Planet - Tasker Milward Physics Website
... These (usually) orbit planets. They can be are used for many purposes, including communications, navigation, and much more! These are the planets closest to the Sun. They are made of rock and metal, like the Earth. These are large balls of dust and ice. They follow very elliptical (oval) orbits arou ...
... These (usually) orbit planets. They can be are used for many purposes, including communications, navigation, and much more! These are the planets closest to the Sun. They are made of rock and metal, like the Earth. These are large balls of dust and ice. They follow very elliptical (oval) orbits arou ...
1 - Quia
... a. An abundance of liquid water c. The moon’s craters b. An oxygen-rich atmosphere d. both (a) and (b) 25. The inner planets are separated from the outer planets by a. the Oort cloud. c. the Milky Way. b. an asteroid belt. d. the moon’s orbit. 26. Which of the following is not a characteristic of ga ...
... a. An abundance of liquid water c. The moon’s craters b. An oxygen-rich atmosphere d. both (a) and (b) 25. The inner planets are separated from the outer planets by a. the Oort cloud. c. the Milky Way. b. an asteroid belt. d. the moon’s orbit. 26. Which of the following is not a characteristic of ga ...
Formation of the Solar System • Questions
... of formation of solar system. • Primitive meteorites have very narrow range of ...
... of formation of solar system. • Primitive meteorites have very narrow range of ...
Scale Model of the Solar System
... 1:1,000,000,000. This sounds difficult to do but actually it’s very easy because at this scale 1mm = 1,000 kilometres. Good approximations of the sizes of the planets are shown in the table below. Object Sun Mercury Venus Earth Mars Asteroid belt Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune Pluto Proxima Centauri ...
... 1:1,000,000,000. This sounds difficult to do but actually it’s very easy because at this scale 1mm = 1,000 kilometres. Good approximations of the sizes of the planets are shown in the table below. Object Sun Mercury Venus Earth Mars Asteroid belt Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune Pluto Proxima Centauri ...
Kylie and Cody
... the sun, revolved around the Earth. Astronomers once thought that planetary orbits were circular and that the sun was in the center. Kepler showed that the orbits are elliptical. The sun is not at the center but slightly to one side. ...
... the sun, revolved around the Earth. Astronomers once thought that planetary orbits were circular and that the sun was in the center. Kepler showed that the orbits are elliptical. The sun is not at the center but slightly to one side. ...
Lecture7 - UCSB Physics
... Many planets about the size of Jupiter orbit closer to their star than Mercury does to our Sun! Early studies subject to a selection bias. Most sensitive to short period planets. ...
... Many planets about the size of Jupiter orbit closer to their star than Mercury does to our Sun! Early studies subject to a selection bias. Most sensitive to short period planets. ...
CLOZE-ing in on Science!
... The planets are different in many ways, but they also have some similar properties to one another. One similar property is that all of the planets orbit, or circle around, the Sun. This path takes the planets different amounts of time depending on how far, or distant, they are from the Sun. The oute ...
... The planets are different in many ways, but they also have some similar properties to one another. One similar property is that all of the planets orbit, or circle around, the Sun. This path takes the planets different amounts of time depending on how far, or distant, they are from the Sun. The oute ...
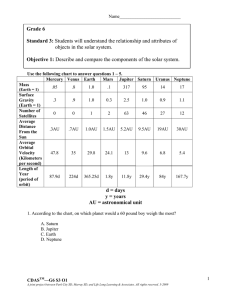
d = days y = years AU = astronomical unit Grade 6 Standard 3
... A. the outer planets B. the inner planets C. the gas giants D. the middle planets 10. How do the inner planets differ from the outer planets? A. they are made of lighter elements B. they do not have moons C. they are extremely large D. they are spaced more closely together 11. What is one factor tha ...
... A. the outer planets B. the inner planets C. the gas giants D. the middle planets 10. How do the inner planets differ from the outer planets? A. they are made of lighter elements B. they do not have moons C. they are extremely large D. they are spaced more closely together 11. What is one factor tha ...
Origin of Our Solar System
... model. The student is expected to: a) analyze how gravitational condensation of solar nebular gas and dust can lead to the accretion of planetesimals and protoplanets; ...
... model. The student is expected to: a) analyze how gravitational condensation of solar nebular gas and dust can lead to the accretion of planetesimals and protoplanets; ...
How is energy stored in atoms? Energy Level Transitions A Simple
... • The young Sun probably had a disk of gas & dust: the Solar Nebula • Small cores in the disk (planetesimals) grow through accretion • Temperature is warmer as you get closer to the center (where the Sun is!) ...
... • The young Sun probably had a disk of gas & dust: the Solar Nebula • Small cores in the disk (planetesimals) grow through accretion • Temperature is warmer as you get closer to the center (where the Sun is!) ...
Benchmark One Study Guide: Science Benchmark Wed
... 4. What unit of measurement do we use to measure distance within the Milky Way Galaxy? ____________________________ What unit of measurement do we use to measure within our solar system? _____________________________ 5. Identify each type of galaxy below. ...
