Memory B Cells and Antibody Function
... any exposure to bacterial antigens to mature. When B cells encounter bacterial and other proteins and sugars that they recognize as foreign materials, they develop in two directions: Some become plasma cells (immunoglobulin and specific antibodies), and others become memory B cells that recognize th ...
... any exposure to bacterial antigens to mature. When B cells encounter bacterial and other proteins and sugars that they recognize as foreign materials, they develop in two directions: Some become plasma cells (immunoglobulin and specific antibodies), and others become memory B cells that recognize th ...
Techniques
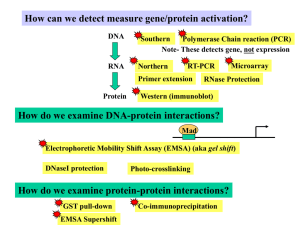
... _________________________ used for RNA and DNA separation ________________________ gel electrophoresis is used for protein separation ...
... _________________________ used for RNA and DNA separation ________________________ gel electrophoresis is used for protein separation ...
Kim Phillips
... complimentary then the ends of the probe can be joined by ligase, if there is a point mutation then the strands cannot be joined. The joined probe target can then be detected with reporter molecules. 12.) Monoclonal antibodies are antibodies that are specific for only one antigenic site on the molec ...
... complimentary then the ends of the probe can be joined by ligase, if there is a point mutation then the strands cannot be joined. The joined probe target can then be detected with reporter molecules. 12.) Monoclonal antibodies are antibodies that are specific for only one antigenic site on the molec ...
RESPON IMUN TERHADAP INFEKSI
... produces a much faster response, and several orders of magnitude higher levels of antibody. Ability of antibody to bind antigen also increases dramatically in the secondary response. ...
... produces a much faster response, and several orders of magnitude higher levels of antibody. Ability of antibody to bind antigen also increases dramatically in the secondary response. ...
Name: - Welcome to the Dendritic Cell Symposium 2017
... Title: Dendritic cells in mice and men Dendritic cells (DCs) are important cells for the presentation of antigens. In dependence of the surroundings, DCs are capable of presentation of antigen in an immature or mature state. Therefore, immune responses are tightly regulated by the DCs, as T cells re ...
... Title: Dendritic cells in mice and men Dendritic cells (DCs) are important cells for the presentation of antigens. In dependence of the surroundings, DCs are capable of presentation of antigen in an immature or mature state. Therefore, immune responses are tightly regulated by the DCs, as T cells re ...
Adaptive Immunity: Specific Defenses of the Host
... antigenic: nucleoproteins, lipoproteins, glycoproteins. Most components of an organism are antigenic. – 3. Antibodies are formed against specific regions on the surface of an antigen called ‘antigenic determinant’ (epitope). Fig 17.1 – 4. Hapten is a low molecular weight compound that cannot induce ...
... antigenic: nucleoproteins, lipoproteins, glycoproteins. Most components of an organism are antigenic. – 3. Antibodies are formed against specific regions on the surface of an antigen called ‘antigenic determinant’ (epitope). Fig 17.1 – 4. Hapten is a low molecular weight compound that cannot induce ...
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM DEFENSES AGAINST INFECTION Pathogens
... For the immune system to work the body needs to the difference between itself (own cells and materials) and nonself (foreign cells and materials) This recognition is based on differences in certain large molecules (proteins) between one organism and another. When the body recognizes that a cell is a ...
... For the immune system to work the body needs to the difference between itself (own cells and materials) and nonself (foreign cells and materials) This recognition is based on differences in certain large molecules (proteins) between one organism and another. When the body recognizes that a cell is a ...
Immune Disorders Allergies 4 Hypersensitivity Types
... Tissue rejection • T cell mediated recognition of foreign ...
... Tissue rejection • T cell mediated recognition of foreign ...
Immunology Notes - Metcalfe County Schools
... • STP, Ligand, CSC, • ECM- glycolipids and glycoproteins are responsible for cell communication. ...
... • STP, Ligand, CSC, • ECM- glycolipids and glycoproteins are responsible for cell communication. ...
