T cells - apbiostafford
... to defend against pathogens. 2. Explain the interplay between the humoral and cell-mediated responses. 3. Demonstrate how the HIV virus leads to a breakdown of the immune system. 4. Explain why a vaccine works. 5. Explain the causes of immune system disruptions and how disruptions of the immune syst ...
... to defend against pathogens. 2. Explain the interplay between the humoral and cell-mediated responses. 3. Demonstrate how the HIV virus leads to a breakdown of the immune system. 4. Explain why a vaccine works. 5. Explain the causes of immune system disruptions and how disruptions of the immune syst ...
transports lymph
... The spleen (see figure 14.5) filters blood and is a site where lymphocytes respond to infections. ...
... The spleen (see figure 14.5) filters blood and is a site where lymphocytes respond to infections. ...
product data sheet - Kamiya Biomedical Company
... µg/mL for mouse heart cells. The optimal dilution for a specific application should be determined by the researcher. ...
... µg/mL for mouse heart cells. The optimal dilution for a specific application should be determined by the researcher. ...
Chapter 1 Notes - Social Circle City Schools
... Cell-mediated immunity: T cells are active against viruses and bacteria that have infected cells; also is crucial in the body’s response against transplanted tissues and cancerous cells - activated T cells become TH or TC; TH activate B cells that produce antibodies, TC destroy infected body cells ...
... Cell-mediated immunity: T cells are active against viruses and bacteria that have infected cells; also is crucial in the body’s response against transplanted tissues and cancerous cells - activated T cells become TH or TC; TH activate B cells that produce antibodies, TC destroy infected body cells ...
Autoimmune diseases
... Autoimmune diseases is a group of disorders in which tissue injury is caused by humoral (by auto-antibodies) or cell mediated immune response (by auto-reactive T cells) to self antigens. Normally, the immune system does not attack the self, the attack can be directed either against a very specific t ...
... Autoimmune diseases is a group of disorders in which tissue injury is caused by humoral (by auto-antibodies) or cell mediated immune response (by auto-reactive T cells) to self antigens. Normally, the immune system does not attack the self, the attack can be directed either against a very specific t ...
The Body`s Defenses Against Disease and Injury
... The end result is that mature B cells produce plasma cells that secrete immunoglobulin antibodies into the blood and secondary organs. Immunoglobulins Antibodies are proteins secreted by plasma cells that are produced by B cells in response to an antigen. All antibodies are immunoglobulins, but it i ...
... The end result is that mature B cells produce plasma cells that secrete immunoglobulin antibodies into the blood and secondary organs. Immunoglobulins Antibodies are proteins secreted by plasma cells that are produced by B cells in response to an antigen. All antibodies are immunoglobulins, but it i ...
Q1. (a) (i) Some diseases can be tackled by using antibiotics and
... ‘The immune system is the body’s defence force. It protects against infections which might enter the body. The potential invaders include bacteria and viruses. The two basic defences are cells and chemicals. The best known action of defence cells is the ingesting and killing of microbes. The best kn ...
... ‘The immune system is the body’s defence force. It protects against infections which might enter the body. The potential invaders include bacteria and viruses. The two basic defences are cells and chemicals. The best known action of defence cells is the ingesting and killing of microbes. The best kn ...
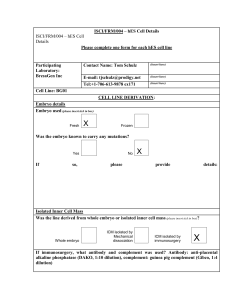
ISCI/FRM/004 – hES Cell Details
... cells were expanded under the same conditions to passage 7, when they were cryoperserved. used The For the work performed here, a p7 culture was thawed into a MEF-CM medium (below), on ...
... cells were expanded under the same conditions to passage 7, when they were cryoperserved. used The For the work performed here, a p7 culture was thawed into a MEF-CM medium (below), on ...
Immunogenetics
... cells. It was originally found in rhesus monkeys. About 85% of people have the Rh antigen (Rh+) and 15% lack it (Rh-). The Rh+ allele is dominant, so heterozygotes are Rh+. Because the + allele is dominant, it is possible for an Rhmother to have an Rh+ baby. In general, the fetus’s blood is separate ...
