Preparation of Myeloma Cells
... Antibodies may be made to a number of different epitopes of the protein. Even antibodies that bind to the same epitope may have different antigen-binding sites and bind the epitope with different affinity. The mixture of antibodies produced in response to an antigen are referred to as polyclonal ant ...
... Antibodies may be made to a number of different epitopes of the protein. Even antibodies that bind to the same epitope may have different antigen-binding sites and bind the epitope with different affinity. The mixture of antibodies produced in response to an antigen are referred to as polyclonal ant ...
Immunology for Dummies_ The B cell receptor and antibodies
... Let’s recall what antibodies are. Well, they are proteins that fight infection. Now, let’s find out what they can actually do. The functions of antibodies are merely neutralisation of viruses and toxins, complement activation and opsonisation, opsonisation and lastly antibody-dependent cell mediated ...
... Let’s recall what antibodies are. Well, they are proteins that fight infection. Now, let’s find out what they can actually do. The functions of antibodies are merely neutralisation of viruses and toxins, complement activation and opsonisation, opsonisation and lastly antibody-dependent cell mediated ...
Epitope mapping
... Antigens can be large and complex substances, and any single antibody can only bind to a small, specific area on the antigen. Consequently, an effective immune response often involves the production of many different antibodies by many different B cells against the same antigen. Hence the term "poly ...
... Antigens can be large and complex substances, and any single antibody can only bind to a small, specific area on the antigen. Consequently, an effective immune response often involves the production of many different antibodies by many different B cells against the same antigen. Hence the term "poly ...
Chapter 9. First symmetry
... inducing the conformational change. Ig receptors can deliver an activating signal following the binding of antigen, antiidiotype antibodies, anti-allotype antibodies or anti-isotype antibodies, each of which binds to a different site. It is unreasonable to expect the same activating conformational c ...
... inducing the conformational change. Ig receptors can deliver an activating signal following the binding of antigen, antiidiotype antibodies, anti-allotype antibodies or anti-isotype antibodies, each of which binds to a different site. It is unreasonable to expect the same activating conformational c ...
Chapter 9
... inducing the conformational change. Ig receptors can deliver an activating signal following the binding of antigen, antiidiotype antibodies, anti-allotype antibodies or anti-isotype antibodies, each of which binds to a different site. It is unreasonable to expect the same activating conformational c ...
... inducing the conformational change. Ig receptors can deliver an activating signal following the binding of antigen, antiidiotype antibodies, anti-allotype antibodies or anti-isotype antibodies, each of which binds to a different site. It is unreasonable to expect the same activating conformational c ...
MORPHOLOGIE DES HEMATIES Normales et Pathologiques
... Must be coupled to a carrier molecule to be antigenic. Once antibodies are formed they will recognize hapten. ...
... Must be coupled to a carrier molecule to be antigenic. Once antibodies are formed they will recognize hapten. ...
Monoclonal Antibody Immunotherapy - Society for Immunotherapy of
... • Cancers employ multiple mechanisms to defeat the immune response • These mechanisms can be targeted to “liberate” underlying anti-cancer immune responses ...
... • Cancers employ multiple mechanisms to defeat the immune response • These mechanisms can be targeted to “liberate” underlying anti-cancer immune responses ...
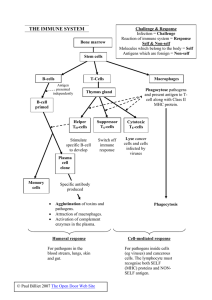
I. Student misconceptions
... The immune system is complex and difficult for students to understand. Take particular care in clarifying the many terms that students encounter in this chapter. Make sure students understand the distinction between the following pairs of terms: a. leukocyte and lymphocyte b. antigen and antibody c. ...
... The immune system is complex and difficult for students to understand. Take particular care in clarifying the many terms that students encounter in this chapter. Make sure students understand the distinction between the following pairs of terms: a. leukocyte and lymphocyte b. antigen and antibody c. ...
Biotechnology
... • Biosensor - a device which makes use of a biological molecule to detect and measure a chemical compound. • Most people now use a biosensor which detects an electric current genetrated during this oxidation reaction, which is read by a meter, and displays blood sugar ...
