
Amino Acid Oxidation, the Production of Urea, and Amino Acid
... intermediates (oxaloacetate & α-ketoglutarate) to detoxify excess free ammonia. Second, the cell must convert the resulting carbon skeletons into intermediates that can enter “mainstream” metabolism, i.e., the TCA Cycle, and ET/OxPhos. When amino acids are utilized for gluconeogenesis or an excess ...
... intermediates (oxaloacetate & α-ketoglutarate) to detoxify excess free ammonia. Second, the cell must convert the resulting carbon skeletons into intermediates that can enter “mainstream” metabolism, i.e., the TCA Cycle, and ET/OxPhos. When amino acids are utilized for gluconeogenesis or an excess ...
Sugars
... The D and L families of sugars: Enantiomers - „mirror images“ (rotate polarized light in opposite directions → optical activity) Fischer projection: ...
... The D and L families of sugars: Enantiomers - „mirror images“ (rotate polarized light in opposite directions → optical activity) Fischer projection: ...
Cellular Respiration
... Stage 2: The Krebs Cycle The Krebs cycle completes the breakdown of sugar It occurs inside the mitochondria In the Krebs cycle, pyruvic acid from glycolysis is first “prepped” into a usable form by combining it with enzyme Co-A to make Acetyl-CoA ...
... Stage 2: The Krebs Cycle The Krebs cycle completes the breakdown of sugar It occurs inside the mitochondria In the Krebs cycle, pyruvic acid from glycolysis is first “prepped” into a usable form by combining it with enzyme Co-A to make Acetyl-CoA ...
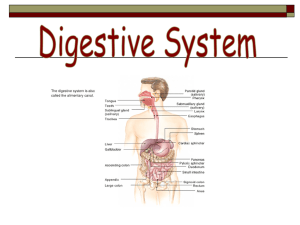
The Digestive System
... 2. If a smooth tube, intestine would have to be 500-600 m long to have a comparable surface area. 3. Each villus contains blood vessels and a lymphatic lacteal. 4. Lacteal is lymphatic vessel in an intestinal villus that aids in absorption of fats. 5. Sugars and amino acids enter villi cells and are ...
... 2. If a smooth tube, intestine would have to be 500-600 m long to have a comparable surface area. 3. Each villus contains blood vessels and a lymphatic lacteal. 4. Lacteal is lymphatic vessel in an intestinal villus that aids in absorption of fats. 5. Sugars and amino acids enter villi cells and are ...
Carbohydrate Metabolism
... Metabolism: is the entire network of chemical reactions carried out by living cells. It is also refer to the intermediate steps within the cells in which the nutrient molecules or foodstuffs are metabolized and converted into cellular components catalysed by enzymes. The fate of dietary components a ...
... Metabolism: is the entire network of chemical reactions carried out by living cells. It is also refer to the intermediate steps within the cells in which the nutrient molecules or foodstuffs are metabolized and converted into cellular components catalysed by enzymes. The fate of dietary components a ...
Practical part
... 8. Objective of biochemical investigations: the whole organism and its organs, tissues, cells, homogenates, subcellular organelles, extracts and molecular biocomplexes. 9. Clinical and diagnostic significance of biochemical investigation. 10. Biological material used in biochemical investigations. 1 ...
... 8. Objective of biochemical investigations: the whole organism and its organs, tissues, cells, homogenates, subcellular organelles, extracts and molecular biocomplexes. 9. Clinical and diagnostic significance of biochemical investigation. 10. Biological material used in biochemical investigations. 1 ...
Document
... are chemically altered and then used in the Krebs cycle • Fats are broken up and fed into glycolysis and the Krebs cycle Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... are chemically altered and then used in the Krebs cycle • Fats are broken up and fed into glycolysis and the Krebs cycle Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Monogastric Nutrition
... Added as an energy source Reduces dustiness of feed and increases palatability To be economical, cost must be no more than 2.5 to 3.0 times the cost of corn ...
... Added as an energy source Reduces dustiness of feed and increases palatability To be economical, cost must be no more than 2.5 to 3.0 times the cost of corn ...
Protein Folding and The Impact of Mutations
... Everyone else would probably move to the opposite side! ...
... Everyone else would probably move to the opposite side! ...
chemistry of phospholipids in relation to biological membranes
... that with evolution the molecular composition of phospholipids has become more complex. As will be discussed later in this paper chemically different phospholipid molecules may be rather similar with respect to their physical properties and may be able to a given extent to fulfil a similar function ...
... that with evolution the molecular composition of phospholipids has become more complex. As will be discussed later in this paper chemically different phospholipid molecules may be rather similar with respect to their physical properties and may be able to a given extent to fulfil a similar function ...
29_Metabolism of amino acids. Digestion of proteins
... • Proteins of animal sources (meat, milk, eggs) have high BV because they contain all the essential amino acids. • Proteins from plant sources (wheat, corn, beans) have low BV thus combination of more than one plant protein is required (a vegetarian diet) to increase its BV. ...
... • Proteins of animal sources (meat, milk, eggs) have high BV because they contain all the essential amino acids. • Proteins from plant sources (wheat, corn, beans) have low BV thus combination of more than one plant protein is required (a vegetarian diet) to increase its BV. ...
Biochemistry I, Spring Term 2000 - Third Exam
... ii) Do high levels of this compound indicate high or low energy reserves in the cell. Why?(3 pts) NAD+ and ADP indicate low energy levels since the energy of ATP hydrolysis is used to drive many biological processes. Low levels of NAD+ indicate that additional ATP cannot be generated by oxidative ph ...
