Solar System
... Solar System Notes – Part 1 Universe: all of space and ________________________________________________ Galaxy: A large group of __________________________________, solar systems, and associated gas and dust in space that is bound by _____________________________ Solar System: Composed of one ...
... Solar System Notes – Part 1 Universe: all of space and ________________________________________________ Galaxy: A large group of __________________________________, solar systems, and associated gas and dust in space that is bound by _____________________________ Solar System: Composed of one ...
Extrasolar planets
... First detection of any carbon-bearing molecule on a planet outside the Solar System! Swain et al., Nature, March 2008 Also confirmed previous discovery of water on this planet ...
... First detection of any carbon-bearing molecule on a planet outside the Solar System! Swain et al., Nature, March 2008 Also confirmed previous discovery of water on this planet ...
Slide 1
... Composed of more than 98 percent nitrogen ice, with traces of methane and carbon monoxide ...
... Composed of more than 98 percent nitrogen ice, with traces of methane and carbon monoxide ...
The Solar System - Belle Vernon Area School District
... it could exist anywhere else in our solar system as we know it. ...
... it could exist anywhere else in our solar system as we know it. ...
Mar - Wadhurst Astronomical Society
... contender could be Silicon but he said carbon attaches itself to all sorts of things whereas silicon doesn’t. Water is also very important as a medium to life. We were told that there is one other possible contender on other planets and that is ammonia. Very basically, life as we know it is self-org ...
... contender could be Silicon but he said carbon attaches itself to all sorts of things whereas silicon doesn’t. Water is also very important as a medium to life. We were told that there is one other possible contender on other planets and that is ammonia. Very basically, life as we know it is self-org ...
Volume 20 Number 5 April 2012 - Forsyth Astronomical Society
... Researchers say that a layer of thin, dark sediment buried in the floor of a lake in central Mexico may have been caused by a cosmic body crashing into Earth nearly 13,000 years ago. Exotic materials in the sediment layer strongly support a belief that a major cosmic impact with Earth coincided with ...
... Researchers say that a layer of thin, dark sediment buried in the floor of a lake in central Mexico may have been caused by a cosmic body crashing into Earth nearly 13,000 years ago. Exotic materials in the sediment layer strongly support a belief that a major cosmic impact with Earth coincided with ...
Fun Facts: Sunshine
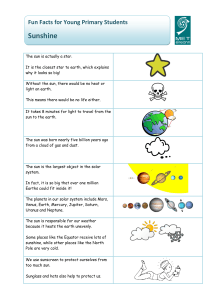
... Without the sun, there would be no heat or light on earth. This means there would be no life either. It takes 8 minutes for light to travel from the sun to the earth. ...
... Without the sun, there would be no heat or light on earth. This means there would be no life either. It takes 8 minutes for light to travel from the sun to the earth. ...
Space Unit Exam /31
... e. ____ In the early days of our solar system, all planets were made of the same solids, liquids and gases. _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ ...
... e. ____ In the early days of our solar system, all planets were made of the same solids, liquids and gases. _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ ...
What is life?
... • Time for life to evolve from simple organic compounds into higher life forms: several billion years. ...
... • Time for life to evolve from simple organic compounds into higher life forms: several billion years. ...
Astronomy Basics
... Beyond the frost line, planetesimals can grow from rock and ice. This leads to the formation of “planetary cores”, which are rocky/icy planetesimals around 10x as massive as Earth. These cores are so massive that they accrete gas, forming gas giant planets. ...
... Beyond the frost line, planetesimals can grow from rock and ice. This leads to the formation of “planetary cores”, which are rocky/icy planetesimals around 10x as massive as Earth. These cores are so massive that they accrete gas, forming gas giant planets. ...
Solar System
... twelve smaller named moons and twentythree more recently discovered but not named moons. We’ll take a look at the four large Galilean moons which were first observed by Galileo in 1610. ...
... twelve smaller named moons and twentythree more recently discovered but not named moons. We’ll take a look at the four large Galilean moons which were first observed by Galileo in 1610. ...
Earth Science
... twelve smaller named moons and twentythree more recently discovered but not named moons. We’ll take a look at the four large Galilean moons which were first observed by Galileo in 1610. ...
... twelve smaller named moons and twentythree more recently discovered but not named moons. We’ll take a look at the four large Galilean moons which were first observed by Galileo in 1610. ...
Earth Science - MrsHeatonsWiki
... Uranus is one of the giant gas planets. Uranus is blue-green because of the methane in its atmosphere. ...
... Uranus is one of the giant gas planets. Uranus is blue-green because of the methane in its atmosphere. ...
Survey of the Solar Systems
... The solar system formed from a cloud of cold gas and dust called the solar nebula about 4.6 ...
... The solar system formed from a cloud of cold gas and dust called the solar nebula about 4.6 ...