... • Biosensor - a device which makes use of a biological molecule to detect and measure a chemical compound. • Most people now use a biosensor which detects an electric current genetrated during this oxidation reaction, which is read by a meter, and displays blood sugar ...
ANNEX B: Selected Biotechnology Terms
... Gene Splicing – see polymerase chain reaction Genome – the section of DNA that carries the complete set of genetic information for a virus, cell, or organism. Monoclonal Antibodies – one of a group of identical antibodies able to react with on and the same antigen. Produced by a clone of engineered ...
... Gene Splicing – see polymerase chain reaction Genome – the section of DNA that carries the complete set of genetic information for a virus, cell, or organism. Monoclonal Antibodies – one of a group of identical antibodies able to react with on and the same antigen. Produced by a clone of engineered ...
5.3 Lymph and Blood Cells Study Guide by Hisrich
... T lymphocytes (T cells) and B lymphocytes (B cells) are the two kinds of lymphocytes. All lymphocytes begin in the bone marrow and then mature into one of these types, with T cells maturing in the bone marrow and B cells maturing in the thymus gland. B cells are like military intelligence, seeking o ...
... T lymphocytes (T cells) and B lymphocytes (B cells) are the two kinds of lymphocytes. All lymphocytes begin in the bone marrow and then mature into one of these types, with T cells maturing in the bone marrow and B cells maturing in the thymus gland. B cells are like military intelligence, seeking o ...
F. Q. How do we control and coordinate our body functions?
... This is done in two ways: 1. B cells produce antibodies which ...
... This is done in two ways: 1. B cells produce antibodies which ...
Microbiology ELISA questions
... 4.) T helper cells are the first cells to detect a foreign substance and will alert B cells and an immune response. By destroying T cells, HIV eliminates the body’s ability to mount a counter offense because the T cells cannot alert B cells nor help in the coordinated immune system response. HIV att ...
... 4.) T helper cells are the first cells to detect a foreign substance and will alert B cells and an immune response. By destroying T cells, HIV eliminates the body’s ability to mount a counter offense because the T cells cannot alert B cells nor help in the coordinated immune system response. HIV att ...
Biology Final Jeopary 2
... A: The type of memory cell that will produce antibodies quickly in response to a pathogen the body has “seen” before; responsible for immunity. ...
... A: The type of memory cell that will produce antibodies quickly in response to a pathogen the body has “seen” before; responsible for immunity. ...
Anti-idiotypes and Immunity
... may underline autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus and myasthenia gravis, which stem from an immunological attack on the body itself. These interactions, known as idiotype-anti-idiotype reactions, can be exploited to manipulate the immune system. ...
... may underline autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus and myasthenia gravis, which stem from an immunological attack on the body itself. These interactions, known as idiotype-anti-idiotype reactions, can be exploited to manipulate the immune system. ...
Antibody Diversity 02/16/06
... • In 1965 proposed radical theory to account for diversity of antibodies • Each antibody was coded for by two separate genes • One for the variable region • One for the constant region • Combined at the DNA level and expressed single mRNA • Suggested 1000’s of variable region genes and only one cons ...
... • In 1965 proposed radical theory to account for diversity of antibodies • Each antibody was coded for by two separate genes • One for the variable region • One for the constant region • Combined at the DNA level and expressed single mRNA • Suggested 1000’s of variable region genes and only one cons ...
Antibodies - UCSF Immunology Program
... •IgM is produced early in an immune response when the affinity for antigen often is low; as an immune response continues, antibody affinity is improved, this is combined by “class switching” to the use of smaller molecules (IgG, IgE and IgA). The increased affinity compensates for the decrease in nu ...
... •IgM is produced early in an immune response when the affinity for antigen often is low; as an immune response continues, antibody affinity is improved, this is combined by “class switching” to the use of smaller molecules (IgG, IgE and IgA). The increased affinity compensates for the decrease in nu ...
immunotherapeutic targeting of aml with a novel cd123 car
... Toronto, Toronto, Canada, 3University Health Network, Toronto, Canada. Chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) are engineered receptors transduced into immune effector cells that combine the antigen binding abilities of an antibody with the cytotoxic potential of T cells. CARs are made up of an antigen re ...
