Judith Wakefield Indian River County Extension August 29, 2004
... Hydrogenation was originally done to make the oils more stable, and vegetable oils were less expensive than butter. Foods made with large amounts of vegetable shortening or stick margarine have been found to contain trans fats which raise the cholesterol level, raise the LDL level and lower the HDL ...
... Hydrogenation was originally done to make the oils more stable, and vegetable oils were less expensive than butter. Foods made with large amounts of vegetable shortening or stick margarine have been found to contain trans fats which raise the cholesterol level, raise the LDL level and lower the HDL ...
What is the immune system?
... - Your body has been exposed to the antigen in the past either through: - Exposure to the actual disease causing antigen – You fought it, you won, you remember it - Planned exposure to a form of the antigen that has been killed or weakened – You detected it, eliminated it, and remember it What is th ...
... - Your body has been exposed to the antigen in the past either through: - Exposure to the actual disease causing antigen – You fought it, you won, you remember it - Planned exposure to a form of the antigen that has been killed or weakened – You detected it, eliminated it, and remember it What is th ...
Colloquim II 1. Which of the definitions of "arterial hyperemia" is
... malignant clone of the cells; +c) transformation of the normal cell into the tumor cell; d) the ability of tumor cells to metastasis; e) activation mechanisms of antineoplastic resistance of the organism. 60. Leads to malignant transformation of cells: +a) activation of oncogenes; +b) inhibition of ...
... malignant clone of the cells; +c) transformation of the normal cell into the tumor cell; d) the ability of tumor cells to metastasis; e) activation mechanisms of antineoplastic resistance of the organism. 60. Leads to malignant transformation of cells: +a) activation of oncogenes; +b) inhibition of ...
L04 Pathophysiology Inflammastion
... Plasma cell is a mature B lymphocyte , the difference between them that plasma cell can produce anti-body . We have many type of T lymphocyte , in asthma we have 2 type : * TH l and TH ll . -Tissue destruction, induced by the persistent offending agent or by the inflammatory cells :the leukocyte the ...
... Plasma cell is a mature B lymphocyte , the difference between them that plasma cell can produce anti-body . We have many type of T lymphocyte , in asthma we have 2 type : * TH l and TH ll . -Tissue destruction, induced by the persistent offending agent or by the inflammatory cells :the leukocyte the ...
Project name: Release of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs) in
... Deficient NET formation predisposes humans to severe infection, while uncontrolled NET formation contributes to inflammation, vascular injury and tissue damage. Making too many or not disposing of NETs at the right time and in the right place is pathogenic. Therefore, regulating NET formation is imp ...
... Deficient NET formation predisposes humans to severe infection, while uncontrolled NET formation contributes to inflammation, vascular injury and tissue damage. Making too many or not disposing of NETs at the right time and in the right place is pathogenic. Therefore, regulating NET formation is imp ...
our Understanding Lipids booklet to learn
... storage for later use is perfect in times of famine or food scarcity. The process is supervised by a well-known hormone called insulin. To help you understand how insulin turns carbohydrates (natural sugars) into cholesterol and triglycerides, let us follow the path of a carbohydrate. Let’s say you ...
... storage for later use is perfect in times of famine or food scarcity. The process is supervised by a well-known hormone called insulin. To help you understand how insulin turns carbohydrates (natural sugars) into cholesterol and triglycerides, let us follow the path of a carbohydrate. Let’s say you ...
Blood Fact - Fulton County Schools
... They are red because they contain a protein called hemoglobin that is red in color Red blood cells are round and thinner in the middle, like a balloon that is partly filled with water. This lets them squeeze through tiny blood vessels without breaking Biconcave shape increases surface area to allow ...
... They are red because they contain a protein called hemoglobin that is red in color Red blood cells are round and thinner in the middle, like a balloon that is partly filled with water. This lets them squeeze through tiny blood vessels without breaking Biconcave shape increases surface area to allow ...
03 PACE Inflammatory process and CV - pace
... causal role of inflammation in atherosclerosis. 2. Clinical studies evaluating whether clinical outcome in patients with coronary disease can be improved by anti-inflammatory strategies are under way. ...
