SOLUTION SET
... 23. The Earth spins about its own axis and revolves around the Sun in the same sense. The length of a sidereal day is 23 hours and 56 minutes. If the Earth’s spin rate were to double, the length of the sidereal day would be: A. 23 hours and 58 minutes B. 11 hours and 56 minutes C. 24 hours and 4 mi ...
... 23. The Earth spins about its own axis and revolves around the Sun in the same sense. The length of a sidereal day is 23 hours and 56 minutes. If the Earth’s spin rate were to double, the length of the sidereal day would be: A. 23 hours and 58 minutes B. 11 hours and 56 minutes C. 24 hours and 4 mi ...
Chapter 13: Earth, Moon, and Beyond
... How Do Earth and Moon Compare? Phases of the Moon: On some nights, the moon seems round while other nights it look like a half circle or sliver. Both the moon and Earth are always moving which make them look different. The moon does not make its own light and only reflects lights from the su ...
... How Do Earth and Moon Compare? Phases of the Moon: On some nights, the moon seems round while other nights it look like a half circle or sliver. Both the moon and Earth are always moving which make them look different. The moon does not make its own light and only reflects lights from the su ...
Introduction to Astronomy
... There are many different types of rock on our planet. These can be divided into three groups: metamorphic, igneous and sedimentary. The category a rock goes into is dependent on how it was formed. Igneous means ‘made by fire’ – for example, granite. Some igneous rocks come from volcanoes. Sedimentar ...
... There are many different types of rock on our planet. These can be divided into three groups: metamorphic, igneous and sedimentary. The category a rock goes into is dependent on how it was formed. Igneous means ‘made by fire’ – for example, granite. Some igneous rocks come from volcanoes. Sedimentar ...
SeasonsPPT
... The Sun is a huge ball of fire - sends energy (light & heat) to the earth - 1/2 of earth is always illuminated - day - 1/2 of earth is always in the dark - night ...
... The Sun is a huge ball of fire - sends energy (light & heat) to the earth - 1/2 of earth is always illuminated - day - 1/2 of earth is always in the dark - night ...
Solutions
... We’re really only going to see the comet well when it is closer to 1 AU away from the Sun, where the Earth is. However, this is when the comet is moving the fastest, so it gets through this closer part of its orbit in much less time than it gets through the more distant part of its orbit. Thus, the ...
... We’re really only going to see the comet well when it is closer to 1 AU away from the Sun, where the Earth is. However, this is when the comet is moving the fastest, so it gets through this closer part of its orbit in much less time than it gets through the more distant part of its orbit. Thus, the ...
AST 301 Fall 2007 Review for Exam 3 This exam covers only
... planet, the nature of asteroids, comets, meteors,… and how they probably got to be where they are (e.g. did you remember to tell your visitor that most comets spend most of their time very far from the sun? Make sure you imagine being asked why this is so and how we know it—can you give a reasonable ...
... planet, the nature of asteroids, comets, meteors,… and how they probably got to be where they are (e.g. did you remember to tell your visitor that most comets spend most of their time very far from the sun? Make sure you imagine being asked why this is so and how we know it—can you give a reasonable ...
The Closest New Stars To Earth
... 200 and 300 new stars, including over 100 X-ray sources (between the Chamaeleon I and II clouds), approximately 50 T-Tauri stars and just a couple of massive, B-class stars. There's a third dark, molecular cloud (Chamaeleon III) that has not yet formed any stars at all. While the majority of new sta ...
... 200 and 300 new stars, including over 100 X-ray sources (between the Chamaeleon I and II clouds), approximately 50 T-Tauri stars and just a couple of massive, B-class stars. There's a third dark, molecular cloud (Chamaeleon III) that has not yet formed any stars at all. While the majority of new sta ...
Astronomy Impacts our Daily Lives
... 19-century curiosity about electricity led to the electric light, and the world wide web has allowed international teams of researcher to communicate more easily. No amount of applied research on the candle would have brought us the electric light; no amount of research and development on the teleph ...