... Toronto, Toronto, Canada, 3University Health Network, Toronto, Canada. Chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) are engineered receptors transduced into immune effector cells that combine the antigen binding abilities of an antibody with the cytotoxic potential of T cells. CARs are made up of an antigen re ...
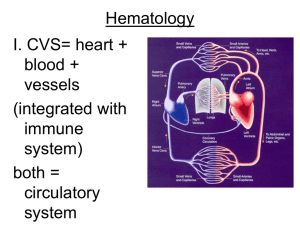
Hematology
... • Occurs when a fetus is Rh+ and mother is Rh− • the mother will produce antibodies against the fetal antigen when blood is exchanged during birth. • complicates future pregnancies, because her antibodies will enter the fetal circulation system and react with fetal blood, causing hemolysis. • Treatm ...
... • Occurs when a fetus is Rh+ and mother is Rh− • the mother will produce antibodies against the fetal antigen when blood is exchanged during birth. • complicates future pregnancies, because her antibodies will enter the fetal circulation system and react with fetal blood, causing hemolysis. • Treatm ...
Document
... • If you inject a monoclonal antibody into a genetically identical recipient then anti-idiotypic antibodies are generated • No anti-isotypic and no anti-allotypic Abs will be generated ...
... • If you inject a monoclonal antibody into a genetically identical recipient then anti-idiotypic antibodies are generated • No anti-isotypic and no anti-allotypic Abs will be generated ...
Document
... The proliferation of lymphocyte cells due to activation by an antigen Useful in primary (first exposure to antigen) and secondary (subsequent exposure to same antigen) immune responses Results in production of many antibodies against the antigen Primary immune response – 10-17 days before maximum re ...
... The proliferation of lymphocyte cells due to activation by an antigen Useful in primary (first exposure to antigen) and secondary (subsequent exposure to same antigen) immune responses Results in production of many antibodies against the antigen Primary immune response – 10-17 days before maximum re ...
AntibodyNoTP
... Anti-isotype Antibodies (Anti-gamma, Anti-Alpha, Anti-Mu, etc) (Also differences in constant regions of kappa and lambda light chains) 2. Different individual mouse strains (or different people): Anti-allotype Antibodies (Antibodies from one person would raise anti-antibodies in a non-identical twin ...
... Anti-isotype Antibodies (Anti-gamma, Anti-Alpha, Anti-Mu, etc) (Also differences in constant regions of kappa and lambda light chains) 2. Different individual mouse strains (or different people): Anti-allotype Antibodies (Antibodies from one person would raise anti-antibodies in a non-identical twin ...
biopresibstandards
... is often lethal, even when antibiotic treatments are give. Anthrax spores have sometimes been used deliberately to infect more people and cause death. Monoclonal antibodies are being developed which neutralize one of the toxins and therefore sustain the patient’s life until their immune system produ ...
... is often lethal, even when antibiotic treatments are give. Anthrax spores have sometimes been used deliberately to infect more people and cause death. Monoclonal antibodies are being developed which neutralize one of the toxins and therefore sustain the patient’s life until their immune system produ ...
Monoclonal antibodies in diagnosis and treatment
... defined antigenic specificity in unlimited quantities represents a milestone in immunological research. Conventional polyclonal antisera are produced by repeated immunisation of animals such as rabbits, sheep, or goats. These antisera contain mixtures of antibodies with differing specificities, and ...
... defined antigenic specificity in unlimited quantities represents a milestone in immunological research. Conventional polyclonal antisera are produced by repeated immunisation of animals such as rabbits, sheep, or goats. These antisera contain mixtures of antibodies with differing specificities, and ...
Monoclonal antibody

Monoclonal antibodies (mAb or moAb) are monospecific antibodies that are made by identical immune cells that are all clones of a unique parent cell, in contrast to polyclonal antibodies which are made from several different immune cells. Monoclonal antibodies have monovalent affinity, in that they bind to the same epitope.Given almost any substance, it is possible to produce monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind to that substance; they can then serve to detect or purify that substance. This has become an important tool in biochemistry, molecular biology and medicine. When used as medications, the non-proprietary drug name ends in -mab (see ""Nomenclature of monoclonal antibodies""), and many immunotherapy specialists use the word mab anacronymically.