1989). On shorter timescales, mean motion resonances can be stable by protecting the asteroid from close approaches: for example, a resonance state w ...
January 2014 - astronomy for beginners
... Moon causes Earth to wobble quite significantly as it rotates around the common centre of rotation with the Moon. The centre of rotation is actually inside the mass of Earth because it is so much more massive. ...
... Moon causes Earth to wobble quite significantly as it rotates around the common centre of rotation with the Moon. The centre of rotation is actually inside the mass of Earth because it is so much more massive. ...
Borexino …..bla bla bla
... To test the validity of the solar models, more than 40 years ago, it was suggested to detect solar neutrinos. The first measurement of the neutrino flux, took place in the Homestake mine in South Dakota in 1968. The experiment detected only one third of the expected value, originating what has been ...
... To test the validity of the solar models, more than 40 years ago, it was suggested to detect solar neutrinos. The first measurement of the neutrino flux, took place in the Homestake mine in South Dakota in 1968. The experiment detected only one third of the expected value, originating what has been ...
Ancient Egyptian Astronomy
... Aryabhatta - was born in 476 A.D., and is widely recognized as the father of Indian astronomy. When he was about 25 years old, he presented astronomical and mathematical theories in which the Earth was taken to be spinning on its axis and the periods of the planets were given with respect to the Sun ...
... Aryabhatta - was born in 476 A.D., and is widely recognized as the father of Indian astronomy. When he was about 25 years old, he presented astronomical and mathematical theories in which the Earth was taken to be spinning on its axis and the periods of the planets were given with respect to the Sun ...
Determination of meteor showers on other planets using comet
... As they traverse their orbits about the Sun, comets slowly evaporate and fragment, leaving small bits of cometary debris along their orbital tracks. Some comet orbits intersect the Earth’s path, and the planet sweeps up a portion of these particulates each year. Generally, these particles are drawn ...
... As they traverse their orbits about the Sun, comets slowly evaporate and fragment, leaving small bits of cometary debris along their orbital tracks. Some comet orbits intersect the Earth’s path, and the planet sweeps up a portion of these particulates each year. Generally, these particles are drawn ...
INPOP06. A new numerical planetary ephemeris
... In this paper, we present the latest version of our short term ephemeris INPOP, INPOP06. We describe the dynamical model used for the integration of the planets and Moon motions and the Earth and Moon rotations. We compare our model with the DE405 solution (Standish, 1998). This first step is import ...
... In this paper, we present the latest version of our short term ephemeris INPOP, INPOP06. We describe the dynamical model used for the integration of the planets and Moon motions and the Earth and Moon rotations. We compare our model with the DE405 solution (Standish, 1998). This first step is import ...
Formation of the Solar System
... © 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley ...
... © 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley ...
Document
... even lower than spectral class M. These bodies which are not truly stars are called Brown Dwarfs- Heat is generated by contraction of gases not Nuclear Fusion. (Give off a lot of light in the infrared range.) ...
... even lower than spectral class M. These bodies which are not truly stars are called Brown Dwarfs- Heat is generated by contraction of gases not Nuclear Fusion. (Give off a lot of light in the infrared range.) ...
Earth Science Standards-with explanations
... addition, misconceptions derived from outdated hypotheses or from science fiction movies, books, and videos may interfere with developing an understanding of accepted scientific evidence. To promote scientific literacy, school libraries should try to keep their collections up to date. Students can b ...
... addition, misconceptions derived from outdated hypotheses or from science fiction movies, books, and videos may interfere with developing an understanding of accepted scientific evidence. To promote scientific literacy, school libraries should try to keep their collections up to date. Students can b ...
... on Near Earth Asteroid (NEA) orbits has been persistent since 1937 (Kostolansky, 1998). Impacts on the NEA population are naturally expected: the same mechanisms that scatter NEAs from the Main Belt (MB) to the nearEarth space, which are the mean motion and secular resonances, simultaneously scatter ...
The Characteristics of Stars
... which are emitting more light and which are emitting less. Although apparent magnitude values help us classify stars according to their observed brightness, they do not help us distinguish between stars that actually give off more energy and those that give off less energy. To overcome this problem, ...
... which are emitting more light and which are emitting less. Although apparent magnitude values help us classify stars according to their observed brightness, they do not help us distinguish between stars that actually give off more energy and those that give off less energy. To overcome this problem, ...
Lecture 13.1
... Consequences for planets • Planets with large escape velocities can retain light gas molecules, e.g. Earth has an atmosphere of oxygen, nitrogen • Moon does not • Conversely Jupiter, Sun manage to retain hydrogen ...
... Consequences for planets • Planets with large escape velocities can retain light gas molecules, e.g. Earth has an atmosphere of oxygen, nitrogen • Moon does not • Conversely Jupiter, Sun manage to retain hydrogen ...