... 19-century curiosity about electricity led to the electric light, and the world wide web has allowed international teams of researcher to communicate more easily. No amount of applied research on the candle would have brought us the electric light; no amount of research and development on the teleph ...
51) If Earth had twice its present mass, but the same radius
... 55) How can you tell if a gravitational force exists in a region of space? 56) Does the earth, the moon, or the sun produce a greater tidal effect on you right now? Why? 57) Compared to the gravitational field on the surface of Earth, the gravitational field well below Earth’s surface is 58) What is ...
... 55) How can you tell if a gravitational force exists in a region of space? 56) Does the earth, the moon, or the sun produce a greater tidal effect on you right now? Why? 57) Compared to the gravitational field on the surface of Earth, the gravitational field well below Earth’s surface is 58) What is ...
Objects In Space -- research questions
... 5. Can we see them from Earth? If so, what do they look like? ...
... 5. Can we see them from Earth? If so, what do they look like? ...
How Telescopes Changed our Universe
... In our own solar system, telescopes found planets our eyes could not see. Are there other planets outside of our solar system? ...
... In our own solar system, telescopes found planets our eyes could not see. Are there other planets outside of our solar system? ...
PRACTICE MINI-EXAM
... 3) Arrange the following objects in order of increasing mass: brown dwarf, Jupiter, Sun, Earth. ...
... 3) Arrange the following objects in order of increasing mass: brown dwarf, Jupiter, Sun, Earth. ...
Wasp-17b: An Ultra-Low Density Planet in a Probable Retrograde
... ⇒ WASP-17b is an example that the formation or planetary systems could be quite complicated ...
... ⇒ WASP-17b is an example that the formation or planetary systems could be quite complicated ...
Study Guide: Chapters 32-‐34 FROSH CHAPTER 32 1. What is
... 49. The Milky Way galaxy contains interstellar matter that may form new _______________. ...
... 49. The Milky Way galaxy contains interstellar matter that may form new _______________. ...
Intelligent Life in the Milky Way Galaxy
... to the size of the U.S. - - How far away is the nearest habitable planet? ...
... to the size of the U.S. - - How far away is the nearest habitable planet? ...
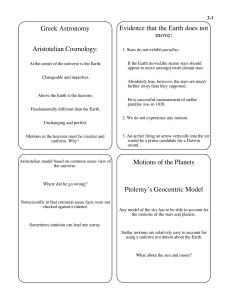
History of Astronomy
... The Greek Frame of Mind • Much of the Greek method of thinking revolved around philosophy instead of scientific reasoning • Greeks valued perfection and therefore any model of the universe should involve the perfect shape, the circle • Greek also had no reason to believe that the Earth was not the ...
... The Greek Frame of Mind • Much of the Greek method of thinking revolved around philosophy instead of scientific reasoning • Greeks valued perfection and therefore any model of the universe should involve the perfect shape, the circle • Greek also had no reason to believe that the Earth was not the ...
Formation of the Solar System
... also incorporates interstellar dust as an essential ingredient in the formation of the planets. This theory claims that the dust grains of the interstellar medium helped cool the nebular cloud by radiating heat away, and also acted as a foundation upon which atoms could attach. These properties of t ...
... also incorporates interstellar dust as an essential ingredient in the formation of the planets. This theory claims that the dust grains of the interstellar medium helped cool the nebular cloud by radiating heat away, and also acted as a foundation upon which atoms could attach. These properties of t ...
Science Investigations: Investigating Astronomy
... Definition: A rare celestial phenomenon involving the explosion of most of the material in a star, resulting in an extremely bright, short-lived object that emits vast amounts of energy Context: A black hole forms when the material from a supernova collapses in on itself. ...