... 4. What unit of measurement do we use to measure distance within the Milky Way Galaxy? ____________________________ What unit of measurement do we use to measure within our solar system? _____________________________ 5. Identify each type of galaxy below. ...
Space is Big…
... You just won’t believe how vastly, hugely, mindbogglingly big it is. I mean, you may think it’s a long way down the road to the chemist’s, but that’s just peanuts to space.” ...
... You just won’t believe how vastly, hugely, mindbogglingly big it is. I mean, you may think it’s a long way down the road to the chemist’s, but that’s just peanuts to space.” ...
jupiter_ppt
... planets combined. The planet contains 71% of all the matter in the Solar System excluding the sun It has differential rotation- this means that its rotational rate is not constant from one area to another…this would indicate that Jupiter is not a solid planet! ...
... planets combined. The planet contains 71% of all the matter in the Solar System excluding the sun It has differential rotation- this means that its rotational rate is not constant from one area to another…this would indicate that Jupiter is not a solid planet! ...
Unit 14_EOC Review_4_24_Space Exploration
... 2. Even though the Sun is much larger with stronger gravity the moon is MUCH 4. It takes the moon the same amount CLOSER to Earth causing it to have a of time to rotate as it does to make one greater effect on tides. full revolution around the Earth. ...
... 2. Even though the Sun is much larger with stronger gravity the moon is MUCH 4. It takes the moon the same amount CLOSER to Earth causing it to have a of time to rotate as it does to make one greater effect on tides. full revolution around the Earth. ...
SUN AND PLANET FACTS
... * formed from cloud of hydrogen gas and dust, 5 billion years ago * holds 99.85% of the mass of our solar system * 92% hydrogen and 8% helium * Core is 27 million degrees Fahrenheit * nuclear reactions of hydrogen atoms being forced together under high temperature and pressure to form helium * heat ...
... * formed from cloud of hydrogen gas and dust, 5 billion years ago * holds 99.85% of the mass of our solar system * 92% hydrogen and 8% helium * Core is 27 million degrees Fahrenheit * nuclear reactions of hydrogen atoms being forced together under high temperature and pressure to form helium * heat ...
Science Study Guide Chapter 7 “Earth in Space” Section 1 Earth`s
... cloud of gas, ice, and dust. 2. Almost all ______________________ in our solar system are located beyond Neptune. 3. The _______________________________ separates the inner and outer planets. 4. __________________________________ are used to measure distances between objects in the solar system. 5. ...
... cloud of gas, ice, and dust. 2. Almost all ______________________ in our solar system are located beyond Neptune. 3. The _______________________________ separates the inner and outer planets. 4. __________________________________ are used to measure distances between objects in the solar system. 5. ...
Powerpoint
... them => growth of first clumps of matter. 2) Accretion: Clumps collide and stick => larger clumps. Eventually, small-moon sized objects: "planetesimals". ...
... them => growth of first clumps of matter. 2) Accretion: Clumps collide and stick => larger clumps. Eventually, small-moon sized objects: "planetesimals". ...
Chapter 5 - AstroStop
... How many stars are there in the solar system? Only one star, the Sun Was the solar system created as a direct result of the formation of the universe? No. All matter and energy were created by the Big Bang, but the solar system formed billions of years after the Big Bang. How long has the Ea ...
... How many stars are there in the solar system? Only one star, the Sun Was the solar system created as a direct result of the formation of the universe? No. All matter and energy were created by the Big Bang, but the solar system formed billions of years after the Big Bang. How long has the Ea ...
Formation and evolution of the Solar System

The formation of the Solar System began 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed.This widely accepted model, known as the nebular hypothesis, was first developed in the 18th century by Emanuel Swedenborg, Immanuel Kant, and Pierre-Simon Laplace. Its subsequent development has interwoven a variety of scientific disciplines including astronomy, physics, geology, and planetary science. Since the dawn of the space age in the 1950s and the discovery of extrasolar planets in the 1990s, the model has been both challenged and refined to account for new observations.The Solar System has evolved considerably since its initial formation. Many moons have formed from circling discs of gas and dust around their parent planets, while other moons are thought to have formed independently and later been captured by their planets. Still others, such as the Moon, may be the result of giant collisions. Collisions between bodies have occurred continually up to the present day and have been central to the evolution of the Solar System. The positions of the planets often shifted due to gravitational interactions. This planetary migration is now thought to have been responsible for much of the Solar System's early evolution.In roughly 5 billion years, the Sun will cool and expand outward many times its current diameter (becoming a red giant), before casting off its outer layers as a planetary nebula and leaving behind a stellar remnant known as a white dwarf. In the far distant future, the gravity of passing stars will gradually reduce the Sun's retinue of planets. Some planets will be destroyed, others ejected into interstellar space. Ultimately, over the course of tens of billions of years, it is likely that the Sun will be left with none of the original bodies in orbit around it.