Formation of the Solar System Target 1 Notes
... What is the Sun? As mentioned before, the sun is a __________________. Next time you look into the night sky and see a star twinkling back at you, hold in your thoughts that this star, is a __________________, and surrounding this sun there could be planets like ours. The sun is the largest ________ ...
... What is the Sun? As mentioned before, the sun is a __________________. Next time you look into the night sky and see a star twinkling back at you, hold in your thoughts that this star, is a __________________, and surrounding this sun there could be planets like ours. The sun is the largest ________ ...
SOL Study Book
... 1. Earth experiences seasons because of its axial tilt and its revolution around the sun. 2. The northern half of the Earth experiences the opposite season than the southern half of the Earth. 3. Locations closets to the equator stay hot or warm all year long. Characteristics of the Earth 1. The Ear ...
... 1. Earth experiences seasons because of its axial tilt and its revolution around the sun. 2. The northern half of the Earth experiences the opposite season than the southern half of the Earth. 3. Locations closets to the equator stay hot or warm all year long. Characteristics of the Earth 1. The Ear ...
Beginnings - Big Picture
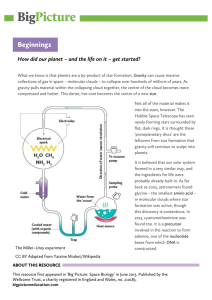
... It seems that the early solar system – including the early Earth – was laced with some of the basic chemicals from which life is built. But what turned an inanimate, prehistoric ‘soup’ of chemicals into the first organisms we would classify as alive? The most famous experiment into the origin of li ...
... It seems that the early solar system – including the early Earth – was laced with some of the basic chemicals from which life is built. But what turned an inanimate, prehistoric ‘soup’ of chemicals into the first organisms we would classify as alive? The most famous experiment into the origin of li ...
Stars & Galaxies
... Earth was heated by kinetic energy of falling debris and decay of radioactive elements within the newly formed Earth, causing it to melt density stratification - Iron sunk to the middle of the planet (developing gravity field), and lighter minerals (Si, Al, Mg) migrated to the surface forming the Ea ...
... Earth was heated by kinetic energy of falling debris and decay of radioactive elements within the newly formed Earth, causing it to melt density stratification - Iron sunk to the middle of the planet (developing gravity field), and lighter minerals (Si, Al, Mg) migrated to the surface forming the Ea ...
PowerPoint
... Big Story: Russia Meteor Blast is Biggest in 100 Years The dramatic fireball that exploded over Russia today (Feb. 15) was apparently the biggest such blast in more than a century, scientists say. The object that caused the Russian fireball, which damaged hundreds of buildings and wounded perhaps 1 ...
... Big Story: Russia Meteor Blast is Biggest in 100 Years The dramatic fireball that exploded over Russia today (Feb. 15) was apparently the biggest such blast in more than a century, scientists say. The object that caused the Russian fireball, which damaged hundreds of buildings and wounded perhaps 1 ...
ASTR 2020, Spring 2015 Professor Jack Burns Final Exam
... expense and risks associated with NASA’s space program. Example: Not only does space exploration excite our natural human curiosity and desire to explore, it also results in more tangible benefits. The requirements for space exploration lead to advances in medicine, engineering, and more. Space expl ...
... expense and risks associated with NASA’s space program. Example: Not only does space exploration excite our natural human curiosity and desire to explore, it also results in more tangible benefits. The requirements for space exploration lead to advances in medicine, engineering, and more. Space expl ...
The Solar system
... •Jupiter is the fastest rotating planet in our solar system ,it rotates so quickly that the days are only 10 hours long. •Jupiter has 63 moons, Jupiter's moon, Ganymede, is the biggest moon in the Solar System. •Jupiter's Red Spot is in fact a storm the size of Earth that has raged for hundreds of y ...
... •Jupiter is the fastest rotating planet in our solar system ,it rotates so quickly that the days are only 10 hours long. •Jupiter has 63 moons, Jupiter's moon, Ganymede, is the biggest moon in the Solar System. •Jupiter's Red Spot is in fact a storm the size of Earth that has raged for hundreds of y ...
Search for Life in the Universe – What can we Learn from our own
... Gribaldo and Forterre in Gargaud et al. 2005). The ocean floor at a submarine alkaline hot spring has been suggested to provide all prerequisites for the emergence of life on the early Earth about 4 billion years ago. Deep-sea hydrothermal systems are producing sites of hydrocarbons, even today. As ...