... cells. It was originally found in rhesus monkeys. About 85% of people have the Rh antigen (Rh+) and 15% lack it (Rh-). The Rh+ allele is dominant, so heterozygotes are Rh+. Because the + allele is dominant, it is possible for an Rhmother to have an Rh+ baby. In general, the fetus’s blood is separate ...
Immunogenetics
... This disease involves a completely non-functional immune system due to a lack of T cells. The “boy in the bubble”. Normally SCID is lethal within the first year of life. One child was immediately put into a sterile environment and kept there until age 12. At this point he was given an experimental t ...
... This disease involves a completely non-functional immune system due to a lack of T cells. The “boy in the bubble”. Normally SCID is lethal within the first year of life. One child was immediately put into a sterile environment and kept there until age 12. At this point he was given an experimental t ...
Slide 1
... have to compete with other peptides for space within the limited number of HLAs on a cells’ surfaces, resulting in fewer of the desired memory T cells being produced • In naturally-occurring infection, the constant peptides that are placed on the cell surface during the HIV life-cycle are so few tha ...
... have to compete with other peptides for space within the limited number of HLAs on a cells’ surfaces, resulting in fewer of the desired memory T cells being produced • In naturally-occurring infection, the constant peptides that are placed on the cell surface during the HIV life-cycle are so few tha ...
Chapter 37 Objectives and other Animal System Material
... Explain how complement proteins may be activated and how they function in cooperation with other defense mechanisms 6. Define phagocytosis and list 2 types of phagocytic cells derived from white blood cells 7. Describe the inflammatory response pattern and how it is triggered 8. Explain how the infl ...
... Explain how complement proteins may be activated and how they function in cooperation with other defense mechanisms 6. Define phagocytosis and list 2 types of phagocytic cells derived from white blood cells 7. Describe the inflammatory response pattern and how it is triggered 8. Explain how the infl ...
Antibody
... target, termed an antigen.[1][2] Each tip of the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope (a structure analogous to a lock) that is specific for one particular epitope (similarly analogous to a key) on an antigen, allowing these two structures to bind together with precision. Using this binding mechan ...
... target, termed an antigen.[1][2] Each tip of the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope (a structure analogous to a lock) that is specific for one particular epitope (similarly analogous to a key) on an antigen, allowing these two structures to bind together with precision. Using this binding mechan ...
Androgen Receptor (D6F11) XP® Rabbit mAb
... XP® Rabbit mAb detects endogenous levels of total androgen receptor protein. Source/Purification: Monoclonal antibody is produced by immunizing animals with recombinant protein corresponding to residues near the amino terminal region of human androgen receptor protein. ...
... XP® Rabbit mAb detects endogenous levels of total androgen receptor protein. Source/Purification: Monoclonal antibody is produced by immunizing animals with recombinant protein corresponding to residues near the amino terminal region of human androgen receptor protein. ...
Benlysta(belimumab)
... • is a systemic autoimmune disease (or autoimmune connective tissue disease) that can affect any part of the body. As occurs in other autoimmune diseases, the immune system attacks the body's cells and tissue, resulting in inflammation and tissue damage. It is a Type III hypersensitivity reaction ca ...
... • is a systemic autoimmune disease (or autoimmune connective tissue disease) that can affect any part of the body. As occurs in other autoimmune diseases, the immune system attacks the body's cells and tissue, resulting in inflammation and tissue damage. It is a Type III hypersensitivity reaction ca ...
35.2 Nonspecific and Specific Defenses
... antigen (“antibody generating”): foreign molecule (protein) that elicits a response by lymphocytes may belong to viruses, bacteria, fungi, protozoa, parasitic worms, pollen, transplanted tissue, etc. stimulate production of antibodies, which bind to antigens B cells and T cells undergo clonal ...
... antigen (“antibody generating”): foreign molecule (protein) that elicits a response by lymphocytes may belong to viruses, bacteria, fungi, protozoa, parasitic worms, pollen, transplanted tissue, etc. stimulate production of antibodies, which bind to antigens B cells and T cells undergo clonal ...
