Document
... Explaining the Characteristics of the Solar System 1. The orbits of the planets lie in the same plane because the rotating solar nebula collapsed into a disk, and the planets formed in that disk. Objects are co-eval (4.) 2. The division into small inner and giant outer planets rests upon the amoun ...
... Explaining the Characteristics of the Solar System 1. The orbits of the planets lie in the same plane because the rotating solar nebula collapsed into a disk, and the planets formed in that disk. Objects are co-eval (4.) 2. The division into small inner and giant outer planets rests upon the amoun ...
Sem one 2011 review KEY
... 42. What is the difference between nuclear fission and nuclear fusion? Fusion: H+H=He + energy; Fission: Uranium splits into “daughter” elements and releases energy and radiation. 43. What element is the main ingredient of most stars? Hydrogen 44. Some stars in the sky that we can see have been gone ...
... 42. What is the difference between nuclear fission and nuclear fusion? Fusion: H+H=He + energy; Fission: Uranium splits into “daughter” elements and releases energy and radiation. 43. What element is the main ingredient of most stars? Hydrogen 44. Some stars in the sky that we can see have been gone ...
Seasons powerpoint File - Galena Park ISD Moodle
... 6 What does point 7 represents, how large is it and what is the results of it on the seasons? Point 7 represents the Earth’s tilt. Earth is tilted 23.50 on its axis. The north end of the axis always points toward the North Star. Tilt Axis results in variations of the angle of light striking Earth. 7 ...
... 6 What does point 7 represents, how large is it and what is the results of it on the seasons? Point 7 represents the Earth’s tilt. Earth is tilted 23.50 on its axis. The north end of the axis always points toward the North Star. Tilt Axis results in variations of the angle of light striking Earth. 7 ...
Cycles - Needham.K12.ma.us
... Tides are caused by gravity pulling on the Earth’s bodies of water and upon the Earth itself. There are 2 gravitational bodies that affect the tides: the sun and the moon. The moon is much closer to the Earth than the sun is, so it has a much greater influence upon the tides. ...
... Tides are caused by gravity pulling on the Earth’s bodies of water and upon the Earth itself. There are 2 gravitational bodies that affect the tides: the sun and the moon. The moon is much closer to the Earth than the sun is, so it has a much greater influence upon the tides. ...
⎯15 Sep Kepler attacks Mars
... ascension of Mars is 7hr 46min (116.5° from the sun on the vernal equinox). – On 1 Jan 1980, Mars is at 11hr 06min (166.5°). – On 15 Jan 1980, Mars is at 11hr 12min (168.0°). – On 6 February 1980 (one Martian year later), Mars is at 11hr 02min ...
... ascension of Mars is 7hr 46min (116.5° from the sun on the vernal equinox). – On 1 Jan 1980, Mars is at 11hr 06min (166.5°). – On 15 Jan 1980, Mars is at 11hr 12min (168.0°). – On 6 February 1980 (one Martian year later), Mars is at 11hr 02min ...
here - Just A Theory
... aside, there is no scientific evidence that we have ever been visited by an alien civilisation. The reason why could lie in just how vast space is. Our nearest star system Alpha Centauri, 4.3 light years away, at the speed of Voyager it would take 80,000 years to reach.[9] Nothing humanity has ever ...
... aside, there is no scientific evidence that we have ever been visited by an alien civilisation. The reason why could lie in just how vast space is. Our nearest star system Alpha Centauri, 4.3 light years away, at the speed of Voyager it would take 80,000 years to reach.[9] Nothing humanity has ever ...
universal gravitation pdf
... square of distance between objects • For a spherical body, distance is measured from its center • If distance is doubled, force is one-fourth as much; if tripled, force is one-ninth (1/3)2 • If distance is halved, force is 4 times as much; if distance is 1/3 as much, force is 9 ...
... square of distance between objects • For a spherical body, distance is measured from its center • If distance is doubled, force is one-fourth as much; if tripled, force is one-ninth (1/3)2 • If distance is halved, force is 4 times as much; if distance is 1/3 as much, force is 9 ...
Physics@Brock - Brock University
... advances in our understanding of the heavens with careful observations and clever reasoning. Their advances in understanding the cosmos are truly remarkable. The ancients were so good at explaining the heavens that progress in our understanding was subsequently very slow for the next 2000 years! Ari ...