... Gribaldo and Forterre in Gargaud et al. 2005). The ocean floor at a submarine alkaline hot spring has been suggested to provide all prerequisites for the emergence of life on the early Earth about 4 billion years ago. Deep-sea hydrothermal systems are producing sites of hydrocarbons, even today. As ...
the universe notes - Cloverleaf Local Schools
... While in flight, the melted pieces solidified and made the asteroid belt (between Mars & Jupiter) Some pieces flew into other locations making up our planets. ...
... While in flight, the melted pieces solidified and made the asteroid belt (between Mars & Jupiter) Some pieces flew into other locations making up our planets. ...
Jovian Planets and Interiors
... Venus has no significant weather at ground level. There aren't significant winds or precipitation. Sulfuric acid clouds are blown about by strong winds in the upper atmosphere. The presence of sulfuric acid indicates that there most be some fairly recent volcanism as the sulfur dioxide needed to pro ...
... Venus has no significant weather at ground level. There aren't significant winds or precipitation. Sulfuric acid clouds are blown about by strong winds in the upper atmosphere. The presence of sulfuric acid indicates that there most be some fairly recent volcanism as the sulfur dioxide needed to pro ...
Our Solar System - After School Astronomy Clubs
... Jupiter, the fifth planet from the Sun, is the largest planet in our solar system. Jupiter is so big that over 1,000 planets the size of Earth could fit into it. It has over 60 moons and 2 rings. Can life exist on Jupiter's moon, Europa? ...
... Jupiter, the fifth planet from the Sun, is the largest planet in our solar system. Jupiter is so big that over 1,000 planets the size of Earth could fit into it. It has over 60 moons and 2 rings. Can life exist on Jupiter's moon, Europa? ...
24. Life Beyond Earth: Prospects for Microbes, Civilizations, and
... on Europa by the Voyager 2 spacecraft. b. This could happen because there is evidence for an ocean underneath the icy surface of Europa and water is a good place to look for life. c. This is fantasy because it would take more than 20 years for a spacecraft to reach Saturn using current rocket techno ...
... on Europa by the Voyager 2 spacecraft. b. This could happen because there is evidence for an ocean underneath the icy surface of Europa and water is a good place to look for life. c. This is fantasy because it would take more than 20 years for a spacecraft to reach Saturn using current rocket techno ...
Topic 3 – Waves and the Universe
... atmosphere of far away planets The Earth’s atmosphere is hospitable to life because of its high content of oxygen in its atmosphere (released by photosynthesising plants) Presence of oxygen in the atmosphere of another planet could be evidence that life may exist on that planet Searching for Intell ...
... atmosphere of far away planets The Earth’s atmosphere is hospitable to life because of its high content of oxygen in its atmosphere (released by photosynthesising plants) Presence of oxygen in the atmosphere of another planet could be evidence that life may exist on that planet Searching for Intell ...
Topic 3 notes - WordPress.com
... atmosphere of far away planets The Earth’s atmosphere is hospitable to life because of its high content of oxygen in its atmosphere (released by photosynthesising plants) Presence of oxygen in the atmosphere of another planet could be evidence that life may exist on that planet Searching for Intell ...
... atmosphere of far away planets The Earth’s atmosphere is hospitable to life because of its high content of oxygen in its atmosphere (released by photosynthesising plants) Presence of oxygen in the atmosphere of another planet could be evidence that life may exist on that planet Searching for Intell ...
File
... • Sometimes they are called terrestrial planets = Earth-like • They are relatively small and have solid cores and rocky crusts ...
... • Sometimes they are called terrestrial planets = Earth-like • They are relatively small and have solid cores and rocky crusts ...
Chapter 8 Survey of Solar Systems
... Rocky Asteroids - mostly found between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter ...
... Rocky Asteroids - mostly found between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter ...
Presentation 2
... circular motions of the stars, Sun, Moon, and planets about the celestial pole? • Hypothesis 1: The Earth is stationary, and the stars, Sun, Moon, and planets revolve around it. • Hypothesis 2: The stars, Sun, Moon, and planets are not revolving about the Earth; it is the Earth which is rotating abo ...
... circular motions of the stars, Sun, Moon, and planets about the celestial pole? • Hypothesis 1: The Earth is stationary, and the stars, Sun, Moon, and planets revolve around it. • Hypothesis 2: The stars, Sun, Moon, and planets are not revolving about the Earth; it is the Earth which is rotating abo ...
solar system - PAMS
... •The moon is 3476 km in diameter. Its diameter is ¼ the size of Earth’s. ______________________________________. It is dry, airless, and barren. Noon is about 100°C or higher, night is –175°C. Has dark areas (plains) called maria and highlands up to 8 km. Its largest crater is called _______________ ...