... Definition: A rare celestial phenomenon involving the explosion of most of the material in a star, resulting in an extremely bright, short-lived object that emits vast amounts of energy Context: A black hole forms when the material from a supernova collapses in on itself. ...
astr100_finalexam
... space travel within, and ouside of, the solar system. List some of the issues that make human space travel within the Solar System difficult. What are the factors that make human interstellar space travel unlikely - even in the distant future? If they exist, what implications does this have for cont ...
... space travel within, and ouside of, the solar system. List some of the issues that make human space travel within the Solar System difficult. What are the factors that make human interstellar space travel unlikely - even in the distant future? If they exist, what implications does this have for cont ...
The Solar System Information Pack
... STRICTLY 7-11 year olds- spaces are restricted. The aim of this experience is to increase young learners’ understanding of the solar system, our planet and the International Space Station in a fun and engaging way. By using the planetarium as part of the experience the stars and planets come alive a ...
... STRICTLY 7-11 year olds- spaces are restricted. The aim of this experience is to increase young learners’ understanding of the solar system, our planet and the International Space Station in a fun and engaging way. By using the planetarium as part of the experience the stars and planets come alive a ...
To know that planets etc. move in elliptical orbits around the Sun.
... said to be in opposition when they are on opposite sides of the sky, viewed from a given place (usually the Earth). Perihelon –When the planet is at the closest to the sun. Aphelion – The point in its orbit when a planet or comet is at its greatest distance from the sun Occulation - An occultation i ...
... said to be in opposition when they are on opposite sides of the sky, viewed from a given place (usually the Earth). Perihelon –When the planet is at the closest to the sun. Aphelion – The point in its orbit when a planet or comet is at its greatest distance from the sun Occulation - An occultation i ...
Earth and the Universe Chapter Problems The Universe Class Work
... 3. List three different types of galaxies. Homework 4. What is the name of the galaxy in which we live? 5. In what type of galaxy do we live? The Sun Class Work 6. What type of celestial object is the sun? 7. When objects that are the same size are located at different distances, which object looks ...
... 3. List three different types of galaxies. Homework 4. What is the name of the galaxy in which we live? 5. In what type of galaxy do we live? The Sun Class Work 6. What type of celestial object is the sun? 7. When objects that are the same size are located at different distances, which object looks ...
Astrobiology

Astrobiology is the study of the origin, evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe: extraterrestrial life and life on Earth. This interdisciplinary field encompasses the search for habitable environments in our Solar System and habitable planets outside our Solar System, the search for evidence of prebiotic chemistry, laboratory and field research into the origins and early evolution of life on Earth, and studies of the potential for life to adapt to challenges on Earth and in outer space. Astrobiology addresses the question of whether life exists beyond Earth, and how humans can detect it if it does. (The term exobiology is similar but more specific—it covers the search for life beyond Earth, and the effects of extraterrestrial environments on living things.)Astrobiology makes use of physics, chemistry, astronomy, biology, molecular biology, ecology, planetary science, geography, and geology to investigate the possibility of life on other worlds and help recognize biospheres that might be different from the biosphere on Earth. The origin and early evolution of life is an inseparable part of the discipline of astrobiology. Astrobiology concerns itself with interpretation of existing scientific data; given more detailed and reliable data from other parts of the universe, the roots of astrobiology itself—physics, chemistry and biology—may have their theoretical bases challenged. Although speculation is entertained to give context, astrobiology concerns itself primarily with hypotheses that fit firmly into existing scientific theories.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. According to research published in August 2015, very large galaxies may be more favorable to the creation and development of habitable planets than smaller galaxies, like the Milky Way galaxy. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently.Current studies on the planet Mars by the Curiosity and Opportunity rovers are now searching for evidence of ancient life as well as plains related to ancient rivers or lakes that may have been habitable. The search for evidence of habitability, taphonomy (related to fossils), and organic molecules on the planet Mars is now a primary NASA objective on Mars.