Unit 1: Earth History 1. Distinguish among eons
... 4. Explain the factors that determine if a planet will have a strong magnetic field/atmosphere? 5. Explain Kepler’s Laws. Calculate a planets period of rotation (using GRASS). 6. Compare and contr ...
... 4. Explain the factors that determine if a planet will have a strong magnetic field/atmosphere? 5. Explain Kepler’s Laws. Calculate a planets period of rotation (using GRASS). 6. Compare and contr ...
Ch. 16 Notes
... • Around 2,000 asteroids have been discovered orbiting the sun between Mars and Jupiter. Most are small only a few miles across. There may be 1 million such objects orbiting inside this area. ...
... • Around 2,000 asteroids have been discovered orbiting the sun between Mars and Jupiter. Most are small only a few miles across. There may be 1 million such objects orbiting inside this area. ...
Twinkle, twinkle little star, how I wonder what you are. Up
... #2 We’re as Different as Day and Night CHORUS We’re as different as day and night. We’re as different as black and white. But in this great big galaxy, I need you and you need me. Part 1 (first time only) I’m the sun, the center of the system. I’m number one, so everybody listen. I wait for all my ...
... #2 We’re as Different as Day and Night CHORUS We’re as different as day and night. We’re as different as black and white. But in this great big galaxy, I need you and you need me. Part 1 (first time only) I’m the sun, the center of the system. I’m number one, so everybody listen. I wait for all my ...
The night sky - Mr. Champion
... note of star formations and have been influenced by them. • As we often do, some claimed through patterns they could see objects or people “hidden” there. • These objects are what’s known as constellations. • They aren’t necessarily found in the same area of space, but the light reaches us around th ...
... note of star formations and have been influenced by them. • As we often do, some claimed through patterns they could see objects or people “hidden” there. • These objects are what’s known as constellations. • They aren’t necessarily found in the same area of space, but the light reaches us around th ...
688 Chapter 21 Review - District 196 e
... a smooth curve to Mercury, Earth, and Mars. You may ignore Venus as an anomaly for the purposes of the graph. a. Estimate the radius of an orbit that would make the average surface temperature 100°C. b. Estimate the radius of an orbit that would make the average surface temperature 0°C. c. This regi ...
... a smooth curve to Mercury, Earth, and Mars. You may ignore Venus as an anomaly for the purposes of the graph. a. Estimate the radius of an orbit that would make the average surface temperature 100°C. b. Estimate the radius of an orbit that would make the average surface temperature 0°C. c. This regi ...
Movement of the Planets Shape of the Earth
... •Revolution around Sun – vavg = 106,000 km/hr (~66,000 mi/hr) •Solar system movement around Milky Way core = 370,000 km/hr (~230,000 mi/hr) •Star group movement relative to others = 1,000,000 km/hr (~700,000 mi/hr) •Galactic movement = 580,000 km/hr (360,000 mi/hr) •Minor changes in Earth orbit, til ...
... •Revolution around Sun – vavg = 106,000 km/hr (~66,000 mi/hr) •Solar system movement around Milky Way core = 370,000 km/hr (~230,000 mi/hr) •Star group movement relative to others = 1,000,000 km/hr (~700,000 mi/hr) •Galactic movement = 580,000 km/hr (360,000 mi/hr) •Minor changes in Earth orbit, til ...
Test 2 review session
... Terrestrial - Jovian Distinction Terrestrial planets: Inner parts of Solar Nebula hotter (due to forming Sun): mostly gas. Accretion of gas atoms onto dust grains relatively inefficient. Jovian planets: Outer parts cooler: ices form (but still much gas), also ice "mantles" on dust grains => much mo ...
... Terrestrial - Jovian Distinction Terrestrial planets: Inner parts of Solar Nebula hotter (due to forming Sun): mostly gas. Accretion of gas atoms onto dust grains relatively inefficient. Jovian planets: Outer parts cooler: ices form (but still much gas), also ice "mantles" on dust grains => much mo ...
`earthlike` and second the probability that they have suitable climate
... parts, first the likelihood of having planets which are ‘earthlike’ and second the probability that they have suitable climate. ...
... parts, first the likelihood of having planets which are ‘earthlike’ and second the probability that they have suitable climate. ...
Astronomy Review - Cockeysville Middle
... To the right, are some light travel times. Even when I look at you, I see what was! The further away we look, the further back in time we see. ...