Kevin Ahern's Biochemistry Course (BB 350) at Oregon State University
... responsible for antibody diversity. The different classes of antibodies vary in the H chains in the constant region. 6. Molecules bound by antibodies are called antigens. Specific structural regions of an antigen bound by an antibody are called epitopes. 7. Antibody diversity arises from recombinati ...
... responsible for antibody diversity. The different classes of antibodies vary in the H chains in the constant region. 6. Molecules bound by antibodies are called antigens. Specific structural regions of an antigen bound by an antibody are called epitopes. 7. Antibody diversity arises from recombinati ...
Powerpoint 5
... microorganisms. A nucleic acid sequence specific for the microorganism of interest must be available in order to design a probe. Perhaps the most widespread use of probebased technology is in the application of gene amplification (PCR) methods. Various DNAbased methodologies are currently used in cl ...
... microorganisms. A nucleic acid sequence specific for the microorganism of interest must be available in order to design a probe. Perhaps the most widespread use of probebased technology is in the application of gene amplification (PCR) methods. Various DNAbased methodologies are currently used in cl ...
lymphatic outline
... b. rid the body of cells that have been infected by viruses as well as cancer cells c. Cytokines are diverse & potent chemical messenger secreted by the cells of the immune syst. that bind to specific receptors on target cells. B. B cells or B lymphocytes: oversee humoral immunity 1. work chiefly by ...
... b. rid the body of cells that have been infected by viruses as well as cancer cells c. Cytokines are diverse & potent chemical messenger secreted by the cells of the immune syst. that bind to specific receptors on target cells. B. B cells or B lymphocytes: oversee humoral immunity 1. work chiefly by ...
PHYSIOLOGY OF THE NEWBORN
... Rapid growth of fetal brain during last half of fetal life with peak near time of birth Posture of late fetal flexion attitude Generalized symmetric muscular activity Simple & stereotyped response to various environmental and internal stimuli ...
... Rapid growth of fetal brain during last half of fetal life with peak near time of birth Posture of late fetal flexion attitude Generalized symmetric muscular activity Simple & stereotyped response to various environmental and internal stimuli ...
PDF
... therapeutic proteins may also neutralize the biological activity of therapeutic proteins and may result in adverse events not only by inhibiting the efficacy of the therapeutic protein product, but by cross-reacting to an endogenous protein counterpart, if present. Because most of the adverse effect ...
... therapeutic proteins may also neutralize the biological activity of therapeutic proteins and may result in adverse events not only by inhibiting the efficacy of the therapeutic protein product, but by cross-reacting to an endogenous protein counterpart, if present. Because most of the adverse effect ...
Supplementary Material (doc 44K)
... in the lysate were determined by Bradford assays and confirmed by applying 10% of the lysate to SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie blue. IP was carried out by incubating with anti-FLAG M2 (1:1000, Stratagene) antibody overnight and protein G beads for further 4 hours. After extensive washing (5 times w ...
... in the lysate were determined by Bradford assays and confirmed by applying 10% of the lysate to SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie blue. IP was carried out by incubating with anti-FLAG M2 (1:1000, Stratagene) antibody overnight and protein G beads for further 4 hours. After extensive washing (5 times w ...
Host Microbe Interations
... 2- M proteins found in strains of Streptococcus pyogenes also inactivate the C3b complement component. 3- Fc receptors found on the surface of Staphylococcus and Streptococcus bind to the fc region of an antibody preventing it from binding correctly! ...
... 2- M proteins found in strains of Streptococcus pyogenes also inactivate the C3b complement component. 3- Fc receptors found on the surface of Staphylococcus and Streptococcus bind to the fc region of an antibody preventing it from binding correctly! ...
Document
... produced by the immune response bind to antigens on the patient's own cell surfaces. • The antigens recognized in this way may be; – intrinsic ("self" antigen, innately part of the patient's cells) or – extrinsic (absorbed onto the cells during exposure to some foreign antigen, possibly as part of i ...