... causal role of inflammation in atherosclerosis. 2. Clinical studies evaluating whether clinical outcome in patients with coronary disease can be improved by anti-inflammatory strategies are under way. ...
Blood
... Stem Cells Immortal, meaning they never die (at least not until you do). Undifferentiated, meaning they have not yet developed into a particular cell type. Stem cells are pluripotent, meaning they have the potential to become any type of blood cell The immortal, undifferentiated, pluripotent st ...
... Stem Cells Immortal, meaning they never die (at least not until you do). Undifferentiated, meaning they have not yet developed into a particular cell type. Stem cells are pluripotent, meaning they have the potential to become any type of blood cell The immortal, undifferentiated, pluripotent st ...
Group A
... Group A – has only the A antigen on red cells (and B antibody in the plasma) Group B – has only the B antigen on red cells (and A antibody in the plasma) Group AB – has both A and B antigens on red cells (but neither A nor B antibody in the plasma) Group O – has neither A nor B antigens on red cell ...
... Group A – has only the A antigen on red cells (and B antibody in the plasma) Group B – has only the B antigen on red cells (and A antibody in the plasma) Group AB – has both A and B antigens on red cells (but neither A nor B antibody in the plasma) Group O – has neither A nor B antigens on red cell ...
The Blood Cells - Immaculateheartacademy.org
... Recipient- is the person who receives the blood Transfusion Reaction- When antibodies in the plasma of the recipient bind to antigens on the red blood cells of the donor, “molecular bridges” are formed that connect the red blood cells causing them to agglutinate and rupture the blood cells ...
... Recipient- is the person who receives the blood Transfusion Reaction- When antibodies in the plasma of the recipient bind to antigens on the red blood cells of the donor, “molecular bridges” are formed that connect the red blood cells causing them to agglutinate and rupture the blood cells ...
Types of autoimmune diseases and their symptoms Disease
... substance found in wheat, rye, and barley, and also some medicines. When people with celiac disease eat foods or use products that have gluten, the immune system responds by damaging the lining of the small intestines. ...
... substance found in wheat, rye, and barley, and also some medicines. When people with celiac disease eat foods or use products that have gluten, the immune system responds by damaging the lining of the small intestines. ...
Chapter 6
... Blood flows through capillaries relatively slowly, allowing sufficient time for diffusion or active transport of substances across walls. Only about 5 to 10% of capillaries have blood flowing through them. Only a few organs (brain and heart) always carry full load of blood. Blood flow to different o ...
... Blood flows through capillaries relatively slowly, allowing sufficient time for diffusion or active transport of substances across walls. Only about 5 to 10% of capillaries have blood flowing through them. Only a few organs (brain and heart) always carry full load of blood. Blood flow to different o ...
Thrd-Lec. م.م حنان ديكان عباس Leukocytes (White Blood Cells) The
... The basophils in the circulating blood are similar to the large tissue mast cells located immediately outside many of the capillaries in the body. Both mast cells and basophils liberate heparin into the blood, a substance that can prevent blood coagulation. The mast cells and basophils also release ...
... The basophils in the circulating blood are similar to the large tissue mast cells located immediately outside many of the capillaries in the body. Both mast cells and basophils liberate heparin into the blood, a substance that can prevent blood coagulation. The mast cells and basophils also release ...
Laboratory Exercise # 17: Blood Lab Purpose: The purpose of this
... Those granules take up the basic stain and become colored dark bluish purple. Basophils have the ability to enter tissues and release their histamine containing granules. There are two types of agranulocytes: monocytes and lymphocytes. Monocytes are the largest of the white blood cells with a kidney ...
... Those granules take up the basic stain and become colored dark bluish purple. Basophils have the ability to enter tissues and release their histamine containing granules. There are two types of agranulocytes: monocytes and lymphocytes. Monocytes are the largest of the white blood cells with a kidney ...
NME2.12 - Lipid Digestion and Absorption
... Lipids are fats (or fat-like substances) that can be either non-polar and completely water insoluble or polar and partially water soluble Dietary lipids consist mainly of triglycerides and phospholipids Lipids are absorbed entirely within the small intestine, mostly in the duodenum Solid fat and oil ...