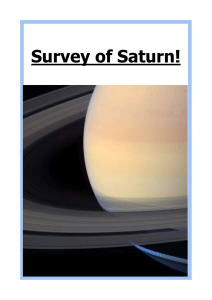
Survey of Saturn! - Primary Resources
... Saturn is 8.2713 x 10 (x14). It means you can fit in 764 Earth sized planets in Saturn comfortably. The surface area is 4.27 x 1010 sq km. This is 84 times that of the Earth. Question 9: 1. Saturn has at least 62 moons but we seem to be discovering more all of the time! Some of the moons around Satu ...
... Saturn is 8.2713 x 10 (x14). It means you can fit in 764 Earth sized planets in Saturn comfortably. The surface area is 4.27 x 1010 sq km. This is 84 times that of the Earth. Question 9: 1. Saturn has at least 62 moons but we seem to be discovering more all of the time! Some of the moons around Satu ...
Getting to Know: Structure of the Universe
... The billions of stars in each galaxy are so far away that their light shines as one. One example is the Andromeda galaxy. It is one of the Milky Way’s closest neighbors at 2.5 million light years away. This means that the light you see when you look at Andromeda left the galaxy 2.5 million years ago ...
... The billions of stars in each galaxy are so far away that their light shines as one. One example is the Andromeda galaxy. It is one of the Milky Way’s closest neighbors at 2.5 million light years away. This means that the light you see when you look at Andromeda left the galaxy 2.5 million years ago ...
session 3.2 - Let There Be Night
... transparency with another piece of paper and move the first piece of paper down to reveal Night 2. (If you are using the CD-ROM, click on the NEXT arrow to move on to Night 2.) Have students record the position of their spots for Night 2, making sure that they mark their observations on the Night 2 ...
... transparency with another piece of paper and move the first piece of paper down to reveal Night 2. (If you are using the CD-ROM, click on the NEXT arrow to move on to Night 2.) Have students record the position of their spots for Night 2, making sure that they mark their observations on the Night 2 ...
The absence of CO from the dust peak around ϵ Eri
... the same orbital distance as the ring. A second, more massive (∼1 M J ) planet may also be orbiting the star at ∼3 au (Hatzes et al. 2000). The established core accretion theory of planet formation (e.g. Boss 2000) generally allows ∼108 yr for the formation of terrestrial planets, but requires gas g ...
... the same orbital distance as the ring. A second, more massive (∼1 M J ) planet may also be orbiting the star at ∼3 au (Hatzes et al. 2000). The established core accretion theory of planet formation (e.g. Boss 2000) generally allows ∼108 yr for the formation of terrestrial planets, but requires gas g ...
What are comets?
... Questions for the video: 1. What is the difference between long period and short period comets? 2. Why are some comets visible and others not? 3. Why do some comets have different tails? 4. How are the two tails formed? 5. Why do scientists think that comets may have been a cause for the extinction ...
... Questions for the video: 1. What is the difference between long period and short period comets? 2. Why are some comets visible and others not? 3. Why do some comets have different tails? 4. How are the two tails formed? 5. Why do scientists think that comets may have been a cause for the extinction ...
Printable Version of this information
... What we are going to talk about today -- seasons! What are seasons? While we might think there is a "correct" answer to this question, in actuality it is a vague question. In addition to winter, spring, summer and fall, here we also have hurricane season. Tropical climates typically have a wet and a ...
... What we are going to talk about today -- seasons! What are seasons? While we might think there is a "correct" answer to this question, in actuality it is a vague question. In addition to winter, spring, summer and fall, here we also have hurricane season. Tropical climates typically have a wet and a ...
Formation and evolution of the Solar System

The formation of the Solar System began 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed.This widely accepted model, known as the nebular hypothesis, was first developed in the 18th century by Emanuel Swedenborg, Immanuel Kant, and Pierre-Simon Laplace. Its subsequent development has interwoven a variety of scientific disciplines including astronomy, physics, geology, and planetary science. Since the dawn of the space age in the 1950s and the discovery of extrasolar planets in the 1990s, the model has been both challenged and refined to account for new observations.The Solar System has evolved considerably since its initial formation. Many moons have formed from circling discs of gas and dust around their parent planets, while other moons are thought to have formed independently and later been captured by their planets. Still others, such as the Moon, may be the result of giant collisions. Collisions between bodies have occurred continually up to the present day and have been central to the evolution of the Solar System. The positions of the planets often shifted due to gravitational interactions. This planetary migration is now thought to have been responsible for much of the Solar System's early evolution.In roughly 5 billion years, the Sun will cool and expand outward many times its current diameter (becoming a red giant), before casting off its outer layers as a planetary nebula and leaving behind a stellar remnant known as a white dwarf. In the far distant future, the gravity of passing stars will gradually reduce the Sun's retinue of planets. Some planets will be destroyed, others ejected into interstellar space. Ultimately, over the course of tens of billions of years, it is likely that the Sun will be left with none of the original bodies in orbit around it.