... produced by the immune response bind to antigens on the patient's own cell surfaces. • The antigens recognized in this way may be; – intrinsic ("self" antigen, innately part of the patient's cells) or – extrinsic (absorbed onto the cells during exposure to some foreign antigen, possibly as part of i ...
Assessment of immune function.Management of patients with im
... • Allow body to respond defensively to presence of specific potential threats ...
... • Allow body to respond defensively to presence of specific potential threats ...
The Immune System - Ms. Lin`s Science Class
... • Its Tuesday. Thanks to your first line of defense you have survived David the Drooler. But, unfortunately for you, Melvin was absent the ...
... • Its Tuesday. Thanks to your first line of defense you have survived David the Drooler. But, unfortunately for you, Melvin was absent the ...
EN90027_Imunology
... immune system. Inate and adaptive immunity. Antigen recognition. The integrated immune response. Antigen presentation. Concept of “T-Help”, TH1 and TH2 responses. Cytokines and lymphokines. Humoural immunity. Structure, isotypes and functions of antibody molecules. Immune system genetics. Origin of ...
... immune system. Inate and adaptive immunity. Antigen recognition. The integrated immune response. Antigen presentation. Concept of “T-Help”, TH1 and TH2 responses. Cytokines and lymphokines. Humoural immunity. Structure, isotypes and functions of antibody molecules. Immune system genetics. Origin of ...
Supplementary Information (doc 47K)
... (Orbigen, Inc.). DU-145 cells were infected with retrovirus, and were grown in selective media containing 1 g/ml puromycin at one day post-infection. We generated stable cell lines expressing pBabe, HBP1, or pmHMG after 14 days of selection. The expression of these vectors in DU-145 cells was detec ...
... (Orbigen, Inc.). DU-145 cells were infected with retrovirus, and were grown in selective media containing 1 g/ml puromycin at one day post-infection. We generated stable cell lines expressing pBabe, HBP1, or pmHMG after 14 days of selection. The expression of these vectors in DU-145 cells was detec ...
Internal defense mechanisms to protect body from pathogens (A
... Skin - mechanical and chemical barrier chemicals in sweat and oil enzymes in tears can kill bacteria mucous membranes and hairs trap pathogens ...
... Skin - mechanical and chemical barrier chemicals in sweat and oil enzymes in tears can kill bacteria mucous membranes and hairs trap pathogens ...
Strive for Five- Ch 31 Concept 31.1 Identify each of these examples
... 10. Suppose that you were exposed to a newly synthesized “artificial” bacterium. After exposure, all signs of the bacterium from your body were gone within 24 hours. Assume further that this bacterium is novel enough that it does not share chemical identity signals with other bacteria. Decide if you ...
... 10. Suppose that you were exposed to a newly synthesized “artificial” bacterium. After exposure, all signs of the bacterium from your body were gone within 24 hours. Assume further that this bacterium is novel enough that it does not share chemical identity signals with other bacteria. Decide if you ...
11.1 Antibody Production and Vaccination
... produced mainly by plasma cells. Antibodies function in different ways, but all functions are a consequence of their initial attachment to the antigen: • Neutralisation – attachment stops toxins from effecting or entering cells, viruses from invading cells, and bacteria from efficiently functioning ...
... produced mainly by plasma cells. Antibodies function in different ways, but all functions are a consequence of their initial attachment to the antigen: • Neutralisation – attachment stops toxins from effecting or entering cells, viruses from invading cells, and bacteria from efficiently functioning ...
Monoclonal antibody

Monoclonal antibodies (mAb or moAb) are monospecific antibodies that are made by identical immune cells that are all clones of a unique parent cell, in contrast to polyclonal antibodies which are made from several different immune cells. Monoclonal antibodies have monovalent affinity, in that they bind to the same epitope.Given almost any substance, it is possible to produce monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind to that substance; they can then serve to detect or purify that substance. This has become an important tool in biochemistry, molecular biology and medicine. When used as medications, the non-proprietary drug name ends in -mab (see ""Nomenclature of monoclonal antibodies""), and many immunotherapy specialists use the word mab anacronymically.