... Lipids are fats (or fat-like substances) that can be either non-polar and completely water insoluble or polar and partially water soluble Dietary lipids consist mainly of triglycerides and phospholipids Lipids are absorbed entirely within the small intestine, mostly in the duodenum Solid fat and oil ...
The First and Second Lines of Defense Against Disease
... Chronic Inflammation: this is long term and can last for months or even years ...
... Chronic Inflammation: this is long term and can last for months or even years ...
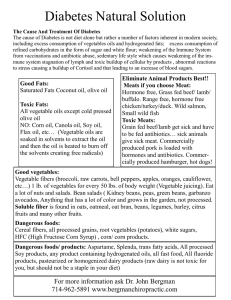
Diabetes - owners
... • Repair the faulty blood sugar control system. This is done simply by substituting clean, healthy, beneficial fats and oils in the diet for the pristine-looking but toxic trans-isomer mix found in attractive plastic containers on supermarket shelves. Consume only flax oil, fish oil and occasionall ...
... • Repair the faulty blood sugar control system. This is done simply by substituting clean, healthy, beneficial fats and oils in the diet for the pristine-looking but toxic trans-isomer mix found in attractive plastic containers on supermarket shelves. Consume only flax oil, fish oil and occasionall ...
Review Article Distinct Functions of Specialized
... Deficiency in CCL17 inhibited atherosclerotic lesion formation at different stages of plaque progression and disease models, that is, diet-induced and spontaneous lesion formation. In Apoe−/− mice deficient in CCL17, atherosclerotic lesions were characterized by a reduction in macrophage and T-cell ...
... Deficiency in CCL17 inhibited atherosclerotic lesion formation at different stages of plaque progression and disease models, that is, diet-induced and spontaneous lesion formation. In Apoe−/− mice deficient in CCL17, atherosclerotic lesions were characterized by a reduction in macrophage and T-cell ...
Immunity (Ag).
... (CBC), which determines the number and types of blood cells present. This test can provide information about the status of the patient’s immune system. ...
... (CBC), which determines the number and types of blood cells present. This test can provide information about the status of the patient’s immune system. ...
Physiology for Pharmacy Students Tortora 13th Ebaa M Alzayadneh
... – Except for lymphocytes – live for months or years – Far less numerous than RBCs – Leukocytosis is a normal protective response to invaders, strenuous exercise, anesthesia and surgery – Leukopenia is never beneficial – General function to combat invaders by phagocytosis or immune responses Universi ...
... – Except for lymphocytes – live for months or years – Far less numerous than RBCs – Leukocytosis is a normal protective response to invaders, strenuous exercise, anesthesia and surgery – Leukopenia is never beneficial – General function to combat invaders by phagocytosis or immune responses Universi ...
Lipid Management in 2013 by Dr. Orringer
... Traditionally ALT and AST have been routinely measured during statin maintenance therapy Irreversible hepatic damage due to statins is extremely rare and likely idiosyncratic (less than 2 per one million patient-years) There are no data to support routine LFT monitoring to identify such patients FDA ...
... Traditionally ALT and AST have been routinely measured during statin maintenance therapy Irreversible hepatic damage due to statins is extremely rare and likely idiosyncratic (less than 2 per one million patient-years) There are no data to support routine LFT monitoring to identify such patients FDA ...
Position Statement On Cholesterol
... carbohydrates (e.g. some low fat dairy products that contain starches and sugars to achieve a similar mouth feel and taste as their full cream counterparts) is not associated with a reduced risk for CVD. According to the body of evidence, saturated fat needs to be replaced by either unsaturated fatt ...
... carbohydrates (e.g. some low fat dairy products that contain starches and sugars to achieve a similar mouth feel and taste as their full cream counterparts) is not associated with a reduced risk for CVD. According to the body of evidence, saturated fat needs to be replaced by either unsaturated fatt ...
Immune System Memory Game
... equipped with a fantastic defense team called the Immune System. The Immune System works with several other major body systems, including the circulatory system, as well as hormones, proteins, white blood cells and red blood cells to help keep our bodies safe from outside invaders. ...
... equipped with a fantastic defense team called the Immune System. The Immune System works with several other major body systems, including the circulatory system, as well as hormones, proteins, white blood cells and red blood cells to help keep our bodies safe from outside invaders. ...
