The immune system protects the body from disease.
... and J genes are randomly selected and combined to form the heavy and light chains that make antibodies. ...
... and J genes are randomly selected and combined to form the heavy and light chains that make antibodies. ...
Executive Summary
... non-small cell lung, hepatocellular, renal cell, nasopharyngeal, bladder, uterine, epithelial ovarian, breast, prostate, and pancreatic carcinomas. Previous studies in our laboratory have shown an increased expression of CD24 in colorectal adenomas and adenocarcinomas as compared to normal adjacent ...
... non-small cell lung, hepatocellular, renal cell, nasopharyngeal, bladder, uterine, epithelial ovarian, breast, prostate, and pancreatic carcinomas. Previous studies in our laboratory have shown an increased expression of CD24 in colorectal adenomas and adenocarcinomas as compared to normal adjacent ...
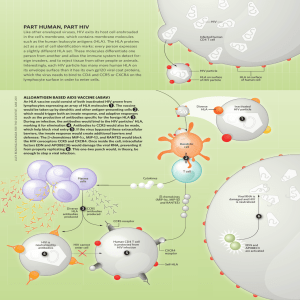
Part human, Part hIV
... During an infection, the antibodies would bind to the HIV particles’ HLA, marking it for elimination 4 . Antibodies to CCR5 would also be made, which help block viral entry 5 . If the virus bypassed these extracellular barriers, the innate response would create additional barriers and defenses: ...
... During an infection, the antibodies would bind to the HIV particles’ HLA, marking it for elimination 4 . Antibodies to CCR5 would also be made, which help block viral entry 5 . If the virus bypassed these extracellular barriers, the innate response would create additional barriers and defenses: ...
The Immune System - Town of Mansfield, CT
... and macrophages. The lymph nodes filter a bodily fluid named lymph. When the lymph goes through the lymph nodes, antigens are filtered before entering the bloodstream again. The lymph nodes are also a place for an immune response. That is why your mom checks the sides of your neck to see if the lymp ...
... and macrophages. The lymph nodes filter a bodily fluid named lymph. When the lymph goes through the lymph nodes, antigens are filtered before entering the bloodstream again. The lymph nodes are also a place for an immune response. That is why your mom checks the sides of your neck to see if the lymp ...
Chap 34 - Resistance of the Body to Infection
... 1. react with specific antigen 2. stimulates activation process 3. T helper cells secrete specific substances (lymphokines) that stimulate B-lymphocytes C. macrophages 1. digests antigens 2. pass antigens to lymphocytes 3. secrete interleukin-1 (promotes the growth and reproduction of specific lymph ...
... 1. react with specific antigen 2. stimulates activation process 3. T helper cells secrete specific substances (lymphokines) that stimulate B-lymphocytes C. macrophages 1. digests antigens 2. pass antigens to lymphocytes 3. secrete interleukin-1 (promotes the growth and reproduction of specific lymph ...
January 6, 2014 - Immunology Overview
... Activation, Differentiation Markers CD25: Interleukin-2 Receptor CD28: Co-stimulatory receptor on T cells CD34: Stem cell marker ...
... Activation, Differentiation Markers CD25: Interleukin-2 Receptor CD28: Co-stimulatory receptor on T cells CD34: Stem cell marker ...
Immunology Module Presentation
... and J genes are randomly selected and combined to form the heavy and light chains that make antibodies. ...
... and J genes are randomly selected and combined to form the heavy and light chains that make antibodies. ...
The Immune System and Allergy
... • Differ from B cell receptors only in the constant (C) region of the heavy chain • The five major types of heavy chain constant regions determine the five major classes of antibodies (M, G, A, E, and D) • Changes in the heavy chain gene that switch B cells from producing one antibody class to anoth ...
... • Differ from B cell receptors only in the constant (C) region of the heavy chain • The five major types of heavy chain constant regions determine the five major classes of antibodies (M, G, A, E, and D) • Changes in the heavy chain gene that switch B cells from producing one antibody class to anoth ...
Antigens
... A certain amount of chemical complexity is required, for example, amino acid homopolymers are less immunogenic than heteropolymers containing two or three different amino acids. ...
... A certain amount of chemical complexity is required, for example, amino acid homopolymers are less immunogenic than heteropolymers containing two or three different amino acids. ...
84. Which of the following describes an adjuvant correctly? A An
... 89. The immune system protects the body from infection. The table contains information about cells of the immune system. (a) Complete the table to identify the cell types and their functions. ...
... 89. The immune system protects the body from infection. The table contains information about cells of the immune system. (a) Complete the table to identify the cell types and their functions. ...
Lymphatic Study Guide - Belle Vernon Area School District
... A. Match these terms with the correct statement or definition: Allergic reaction, Foreign antigens, Antigens, Self antigens, _________________________1. General term for substances that stimulate adaptive immunity responses. _________________________2. Antigens introduced from outside the body. ____ ...
... A. Match these terms with the correct statement or definition: Allergic reaction, Foreign antigens, Antigens, Self antigens, _________________________1. General term for substances that stimulate adaptive immunity responses. _________________________2. Antigens introduced from outside the body. ____ ...
File
... -Transferred through blood, semen and vaginal secretions that come into contact with broken skin and mucus membranes ( wet- thin tissue found in certain openings such as eyes, nose, rectum, vagina and penis) - Virus finds and destroys T-cells - Death usually comes not from the disease ...
... -Transferred through blood, semen and vaginal secretions that come into contact with broken skin and mucus membranes ( wet- thin tissue found in certain openings such as eyes, nose, rectum, vagina and penis) - Virus finds and destroys T-cells - Death usually comes not from the disease ...