... To the right, are some light travel times. Even when I look at you, I see what was! The further away we look, the further back in time we see. ...
Mon May 27, 2013 THE VENERABLE BEDE FEAST DAY On May
... a standstill! As the historian Herodotus tells us: “Just as the battle was growing warm, day was suddenly changed into night. When the Lydians and the Medes observed the change, they ceased their fighting and were anxious to conclude peace.” The sun-worshipping armies recognized divine displeasure w ...
... a standstill! As the historian Herodotus tells us: “Just as the battle was growing warm, day was suddenly changed into night. When the Lydians and the Medes observed the change, they ceased their fighting and were anxious to conclude peace.” The sun-worshipping armies recognized divine displeasure w ...
PISGAH Text by Dr. Bob Hayward ASTRONOMICAL Astronomer
... To the east of Jupiter as the sky darkens is the red planet Mars now hanging around in the middle of Libra the scales. Mars was at its closest point to the earth on May 30 and, thus, is very bright right now, almost as bright as Jupiter the second brightest planet in the sky. Look for Mars well up i ...
... To the east of Jupiter as the sky darkens is the red planet Mars now hanging around in the middle of Libra the scales. Mars was at its closest point to the earth on May 30 and, thus, is very bright right now, almost as bright as Jupiter the second brightest planet in the sky. Look for Mars well up i ...
Revolving and Rotating
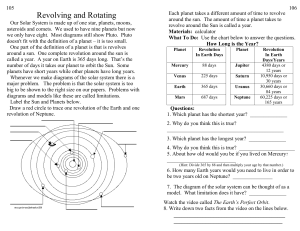
... Revolving and Rotating Our Solar System is made up of one star, planets, moons, asteroids and comets. We used to have nine planets but now we only have eight. Most diagrams still show Pluto. Pluto doesn't fit with the definition of a planet – it is too small. One part of the definition of a planet i ...
... Revolving and Rotating Our Solar System is made up of one star, planets, moons, asteroids and comets. We used to have nine planets but now we only have eight. Most diagrams still show Pluto. Pluto doesn't fit with the definition of a planet – it is too small. One part of the definition of a planet i ...
How much do we make
... Revolving and Rotating Our Solar System is made up of one star, planets, moons, asteroids and comets. We used to have nine planets but now we only have eight. Most diagrams still show Pluto. Pluto doesn't fit with the definition of a planet – it is too small. One part of the definition of a planet i ...
... Revolving and Rotating Our Solar System is made up of one star, planets, moons, asteroids and comets. We used to have nine planets but now we only have eight. Most diagrams still show Pluto. Pluto doesn't fit with the definition of a planet – it is too small. One part of the definition of a planet i ...
The Planets
... • Mercury’s hot side is hot enough to melt metal but it’s cold side is cold enough to freeze you to death. •Mercury has a diameter of 3031 miles across. ...
... • Mercury’s hot side is hot enough to melt metal but it’s cold side is cold enough to freeze you to death. •Mercury has a diameter of 3031 miles across. ...
Interiors of Jupiter and Saturn - University of Iowa Astrophysics
... In earlier lectures we saw how much we learned from studies of the Earth s moon (the Moon). It is the key to understanding the solar system How much can we learn from the moons (or satel ...
... In earlier lectures we saw how much we learned from studies of the Earth s moon (the Moon). It is the key to understanding the solar system How much can we learn from the moons (or satel ...
Matter and Chemical Change Quick Summary
... -The position of a star can be determined using an astrolabe. The astrolabe provides information on the azimuth (compass direction) and the altitude (height readings) - Triangulation and parallax are used to determine the distance of objects in space. Triangulation uses an imaginary triangle between ...
... -The position of a star can be determined using an astrolabe. The astrolabe provides information on the azimuth (compass direction) and the altitude (height readings) - Triangulation and parallax are used to determine the distance of objects in space. Triangulation uses an imaginary triangle between ...
Goal to get to know the moons of Saturn a bit better
... frozen water. • But at these temperatures, water is hard as rock. • Surroundings is a watery, tarry version of sand. ...
... frozen water. • But at these temperatures, water is hard as rock. • Surroundings is a watery, tarry version of sand. ...
Objects in the Sky Power Point
... On the first day of January 1801, Giuseppe Piazzi discovered an object which he first thought was a new comet. But after its orbit was better determined it was clear that it was not a comet but more like a small planet. Piazzi named it Ceres, after the Sicilian goddess of grain. Three other small b ...