Presentation 2
... • Platelets stick tenaciously to the collagen exposed in damaged blood vessels • A large protein Factor 8 (with Von Willibrand factor) links platelets at the plug to each other and to the collagen in the vessel wall • ADP and serotonin released from platelets also increase the platelet aggregation t ...
... • Platelets stick tenaciously to the collagen exposed in damaged blood vessels • A large protein Factor 8 (with Von Willibrand factor) links platelets at the plug to each other and to the collagen in the vessel wall • ADP and serotonin released from platelets also increase the platelet aggregation t ...
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis (also known as arteriosclerotic vascular disease or ASVD) is a specific form of arteriosclerosis in which an artery wall thickens as a result of invasion and accumulation of white blood cells (WBCs) (foam cell) and proliferation of intimal smooth muscle cell creating a fibrofatty plaque.The accumulation of the WBCs is termed ""fatty streaks"" early on because of the appearance being similar to that of marbled steak. These accumulations contain both living, active WBCs (producing inflammation) and remnants of dead cells, including cholesterol and triglycerides. The remnants eventually include calcium and other crystallized materials within the outermost and oldest plaque. The ""fatty streaks"" reduce the elasticity of the artery walls. However, they do not affect blood flow for decades because the artery muscular wall enlarges at the locations of plaque. The wall stiffening may eventually increase pulse pressure; widened pulse pressure is one possible result of advanced disease within the major arteries.Atherosclerosis is therefore a syndrome affecting arterial blood vessels due to a chronic inflammatory response of WBCs in the walls of arteries. This is promoted by low-density lipoproteins (LDL, plasma proteins that carry cholesterol and triglycerides) without adequate removal of fats and cholesterol from the macrophages by functional high-density lipoproteins (HDL). It is commonly referred to as a ""hardening"" or furring of the arteries. It is caused by the formation of multiple atheromatous plaques within the arteries.The plaque is divided into three distinct components: The atheroma (""lump of gruel"", from Greek ἀθήρα (athera), meaning ""gruel""), which is the nodular accumulation of a soft, flaky, yellowish material at the center of large plaques, composed of macrophages nearest the lumen of the artery Underlying areas of cholesterol crystals Calcification at the outer base of older or more advanced lesions.Atherosclerosis is a chronic disease that remains asymptomatic for decades. Atherosclerotic lesions, or atherosclerotic plaques, are separated into two broad categories: Stable and unstable (also called vulnerable). The pathobiology of atherosclerotic lesions is very complicated, but generally, stable atherosclerotic plaques, which tend to be asymptomatic, are rich in extracellular matrix and smooth muscle cells. On the other hand, unstable plaques are rich in macrophages and foam cells, and the extracellular matrix separating the lesion from the arterial lumen (also known as the fibrous cap) is usually weak and prone to rupture. Ruptures of the fibrous cap expose thrombogenic material, such as collagen, to the circulation and eventually induce thrombus formation in the lumen. Upon formation, intraluminal thrombi can occlude arteries outright (e.g., coronary occlusion), but more often they detach, move into the circulation, and eventually occlude smaller downstream branches causing thromboembolism. Apart from thromboembolism, chronically expanding atherosclerotic lesions can cause complete closure of the lumen. Chronically expanding lesions are often asymptomatic until lumen stenosis is so severe (usually over 80%) that blood supply to downstream tissue(s) is insufficient, resulting in ischemia.These complications of advanced atherosclerosis are chronic, slowly progressive and cumulative. Most commonly, soft plaque suddenly ruptures (see vulnerable plaque), causing the formation of a thrombus that will rapidly slow or stop blood flow, leading to death of the tissues fed by the artery in approximately five minutes. This catastrophic event is called an infarction. One of the most common recognized scenarios is called coronary thrombosis of a coronary artery, causing myocardial infarction (a heart attack). The same process in an artery to the brain is commonly called stroke. Another common scenario in very advanced disease is claudication from insufficient blood supply to the legs. Atherosclerosis affects the entire artery tree, but mostly larger, high-pressure vessels such as the coronary, renal, femoral, cerebral, and carotid arteries. These are termed ""clinically silent"" because the person having the infarction does not notice the problem and does not seek medical help, or when they do, physicians do not recognize what has happened.