A population of atypical CD56вˆ`CD16+ natural killer cells is
... state. Natural killer (NK) cells, a key component of the innate immune system, have been less wellstudied in PTSD despite their importance in immunity. Methods: We studied two independent samples of combat-exposed male war veterans with or without PTSD, the first (‘‘Discovery Sample”) to generate hy ...
... state. Natural killer (NK) cells, a key component of the innate immune system, have been less wellstudied in PTSD despite their importance in immunity. Methods: We studied two independent samples of combat-exposed male war veterans with or without PTSD, the first (‘‘Discovery Sample”) to generate hy ...
Cleavage of Anti-Apoptotic Bcl-2 Family Members after TCR
... Mean 6 SDs from triplicate wells are displayed. **p , 0.01 (n = 3). ...
... Mean 6 SDs from triplicate wells are displayed. **p , 0.01 (n = 3). ...
Characteristics of human IgG Fc Receptors
... Unlike mouse the human IgG subclasses are very similar in sequence but they still have different properties ...
... Unlike mouse the human IgG subclasses are very similar in sequence but they still have different properties ...
Poly I: C-activated dendritic cells that were generated in CellGro for
... Figure 1 Characteristics of immature dendritic cells that were generated in different culture media. A. Morphology and density of adherent monocytes after 2 h of adhesion in in CellGro or RPMI+5% human AB serum. B. Total number of immature DCs that were generated from 1 × 107 of PBMCs in CellGro or ...
... Figure 1 Characteristics of immature dendritic cells that were generated in different culture media. A. Morphology and density of adherent monocytes after 2 h of adhesion in in CellGro or RPMI+5% human AB serum. B. Total number of immature DCs that were generated from 1 × 107 of PBMCs in CellGro or ...
From Donor to Recipient: Current Questions Relating to Humoral
... T-cells, anti-idiotypic T and B-cell responses, suppression of Natural Killer cell activity, switching from Th1 to Th2 type responses, selection of non-responder type immune cells, induction of apoptosis and favoring accumulation of regulatory factors, such as soluble MHC Class I molecules [34,35]. ...
... T-cells, anti-idiotypic T and B-cell responses, suppression of Natural Killer cell activity, switching from Th1 to Th2 type responses, selection of non-responder type immune cells, induction of apoptosis and favoring accumulation of regulatory factors, such as soluble MHC Class I molecules [34,35]. ...
Chapter 13: The Lymphatic System and Immunity
... 41. Describe the structure and function of the spleen and the thymus. Ans: The spleen is structured like a lymph node but it filters blood. The thymus gland varies in size. It contains lymphocytes, which are destined to become T cells. It secretes a hormone called thymosin, which stimulates the immu ...
... 41. Describe the structure and function of the spleen and the thymus. Ans: The spleen is structured like a lymph node but it filters blood. The thymus gland varies in size. It contains lymphocytes, which are destined to become T cells. It secretes a hormone called thymosin, which stimulates the immu ...
17-Estradiol (E2) modulates cytokine and
... were routinely more than 97% pure. To obtain iDCs, CD14⫹ cells were seeded at a density of 3 ⫻ 106 cells/mL in 6-well plates in 5 mL RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; BioWhittaker, Walkersville, MD), human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF; 100 ng ...
... were routinely more than 97% pure. To obtain iDCs, CD14⫹ cells were seeded at a density of 3 ⫻ 106 cells/mL in 6-well plates in 5 mL RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; BioWhittaker, Walkersville, MD), human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF; 100 ng ...
Immune Response and Interventions
... After dissecting the effector mechanisms needed to achieve efficient pathogen clearance upon infection, the most appropriate targets should be identified (e.g. antigens). Then, it is crucial to select optimal tools (e.g. delivery systems, adjuvants) to stimulate protective responses in a highly pred ...
... After dissecting the effector mechanisms needed to achieve efficient pathogen clearance upon infection, the most appropriate targets should be identified (e.g. antigens). Then, it is crucial to select optimal tools (e.g. delivery systems, adjuvants) to stimulate protective responses in a highly pred ...
chapter 20-the lymphatic system
... A. These vessels remove interstitial fluid and proteins and return them to the bloodstream. Once the Interstitial fluid enters lymphatic vessels, it is known as lymph. B. The Lymphatic Vessels 1. These vessels begin as Lymphatic Capillaries which are small vessels located in the spaces between cells ...
... A. These vessels remove interstitial fluid and proteins and return them to the bloodstream. Once the Interstitial fluid enters lymphatic vessels, it is known as lymph. B. The Lymphatic Vessels 1. These vessels begin as Lymphatic Capillaries which are small vessels located in the spaces between cells ...
The Lymph Node B Cell Immune Response
... different types of cells must meet and interact with an immunogenic antigen: B cells, T cells and antigenpresenting cells (APC). The interacting B cells and T cells both have to express antigen receptors specific to epitopes of the immunogenic antigen. The APC take up and process the immunogenic mol ...
... different types of cells must meet and interact with an immunogenic antigen: B cells, T cells and antigenpresenting cells (APC). The interacting B cells and T cells both have to express antigen receptors specific to epitopes of the immunogenic antigen. The APC take up and process the immunogenic mol ...
PDF - Blood Journal
... tissues of small isolated droplets and may undercool without freezing. It is the ...