... advances in our understanding of the heavens with careful observations and clever reasoning. Their advances in understanding the cosmos are truly remarkable. The ancients were so good at explaining the heavens that progress in our understanding was subsequently very slow for the next 2000 years! Ari ...
AstronomyQuotes
... star lost in a galaxy tucked away in some forgotten corner of a universe in which there are far more galaxies than people. ...
... star lost in a galaxy tucked away in some forgotten corner of a universe in which there are far more galaxies than people. ...
THE DOCTRINE OF ORIGINAL SPIN
... but colder so the fact that it rotates 1.75 times slower than Saturn is in line with expectations. Uranus’ axis of rotation is almost at right angles to its equatorial axis (obliquity), a fact that is not explainable by our model. Neptune’s rotation rate is in line with expectations as compared to e ...
... but colder so the fact that it rotates 1.75 times slower than Saturn is in line with expectations. Uranus’ axis of rotation is almost at right angles to its equatorial axis (obliquity), a fact that is not explainable by our model. Neptune’s rotation rate is in line with expectations as compared to e ...
Searching for planets around evolved stars with COROT
... Recently we have undertaken the detection of two new extrasolar planets, orbiting the giant stars HD 47536 (ref b) and HD 122430 (ref c). These results were consequences of our precise radial velocity (RV) measurements of G and K giants (ref a). A number of stars from our list of 80 targets have bee ...
... Recently we have undertaken the detection of two new extrasolar planets, orbiting the giant stars HD 47536 (ref b) and HD 122430 (ref c). These results were consequences of our precise radial velocity (RV) measurements of G and K giants (ref a). A number of stars from our list of 80 targets have bee ...
Chapter 4 The Solar System
... rotation rate must be constant: Therefore, as a dust cloud collapses, its rate of rotation will increase. ...
... rotation rate must be constant: Therefore, as a dust cloud collapses, its rate of rotation will increase. ...
Apophis - Killer Asteroid?
... How old will you be on Friday 13, 2029? That is how old you will be when a large asteroid (1)_______ very close to our planet. Asteroids are (2)_______ that circle the sun in space and sometimes come close to Earth and even hit it. Most asteroids (3)_______ small, and you can sometimes see them as “ ...
... How old will you be on Friday 13, 2029? That is how old you will be when a large asteroid (1)_______ very close to our planet. Asteroids are (2)_______ that circle the sun in space and sometimes come close to Earth and even hit it. Most asteroids (3)_______ small, and you can sometimes see them as “ ...
Unit 6: Space
... SC.8.E.5.In.11: Identify technology used by scientists to locate, view, and study objects in space. SC.8.E.5.Su.8: Recognize that scientists use special tools to examine objects in space. SC.8.E.5.Pa.4: Recognize a technology tool created for space exploration and adapted for personal use, such as c ...
... SC.8.E.5.In.11: Identify technology used by scientists to locate, view, and study objects in space. SC.8.E.5.Su.8: Recognize that scientists use special tools to examine objects in space. SC.8.E.5.Pa.4: Recognize a technology tool created for space exploration and adapted for personal use, such as c ...
Perspectives of the Earth, Moon and Sun
... 3. Students know that our solar system consists of one star, eight planets and numerous other smaller objects. (10 mins) The view zooms into our solar system, showing the eight planets, the Sun and the asteroid belt in between the terrestrial planets and the gas giants. Students consider what the Ea ...
... 3. Students know that our solar system consists of one star, eight planets and numerous other smaller objects. (10 mins) The view zooms into our solar system, showing the eight planets, the Sun and the asteroid belt in between the terrestrial planets and the gas giants. Students consider what the Ea ...
Time From the Perspective of a Particle Physicist
... more massive stars burn their fuel faster and may only exist for 1 million years while stars like our Sun (or smaller) will exist for 10 billion years or longer • Clusters of Stars stars are formed in groups with some massive and some small. The size of the largest stars in the cluster tells us how ...
... more massive stars burn their fuel faster and may only exist for 1 million years while stars like our Sun (or smaller) will exist for 10 billion years or longer • Clusters of Stars stars are formed in groups with some massive and some small. The size of the largest stars in the cluster tells us how ...
What theories account for the origin of the solar system?
... as the sun, still found in the Sun’s atmosphere. Rocky planet material formed from clumping together of dust grains in the protostellar cloud. ...
... as the sun, still found in the Sun’s atmosphere. Rocky planet material formed from clumping together of dust grains in the protostellar cloud. ...