... •The moon is 3476 km in diameter. Its diameter is ¼ the size of Earth’s. ______________________________________. It is dry, airless, and barren. Noon is about 100°C or higher, night is –175°C. Has dark areas (plains) called maria and highlands up to 8 km. Its largest crater is called _______________ ...
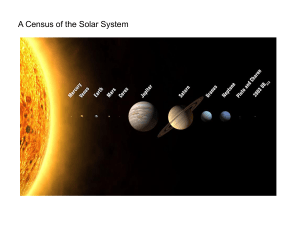
A Census of the Solar System
... 1. Planets and their satellites all lie in the same plane - the ecliptic – to within a few degrees 2. Sun’s rotational equator aligned with ecliptic 3. Planetary orbits are nearly circular ellipses 4. Planets all revolve in same W -> E direction 5. Sun and planets all rotate on axes in same W –E dir ...
... 1. Planets and their satellites all lie in the same plane - the ecliptic – to within a few degrees 2. Sun’s rotational equator aligned with ecliptic 3. Planetary orbits are nearly circular ellipses 4. Planets all revolve in same W -> E direction 5. Sun and planets all rotate on axes in same W –E dir ...
Geocentric Model of the Solar System
... light. Very bright planets, such as Venus and our moon, appear bright because they are reflecting sunlight. Remember: Stars produce light. Planets reflect light. • Our sun is classified as a yellow main sequence star. A star’s temperature determines its “color.” The coldest stars are red. The hottes ...
... light. Very bright planets, such as Venus and our moon, appear bright because they are reflecting sunlight. Remember: Stars produce light. Planets reflect light. • Our sun is classified as a yellow main sequence star. A star’s temperature determines its “color.” The coldest stars are red. The hottes ...
Earth Science – Quiz 2
... 38. Compared to Earth's atmosphere, the atmosphere of Mars has surface pressures that are ________. A) 3 times those on Earth; major gases are water vapor and carbon dioxide B) 0.1 times those on Earth; major gases are water vapor and carbon dioxide C) one-half those on Earth; main gases are methane ...
... 38. Compared to Earth's atmosphere, the atmosphere of Mars has surface pressures that are ________. A) 3 times those on Earth; major gases are water vapor and carbon dioxide B) 0.1 times those on Earth; major gases are water vapor and carbon dioxide C) one-half those on Earth; main gases are methane ...
The Roots of Astronomy Stonehenge
... Tycho Brahe (1546 – 1601) to study planetary motion mathematically. • Found a consistent description by abandoning both ...
... Tycho Brahe (1546 – 1601) to study planetary motion mathematically. • Found a consistent description by abandoning both ...
Astrobiology

Astrobiology is the study of the origin, evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe: extraterrestrial life and life on Earth. This interdisciplinary field encompasses the search for habitable environments in our Solar System and habitable planets outside our Solar System, the search for evidence of prebiotic chemistry, laboratory and field research into the origins and early evolution of life on Earth, and studies of the potential for life to adapt to challenges on Earth and in outer space. Astrobiology addresses the question of whether life exists beyond Earth, and how humans can detect it if it does. (The term exobiology is similar but more specific—it covers the search for life beyond Earth, and the effects of extraterrestrial environments on living things.)Astrobiology makes use of physics, chemistry, astronomy, biology, molecular biology, ecology, planetary science, geography, and geology to investigate the possibility of life on other worlds and help recognize biospheres that might be different from the biosphere on Earth. The origin and early evolution of life is an inseparable part of the discipline of astrobiology. Astrobiology concerns itself with interpretation of existing scientific data; given more detailed and reliable data from other parts of the universe, the roots of astrobiology itself—physics, chemistry and biology—may have their theoretical bases challenged. Although speculation is entertained to give context, astrobiology concerns itself primarily with hypotheses that fit firmly into existing scientific theories.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. According to research published in August 2015, very large galaxies may be more favorable to the creation and development of habitable planets than smaller galaxies, like the Milky Way galaxy. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently.Current studies on the planet Mars by the Curiosity and Opportunity rovers are now searching for evidence of ancient life as well as plains related to ancient rivers or lakes that may have been habitable. The search for evidence of habitability, taphonomy (related to fossils), and organic molecules on the planet Mars is now a primary NASA objective on Mars.