... tissues of small isolated droplets and may undercool without freezing. It is the ...
Low natural killer cell cytotoxic activity in autism
... the requirement for prior immune sensitization of the host (Kiessling et al., 1975; Herberman et al., 1975). Since then, much knowledge has been accumulated regarding their origin, differentiation, receptor repertoire and effector functions, as well as their ability to shape adaptive immune response ...
... the requirement for prior immune sensitization of the host (Kiessling et al., 1975; Herberman et al., 1975). Since then, much knowledge has been accumulated regarding their origin, differentiation, receptor repertoire and effector functions, as well as their ability to shape adaptive immune response ...
Glucocorticoids and the Th1/Th2 Balance
... on the immune system and on the onset and course of certain infectious, autoimmune, and atopic/allergic diseases. This new understanding is briefly outlined below. THE TH1/TH2 PARADIGM: ROLE OF TH1 AND TH2 CYTOKINES The immune system is classified into innate (or non-specific, natural) and adaptive ...
... on the immune system and on the onset and course of certain infectious, autoimmune, and atopic/allergic diseases. This new understanding is briefly outlined below. THE TH1/TH2 PARADIGM: ROLE OF TH1 AND TH2 CYTOKINES The immune system is classified into innate (or non-specific, natural) and adaptive ...
Immune Cell Repertoire and Their Mediators in Patients with Acute
... cytology levels in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI), stable angina pectoris (SAP) and controls. Methods: 210 patients with AMI, 210 with SAP, and 250 clinical controls were recruited. Whole human genome microarray analysis was performed in 20 rand ...
... cytology levels in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI), stable angina pectoris (SAP) and controls. Methods: 210 patients with AMI, 210 with SAP, and 250 clinical controls were recruited. Whole human genome microarray analysis was performed in 20 rand ...
Immunization Competencies Education Program Module 1
... (e.g. tetanus toxoids), recombinant components or the constituents of cell walls. Some vaccines contain inactivated bacteria or viruses. Other vaccines contain only the antigens that are ...
... (e.g. tetanus toxoids), recombinant components or the constituents of cell walls. Some vaccines contain inactivated bacteria or viruses. Other vaccines contain only the antigens that are ...
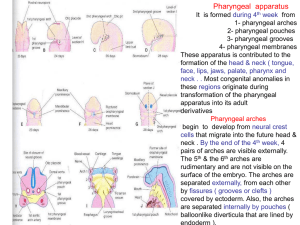
02-pharyngeal arches ,pouchs
... 4- pharyngeal membranes These apparatus is contributed to the formation of the head & neck ( tongue, face, lips, jaws, palate, pharynx and neck . . Most congenital anomalies in these regions originate during transformation of the pharyngeal apparatus into its adult derivatives Pharyngeal arches begi ...
... 4- pharyngeal membranes These apparatus is contributed to the formation of the head & neck ( tongue, face, lips, jaws, palate, pharynx and neck . . Most congenital anomalies in these regions originate during transformation of the pharyngeal apparatus into its adult derivatives Pharyngeal arches begi ...
Oncomedicine Immunological Role of Vitamin D in Skin Diseases
... or induced by chemokines, predominantly by the expression of Foxp3+. Mounting research exploring Treg interactions are elucidating not only the impact of Treg dysfunction in normal immune function, but also its interaction with vitamin D3. [14] In activated CD4+CD25− Treg cells, vitamin D3 inhibits ...
... or induced by chemokines, predominantly by the expression of Foxp3+. Mounting research exploring Treg interactions are elucidating not only the impact of Treg dysfunction in normal immune function, but also its interaction with vitamin D3. [14] In activated CD4+CD25− Treg cells, vitamin D3 inhibits ...
... inflammation, the additional appearance of oxygen radicals from any source may lead to prolonged and additive inflammatory effects, mediated in part through the transcription factor NF-κB. How this synergistic effect is mediated, remains unknown. The variations of the effect of the different agents ...
Immunology and Blood Groups
... Memory cells are the basis for immunological memory – they last for many years, often a lifetime. It is possible for suffer repeated infections from a single pathogen because pathogens occur in different form, each having minor changes in the shape of the antigen, due to a possible mutation, and the ...
... Memory cells are the basis for immunological memory – they last for many years, often a lifetime. It is possible for suffer repeated infections from a single pathogen because pathogens occur in different form, each having minor changes in the shape of the antigen, due to a possible mutation, and the ...
Microbiology
... The original theoretical concepts of an antibody called for a rod with antigenic determinants at each end. What is the primary advantage of the Yshaped structure that eventually emerged? 17-4 Which class of antibody is most likely to protect you from a common cold? 17-5 ...
... The original theoretical concepts of an antibody called for a rod with antigenic determinants at each end. What is the primary advantage of the Yshaped structure that eventually emerged? 17-4 Which class of antibody is most likely to protect you from a common cold? 17-5 ...
Lymphopoiesis
Lymphopoiesis (lĭm'fō-poi-ē'sĭs) (or lymphocytopoiesis) is the generation of lymphocytes, one of the five types of white blood cell (WBC). It is more formally known as lymphoid hematopoiesis.Pathosis in lymphopoiesis leads to any of various lymphoproliferative disorders, such as the lymphomas and lymphoid leukemias.