... ii) Do high levels of this compound indicate high or low energy reserves in the cell. Why?(3 pts) NAD+ and ADP indicate low energy levels since the energy of ATP hydrolysis is used to drive many biological processes. Low levels of NAD+ indicate that additional ATP cannot be generated by oxidative ph ...
Presentation
... • Lactate formed in skeletal muscles during exercise is transported to the liver • Liver lactate dehydrogenase can reconvert lactate to pyruvate • Lactic acidosis can result from insufficient oxygen (an increase in lactic acid and decrease in blood pH) ...
... • Lactate formed in skeletal muscles during exercise is transported to the liver • Liver lactate dehydrogenase can reconvert lactate to pyruvate • Lactic acidosis can result from insufficient oxygen (an increase in lactic acid and decrease in blood pH) ...
PDF
... The homeodomain is a DNA binding domain about 60 amino acids in length that occurs in many developmental regulatory proteins. Based on their degree of relatedness, homeodomain sequences have been grouped into 10 different families plus some unclassified sequences (1). Using a set of degenerate oligo ...
... The homeodomain is a DNA binding domain about 60 amino acids in length that occurs in many developmental regulatory proteins. Based on their degree of relatedness, homeodomain sequences have been grouped into 10 different families plus some unclassified sequences (1). Using a set of degenerate oligo ...
Lecture 17 Glycolysis (continued) Recap Phases: priming: glucose
... But relative to complete oxidation of glucose: glucose + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O ΔGo’ = -2840 kJ/mol glucose → 2 ethanol + 2 CO2 is 61/2840 = 2.1% glucose → 2 lactate: lactate from muscles recycled in the liver Control of the rate of glycolysis Note ATP inhibition, glycogen storage at rest; AMP, FBP s ...
... But relative to complete oxidation of glucose: glucose + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O ΔGo’ = -2840 kJ/mol glucose → 2 ethanol + 2 CO2 is 61/2840 = 2.1% glucose → 2 lactate: lactate from muscles recycled in the liver Control of the rate of glycolysis Note ATP inhibition, glycogen storage at rest; AMP, FBP s ...
Lecture 7
... compartment. Six carbon atoms enter these reactions (in two pyruvate), and six leave (in six CO2). Many coenzymes form. ...
... compartment. Six carbon atoms enter these reactions (in two pyruvate), and six leave (in six CO2). Many coenzymes form. ...
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acids
... How do amino acid monomers polymerize to form protein polymers? In other words, how are proteins put together? ...
... How do amino acid monomers polymerize to form protein polymers? In other words, how are proteins put together? ...
Chapter 1 - Private Label Fitness
... During aerobic glycolysis, oxygen inhibits The accumulation of sweat The accumulation of fat The accumulation of lactic acid ...
... During aerobic glycolysis, oxygen inhibits The accumulation of sweat The accumulation of fat The accumulation of lactic acid ...
Digestion
... Your stools may be very hard, making them so difficult to pass that you have to strain. Or you may feel like you still need to have a bowel movement even after you've had one. ...
... Your stools may be very hard, making them so difficult to pass that you have to strain. Or you may feel like you still need to have a bowel movement even after you've had one. ...
Digestive System
... cholesterol, fatty acids, lecithin, inorganic salts 2. Only bile salts (cholesterol product) are important in digestion 3. Bile salts emulsify fats by reducing surface tension 4. Bile salts also important in absorption of fatty acids 5. Bile flow and production regulated by hormone secretion 6. Chol ...
... cholesterol, fatty acids, lecithin, inorganic salts 2. Only bile salts (cholesterol product) are important in digestion 3. Bile salts emulsify fats by reducing surface tension 4. Bile salts also important in absorption of fatty acids 5. Bile flow and production regulated by hormone secretion 6. Chol ...
Physio Chap 65 - Digestion and Absorption in the GI Tract [10-26-13].
... This active transport causes a steep electrochemical gradient inside the cell so sodium slides down that gradient by facilitated diffusion with glucose INTO the epithelial cells Once inside the cell, other facilitated diffusion gets the glucose into the blood. The first step of sodium transpor ...
... This active transport causes a steep electrochemical gradient inside the cell so sodium slides down that gradient by facilitated diffusion with glucose INTO the epithelial cells Once inside the cell, other facilitated diffusion gets the glucose into the blood. The first step of sodium transpor ...
Microbial Metabolism
... a. Oxidation is the removal of electrons b. Reduction is the gaining of electrons c. Oxidation and reduction always occur together. d. Most microorganisms oxidize carbohydrates as their primary source of energy. ...
... a. Oxidation is the removal of electrons b. Reduction is the gaining of electrons c. Oxidation and reduction always occur together. d. Most microorganisms oxidize carbohydrates as their primary source of energy. ...
ch5_SP13x
... • Between inner and outer membranes • Also within the cristae • Acidified ( high [H+] ) by action of the Electron Transport Chain (ETC) – H+ are pumped from matrix into this compartment – ATP synthase lets them back into the matrix ...
... • Between inner and outer membranes • Also within the cristae • Acidified ( high [H+] ) by action of the Electron Transport Chain (ETC) – H+ are pumped from matrix into this compartment – ATP synthase lets them back into the matrix ...




















![Physio Chap 65 - Digestion and Absorption in the GI Tract [10-26-13].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000775560_1-a59ff73af15bb99be2e8cb372c3152c6-300x300.png)