Astronomy Notes - Science with Ms. Peralez
... wavelengths, stars emit using an instrument called a spectroscope, which can spread the light into different wavelengths. A star is “born” when the contracting gas and dust from a nebula, or large cloud, become so dense and hot that nuclear fusion starts. After a star runs out of fuel, it becomes a ...
... wavelengths, stars emit using an instrument called a spectroscope, which can spread the light into different wavelengths. A star is “born” when the contracting gas and dust from a nebula, or large cloud, become so dense and hot that nuclear fusion starts. After a star runs out of fuel, it becomes a ...
T 4
... permanent loss of water could have happened on Venus • Venus has very high D/H (~120 times higher than Earth’s) ratio suggesting huge hydrogen loss ...
... permanent loss of water could have happened on Venus • Venus has very high D/H (~120 times higher than Earth’s) ratio suggesting huge hydrogen loss ...
stars and planets
... There are around 200 billion stars in the Milky Way alone. VY Canis Majoris is the largest known star in our galaxy, if this star was in the center of our solar system it would reach the orbit of Saturn. One of the smallest known stars in the galaxy is VB 10, it is only around 20% larger than Jupite ...
... There are around 200 billion stars in the Milky Way alone. VY Canis Majoris is the largest known star in our galaxy, if this star was in the center of our solar system it would reach the orbit of Saturn. One of the smallest known stars in the galaxy is VB 10, it is only around 20% larger than Jupite ...
Astronomy Library wk 4 .cwk (WP)
... As each scientist makes his or her contribution, scientific thought continually evolves Communication is important! ...
... As each scientist makes his or her contribution, scientific thought continually evolves Communication is important! ...
AN INTRODUCTION TO ASTRONOMY Dr. Uri Griv Department of Physics, Ben-Gurion University
... near-infrared wavelengths the planet appears substantially darkened, improving the contrast between the otherwise relatively bright planet and the normally faint rings. In fact, the narrow Uranian rings are all but impossible to see in visible light with earthbound telescopes and were discovered onl ...
... near-infrared wavelengths the planet appears substantially darkened, improving the contrast between the otherwise relatively bright planet and the normally faint rings. In fact, the narrow Uranian rings are all but impossible to see in visible light with earthbound telescopes and were discovered onl ...
Introduction to cosmology I
... 1st public commitment by professional astronomer to Copernican system ...
... 1st public commitment by professional astronomer to Copernican system ...
Astrobiology

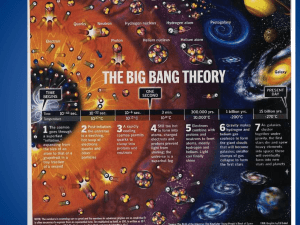
Astrobiology is the study of the origin, evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe: extraterrestrial life and life on Earth. This interdisciplinary field encompasses the search for habitable environments in our Solar System and habitable planets outside our Solar System, the search for evidence of prebiotic chemistry, laboratory and field research into the origins and early evolution of life on Earth, and studies of the potential for life to adapt to challenges on Earth and in outer space. Astrobiology addresses the question of whether life exists beyond Earth, and how humans can detect it if it does. (The term exobiology is similar but more specific—it covers the search for life beyond Earth, and the effects of extraterrestrial environments on living things.)Astrobiology makes use of physics, chemistry, astronomy, biology, molecular biology, ecology, planetary science, geography, and geology to investigate the possibility of life on other worlds and help recognize biospheres that might be different from the biosphere on Earth. The origin and early evolution of life is an inseparable part of the discipline of astrobiology. Astrobiology concerns itself with interpretation of existing scientific data; given more detailed and reliable data from other parts of the universe, the roots of astrobiology itself—physics, chemistry and biology—may have their theoretical bases challenged. Although speculation is entertained to give context, astrobiology concerns itself primarily with hypotheses that fit firmly into existing scientific theories.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. According to research published in August 2015, very large galaxies may be more favorable to the creation and development of habitable planets than smaller galaxies, like the Milky Way galaxy. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently.Current studies on the planet Mars by the Curiosity and Opportunity rovers are now searching for evidence of ancient life as well as plains related to ancient rivers or lakes that may have been habitable. The search for evidence of habitability, taphonomy (related to fossils), and organic molecules on the planet Mars is now a primary NASA objective on Mars.