Immunity
... they must pass through lymphoid tissues in other parts of the body. As they do so, they become committed to becoming either T cells or B cells Cells that migrate through the bone marrow become B cells, and will produce antigens and participate in humoral immunity. ...
... they must pass through lymphoid tissues in other parts of the body. As they do so, they become committed to becoming either T cells or B cells Cells that migrate through the bone marrow become B cells, and will produce antigens and participate in humoral immunity. ...
Specificity of primary and secondary responses
... that the immunogen has been eliminated from the body and consequently there is no stimulus for continued antibody production. When a similar antigen enters the host for the second and subsequent times, the immune responses induced are called secondary immune responses. During secondary immune respon ...
... that the immunogen has been eliminated from the body and consequently there is no stimulus for continued antibody production. When a similar antigen enters the host for the second and subsequent times, the immune responses induced are called secondary immune responses. During secondary immune respon ...
Immune Hemolytic Anemias
... • DAT+ for IgG and possibly complement • Eluate negative • Nonreactive for unexpected antibodies • Antibody eluted off red cells reacts with cells+drug but not cells alone • Hemolysis develops gradually • Discontinue the drug and red cell survival increases ...
... • DAT+ for IgG and possibly complement • Eluate negative • Nonreactive for unexpected antibodies • Antibody eluted off red cells reacts with cells+drug but not cells alone • Hemolysis develops gradually • Discontinue the drug and red cell survival increases ...
immune-system-notes
... microbes and secretes lysozyme, which digests bacterial cell walls o If there is a break in the skin, it will try to heal and blood flows outward preventing the infection from getting inside o Our breathing passages are covered in hairs and mucus that are meant to trap foreign organisms and expel th ...
... microbes and secretes lysozyme, which digests bacterial cell walls o If there is a break in the skin, it will try to heal and blood flows outward preventing the infection from getting inside o Our breathing passages are covered in hairs and mucus that are meant to trap foreign organisms and expel th ...
Antigen arrays for antibody profiling - Robinson Lab
... developed and applied myelin antigen arrays to profile autoantibody responses in a rodent model for multiple sclerosis (MS), experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). We further developed tolerizing DNA vaccines [38] based on the specificity of anti-myelin autoantibody responses identified wi ...
... developed and applied myelin antigen arrays to profile autoantibody responses in a rodent model for multiple sclerosis (MS), experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). We further developed tolerizing DNA vaccines [38] based on the specificity of anti-myelin autoantibody responses identified wi ...
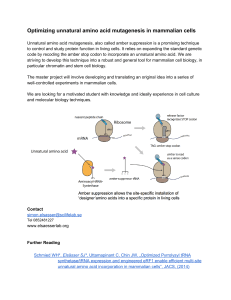
Optimizing unnatural amino acid mutagenesis in mammalian cells
... Unnatural amino acid mutagenesis, also called amber suppression is a promising technique to control and study protein function in living cells. It relies on expanding the standard genetic code by recoding the amber stop codon to incorporate an unnatural amino acid. We are striving to develop this ...
... Unnatural amino acid mutagenesis, also called amber suppression is a promising technique to control and study protein function in living cells. It relies on expanding the standard genetic code by recoding the amber stop codon to incorporate an unnatural amino acid. We are striving to develop this ...
Immune3-Innate and adaptive immunity,Igs , Cytokines
... infections and the only one that can cross the placenta. • IgM is the most important in the primary exposure and in complement ...
... infections and the only one that can cross the placenta. • IgM is the most important in the primary exposure and in complement ...
AQA AS Level Biology Unit 1 Why do we calculate ratios or
... Why do we calculate ratios or percentages with data? for easier comparison, because different groups have different starting numbers/masses Why do we take a large sample size? more representative, findings not due to chance Why do we take random samples? avoid bias Why do we take repeats? identify a ...
... Why do we calculate ratios or percentages with data? for easier comparison, because different groups have different starting numbers/masses Why do we take a large sample size? more representative, findings not due to chance Why do we take random samples? avoid bias Why do we take repeats? identify a ...
Chapter 40-2
... that breaks down the cell walls of bacteria Oil & sweat glands produce an acidic environment on the skin that kills many bacteria Mucus in mouth & nose help trap pathogens Stomach acids & digestive enzymes destroy many pathogens that get in your stomach ...
... that breaks down the cell walls of bacteria Oil & sweat glands produce an acidic environment on the skin that kills many bacteria Mucus in mouth & nose help trap pathogens Stomach acids & digestive enzymes destroy many pathogens that get in your stomach ...
The Journal of Clinical Investigation
... Generation of dendritic cell vaccines from peripheral blood monocytes: 1) Monocytes cultures with GM-CSF +IL-4 to produce DCs 2) Matured with CD40 ligand 3) Pulsed with peptide or tumour lysate 4) Re-injected as vaccine to induce T-cell immune response against tumour ...
... Generation of dendritic cell vaccines from peripheral blood monocytes: 1) Monocytes cultures with GM-CSF +IL-4 to produce DCs 2) Matured with CD40 ligand 3) Pulsed with peptide or tumour lysate 4) Re-injected as vaccine to induce T-cell immune response against tumour ...
Monoclonal antibody

Monoclonal antibodies (mAb or moAb) are monospecific antibodies that are made by identical immune cells that are all clones of a unique parent cell, in contrast to polyclonal antibodies which are made from several different immune cells. Monoclonal antibodies have monovalent affinity, in that they bind to the same epitope.Given almost any substance, it is possible to produce monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind to that substance; they can then serve to detect or purify that substance. This has become an important tool in biochemistry, molecular biology and medicine. When used as medications, the non-proprietary drug name ends in -mab (see ""Nomenclature of monoclonal antibodies""), and many immunotherapy specialists use the word mab anacronymically.