... On the first day of January 1801, Giuseppe Piazzi discovered an object which he first thought was a new comet. But after its orbit was better determined it was clear that it was not a comet but more like a small planet. Piazzi named it Ceres, after the Sicilian goddess of grain. Three other small b ...
Models of the Solar System
... • His model was not accepted by most ancient Greeks. • The geocentric model could explain all observations ...
... • His model was not accepted by most ancient Greeks. • The geocentric model could explain all observations ...
Lesson 2_GoingSolar
... million kilometers closer to the sun during January than in July. The change in Earth’s distance from the sun doesn’t affect ...
... million kilometers closer to the sun during January than in July. The change in Earth’s distance from the sun doesn’t affect ...
1 HoNoRS227 Examination #3 Name
... receive the radio signals from such a planet. B Because the star is so close that we should have received radio signals from the planet years ago. C Because the radio signals cannot penetrate the Earth’s atmosphere from outer space. D Because we are able to hear radio waves, this should have been di ...
... receive the radio signals from such a planet. B Because the star is so close that we should have received radio signals from the planet years ago. C Because the radio signals cannot penetrate the Earth’s atmosphere from outer space. D Because we are able to hear radio waves, this should have been di ...
The Universe and Space Travel
... a net flux of lines of force, through what topologists would call "a handle" of the multiply-connected space, and what physicists might perhaps be excused for more vividly terming a "wormhole”.” — John Wheeler in Annals of Physics ...
... a net flux of lines of force, through what topologists would call "a handle" of the multiply-connected space, and what physicists might perhaps be excused for more vividly terming a "wormhole”.” — John Wheeler in Annals of Physics ...
ExoplanetWorksheet
... mass’ do you get better detail when you plot with linear or logarithmic data points? __________________________________ *All of the rocky planets in our Solar System are at least 3 times more dense than Jupiter. Does it look like we’ve found very many or very few rocky exoplanets? __________________ ...
... mass’ do you get better detail when you plot with linear or logarithmic data points? __________________________________ *All of the rocky planets in our Solar System are at least 3 times more dense than Jupiter. Does it look like we’ve found very many or very few rocky exoplanets? __________________ ...
Acquaintance with solar system. By Edgaras Montvila 6D
... Uranus is named after the ancient Greek deity of the sky Uranus, the father of Cronus (Saturn ) and grandfather of Zeus( Jupiter). Surface temperature varies from –197.2 °C to ? °C. Uranus has a ring system. The planet system has a unique configuration among those of the planets because its axis of ...
... Uranus is named after the ancient Greek deity of the sky Uranus, the father of Cronus (Saturn ) and grandfather of Zeus( Jupiter). Surface temperature varies from –197.2 °C to ? °C. Uranus has a ring system. The planet system has a unique configuration among those of the planets because its axis of ...
Astrobiology

Astrobiology is the study of the origin, evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe: extraterrestrial life and life on Earth. This interdisciplinary field encompasses the search for habitable environments in our Solar System and habitable planets outside our Solar System, the search for evidence of prebiotic chemistry, laboratory and field research into the origins and early evolution of life on Earth, and studies of the potential for life to adapt to challenges on Earth and in outer space. Astrobiology addresses the question of whether life exists beyond Earth, and how humans can detect it if it does. (The term exobiology is similar but more specific—it covers the search for life beyond Earth, and the effects of extraterrestrial environments on living things.)Astrobiology makes use of physics, chemistry, astronomy, biology, molecular biology, ecology, planetary science, geography, and geology to investigate the possibility of life on other worlds and help recognize biospheres that might be different from the biosphere on Earth. The origin and early evolution of life is an inseparable part of the discipline of astrobiology. Astrobiology concerns itself with interpretation of existing scientific data; given more detailed and reliable data from other parts of the universe, the roots of astrobiology itself—physics, chemistry and biology—may have their theoretical bases challenged. Although speculation is entertained to give context, astrobiology concerns itself primarily with hypotheses that fit firmly into existing scientific theories.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. According to research published in August 2015, very large galaxies may be more favorable to the creation and development of habitable planets than smaller galaxies, like the Milky Way galaxy. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently.Current studies on the planet Mars by the Curiosity and Opportunity rovers are now searching for evidence of ancient life as well as plains related to ancient rivers or lakes that may have been habitable. The search for evidence of habitability, taphonomy (related to fossils), and organic molecules on the planet Mars is now a primary NASA objective on Mars.