ภาพนิ่ง 1 - ILM.COM.PK
... size to Earth, (0.815 Earth masses) and like Earth, has a thick silicate mantle around an iron core, a substantial atmosphere and evidence of internal geological activity. However, it is much drier than Earth and its atmosphere is ninety times as dense. Venus has no natural satellites. It is the hot ...
... size to Earth, (0.815 Earth masses) and like Earth, has a thick silicate mantle around an iron core, a substantial atmosphere and evidence of internal geological activity. However, it is much drier than Earth and its atmosphere is ninety times as dense. Venus has no natural satellites. It is the hot ...
Planetarium Field Guide 2015-2016 Third Grade
... How are the inner planets different than the outer planets? Program: “Nine Planets and Counting” The program takes students on a tour to explore the many objects that populate our solar system. The students will be able to examine each individual planet and move outside to see where the Earth fits i ...
... How are the inner planets different than the outer planets? Program: “Nine Planets and Counting” The program takes students on a tour to explore the many objects that populate our solar system. The students will be able to examine each individual planet and move outside to see where the Earth fits i ...
The Structure of Our Solar System
... Size Small planets are those with a diameter than is equal to or less than 13,000 km. These planets are Mercury, Mars, Earth, Venus and Pluto. Giant planets are classified as those with a diameter greater than 48,000 km. These planets are Neptune Uranus, Jupiter and Saturn. ...
... Size Small planets are those with a diameter than is equal to or less than 13,000 km. These planets are Mercury, Mars, Earth, Venus and Pluto. Giant planets are classified as those with a diameter greater than 48,000 km. These planets are Neptune Uranus, Jupiter and Saturn. ...
Slide 20 - International Year of Astronomy 2009
... September: Jupiter without its Moons As amateur astronomers know, anyone with a small telescope can see the planet Jupiter and its four brightest moons. They appear as pinpricks of light, orbiting the gas giant. They were first seen by Galileo in 1610. ...
... September: Jupiter without its Moons As amateur astronomers know, anyone with a small telescope can see the planet Jupiter and its four brightest moons. They appear as pinpricks of light, orbiting the gas giant. They were first seen by Galileo in 1610. ...
Our Solar System
... relative to the sun and composition of atmosphere it makes it an ideal planet for supporting life. ...
... relative to the sun and composition of atmosphere it makes it an ideal planet for supporting life. ...
Midterm 2 - SwRI Boulder
... atmosphere to help hold in heat and it is still possible that slow life living in the cold methane seas could survive. Extra credit: Why have there been so many more missions (and mission attempts) to Mars than to any other planet in the solar system? There are both scientific reasons and engineerin ...
... atmosphere to help hold in heat and it is still possible that slow life living in the cold methane seas could survive. Extra credit: Why have there been so many more missions (and mission attempts) to Mars than to any other planet in the solar system? There are both scientific reasons and engineerin ...
Earth - Capital High School
... • objects are so far away, we are seeing what they looked like millions of years ago – it takes one year for light to travel 5+ trillion miles (a light year) ...
... • objects are so far away, we are seeing what they looked like millions of years ago – it takes one year for light to travel 5+ trillion miles (a light year) ...
Astrobiology

Astrobiology is the study of the origin, evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe: extraterrestrial life and life on Earth. This interdisciplinary field encompasses the search for habitable environments in our Solar System and habitable planets outside our Solar System, the search for evidence of prebiotic chemistry, laboratory and field research into the origins and early evolution of life on Earth, and studies of the potential for life to adapt to challenges on Earth and in outer space. Astrobiology addresses the question of whether life exists beyond Earth, and how humans can detect it if it does. (The term exobiology is similar but more specific—it covers the search for life beyond Earth, and the effects of extraterrestrial environments on living things.)Astrobiology makes use of physics, chemistry, astronomy, biology, molecular biology, ecology, planetary science, geography, and geology to investigate the possibility of life on other worlds and help recognize biospheres that might be different from the biosphere on Earth. The origin and early evolution of life is an inseparable part of the discipline of astrobiology. Astrobiology concerns itself with interpretation of existing scientific data; given more detailed and reliable data from other parts of the universe, the roots of astrobiology itself—physics, chemistry and biology—may have their theoretical bases challenged. Although speculation is entertained to give context, astrobiology concerns itself primarily with hypotheses that fit firmly into existing scientific theories.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. According to research published in August 2015, very large galaxies may be more favorable to the creation and development of habitable planets than smaller galaxies, like the Milky Way galaxy. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently.Current studies on the planet Mars by the Curiosity and Opportunity rovers are now searching for evidence of ancient life as well as plains related to ancient rivers or lakes that may have been habitable. The search for evidence of habitability, taphonomy (related to fossils), and organic molecules on the planet Mars is now a primary NASA objective on Mars.