Immune Notes - The Lesson Locker
... Macrophages release chemicals which set the body’s thermostat at a higher temperature, resulting in a fever. b. The fever may increase phagocytosis, speed tissue repair, and inhibit bacterial growth. Natural killer (NK) cells do not attack microorganisms directly but destroy virus-infected body cell ...
... Macrophages release chemicals which set the body’s thermostat at a higher temperature, resulting in a fever. b. The fever may increase phagocytosis, speed tissue repair, and inhibit bacterial growth. Natural killer (NK) cells do not attack microorganisms directly but destroy virus-infected body cell ...
Self tolerance
... Antibodies may also contribute to the disease. About 80% of patients have serum immunoglobulin M (IgM) (and, less frequently, IgA) autoantibodies that bind to the Fc portions of their own (self ) IgG.. ...
... Antibodies may also contribute to the disease. About 80% of patients have serum immunoglobulin M (IgM) (and, less frequently, IgA) autoantibodies that bind to the Fc portions of their own (self ) IgG.. ...
Chapter 22 - FacultyWeb
... 2. Cytotoxic T cells proliferate. 3. Class II MHC proteins appear in the cell membrane. 4. Immune response is unaffected by loss of helper T cells. ...
... 2. Cytotoxic T cells proliferate. 3. Class II MHC proteins appear in the cell membrane. 4. Immune response is unaffected by loss of helper T cells. ...
BIOT 307 Kuby, Ch. 3, Antigens
... • More potential antigenic sites than number recognized by immune system – Varies from species to species – Within species, individuals can • recognize different epitopes as immunogenic and • mount immune responses that are stronger (immunodominant) against different epitopes ...
... • More potential antigenic sites than number recognized by immune system – Varies from species to species – Within species, individuals can • recognize different epitopes as immunogenic and • mount immune responses that are stronger (immunodominant) against different epitopes ...
Characterization of the protein recognized by the monoclonal
... In Europe, Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato isolates belong to 4 major species: B. burgdorferi sensu stricto, B. afzelii, B. garinii and B. valaisiana. The objective of this study was to characterize low molecular weight proteins of B. burgdorferi sensu lato. Our main focus was a protein around 12 kD ...
... In Europe, Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato isolates belong to 4 major species: B. burgdorferi sensu stricto, B. afzelii, B. garinii and B. valaisiana. The objective of this study was to characterize low molecular weight proteins of B. burgdorferi sensu lato. Our main focus was a protein around 12 kD ...
EpiTan in Collaboration to Develop Sustained Release Form of
... treatment for a wide range of cancers as the antibody targets many types of cancers and based on experiments to date, it has the added benefit that it does not affect normal healthy tissue.” Mr. Clark said, “Our plans with the new antibody project are to proceed through latter stage pre-clinical dev ...
... treatment for a wide range of cancers as the antibody targets many types of cancers and based on experiments to date, it has the added benefit that it does not affect normal healthy tissue.” Mr. Clark said, “Our plans with the new antibody project are to proceed through latter stage pre-clinical dev ...
No Slide Title
... •often high affinity binding; •multiple paratopes allow Ab-Ag aggregates & precipitates to form. A unique combination at each bleeding of each animal ==> limited supplies of any particular preparation. ...
... •often high affinity binding; •multiple paratopes allow Ab-Ag aggregates & precipitates to form. A unique combination at each bleeding of each animal ==> limited supplies of any particular preparation. ...
Monoclonal antibody

Monoclonal antibodies (mAb or moAb) are monospecific antibodies that are made by identical immune cells that are all clones of a unique parent cell, in contrast to polyclonal antibodies which are made from several different immune cells. Monoclonal antibodies have monovalent affinity, in that they bind to the same epitope.Given almost any substance, it is possible to produce monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind to that substance; they can then serve to detect or purify that substance. This has become an important tool in biochemistry, molecular biology and medicine. When used as medications, the non-proprietary drug name ends in -mab (see ""Nomenclature of monoclonal antibodies""), and many immunotherapy specialists use the word mab anacronymically.