Synthetic bile acid derivatives induce apoptosis through a c
... in human breast carcinoma cells through a p53-independent pathway. Here, we present that the synthetic bile acid derivatives induce apoptosis in SiHa human cervical carcinoma cells as well. The parental compounds, UDCA and CDCA, exhibited no significant effect on the cell viability at the concentrat ...
... in human breast carcinoma cells through a p53-independent pathway. Here, we present that the synthetic bile acid derivatives induce apoptosis in SiHa human cervical carcinoma cells as well. The parental compounds, UDCA and CDCA, exhibited no significant effect on the cell viability at the concentrat ...
Designing State-of-the-Art Pharmaceutical Profiling
... Edward H. Kerns – Staff Scientist, NIH – NCATS Over 30 years in drug discovery and development ...
... Edward H. Kerns – Staff Scientist, NIH – NCATS Over 30 years in drug discovery and development ...
plant has cell wall, chloroplast, and huge vacuole
... activities of the cell (NOT AN ORGANELLE) Cell Wall – “rigid”, stiff outer layer of plant cell, helps cell keep shape Lysosome – “recycling center”, breaks down dead organelles and waste ...
... activities of the cell (NOT AN ORGANELLE) Cell Wall – “rigid”, stiff outer layer of plant cell, helps cell keep shape Lysosome – “recycling center”, breaks down dead organelles and waste ...
Summary notes on Genetics and Gene expression
... A nonsense mutation –base substitution results in a stop codon being transcribed on to mRNA so polypeptide chain is stopped prematurely and will often not function A mis-sense mutation –base substitution results in a different amino acid being coded for which could change the tertiary structure A Si ...
... A nonsense mutation –base substitution results in a stop codon being transcribed on to mRNA so polypeptide chain is stopped prematurely and will often not function A mis-sense mutation –base substitution results in a different amino acid being coded for which could change the tertiary structure A Si ...
Quarter 4 Study Guide
... The volume of urine produced will be less as the person has lost water via sweat. The body will try to conserve the rest of the water that it has by only producing a small volume of urine. ...
... The volume of urine produced will be less as the person has lost water via sweat. The body will try to conserve the rest of the water that it has by only producing a small volume of urine. ...
Inverse mapping
... 2130 identical protein units, each with 158 amino acid residues, that form the viral protein coat around a single stretch of RNA that comprises 6400 nucleotides. ...
... 2130 identical protein units, each with 158 amino acid residues, that form the viral protein coat around a single stretch of RNA that comprises 6400 nucleotides. ...
Cell Architecture 2 Dr Mahjabeen
... Structural function Intercellular junctions Nuclear lamina Identification by means of immunocytochemical methods • Tissue specificity ...
... Structural function Intercellular junctions Nuclear lamina Identification by means of immunocytochemical methods • Tissue specificity ...
Chapter 5 Lecture Notes: Microbial Nutrition
... 5. Passage of nutrients is through a selectively permeable plasma membrane by the mechanisms described below: B. Passive diffusion 1. Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to one of lower concentration as a result of random thermal agitation 2. Rate of transport depends on the d ...
... 5. Passage of nutrients is through a selectively permeable plasma membrane by the mechanisms described below: B. Passive diffusion 1. Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to one of lower concentration as a result of random thermal agitation 2. Rate of transport depends on the d ...
Lesson 2: DNA Transcription and Translation Introduction This
... (called a codon) of mRNA at a time. Each amino acid has a set of codons that code for that particular molecule. Each protein has a specific shape; determined by the sequence of amino acids that it consists of. A protein’s structure determines its function. Hemoglobin is the protein that is responsib ...
... (called a codon) of mRNA at a time. Each amino acid has a set of codons that code for that particular molecule. Each protein has a specific shape; determined by the sequence of amino acids that it consists of. A protein’s structure determines its function. Hemoglobin is the protein that is responsib ...
Cell Cycle PowerPoint
... reproducing by splitting itself into two… one cell becomes two! See pages 150 - 153 (c) McGraw Hill Ryerson 2007 ...
... reproducing by splitting itself into two… one cell becomes two! See pages 150 - 153 (c) McGraw Hill Ryerson 2007 ...
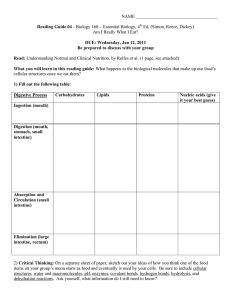
Reading Guide 04- Digestion
... What you will learn in this reading guide: What happens to the biological molecules that make up our food’s cellular structures once we eat them? 1) Fill out the following table: Digestive Process ...
... What you will learn in this reading guide: What happens to the biological molecules that make up our food’s cellular structures once we eat them? 1) Fill out the following table: Digestive Process ...
Big Ideas I. Organisms share common characteristics of life.
... Structure is related to function at the cellular and organelle levels of biological organization. G. Cells come only from the division of a pre-existing cell. IV. Structure is related to function at all biological levels of organization. (Chapter 7; Chapter 18) Essential Question: How is structure r ...
... Structure is related to function at the cellular and organelle levels of biological organization. G. Cells come only from the division of a pre-existing cell. IV. Structure is related to function at all biological levels of organization. (Chapter 7; Chapter 18) Essential Question: How is structure r ...
Biology 1 – Big Ideas I. Organisms share common characteristics of
... Enzymes are special proteins designed to catalyze most biochemical reactions that otherwise would not occur. VIII. New cells arise from the division of pre-existing cells. (Chapter 10) Essential Question: How do cells grow and reproduce? Concepts A. Cells grow when they can take in more nutrients th ...
... Enzymes are special proteins designed to catalyze most biochemical reactions that otherwise would not occur. VIII. New cells arise from the division of pre-existing cells. (Chapter 10) Essential Question: How do cells grow and reproduce? Concepts A. Cells grow when they can take in more nutrients th ...
Cells
... 2. Most the lipid layer is Phospholipids, but there is also a large amount of Cholesterol. 3. Explain the shape of the Phospholipid molecule and explain the hydrophilic (water loving) polar head and Hydrophobic (water hating) nonpolar tail. a. makes the membrane impermeable to most water soluble mol ...
... 2. Most the lipid layer is Phospholipids, but there is also a large amount of Cholesterol. 3. Explain the shape of the Phospholipid molecule and explain the hydrophilic (water loving) polar head and Hydrophobic (water hating) nonpolar tail. a. makes the membrane impermeable to most water soluble mol ...
Genetic Information DNA - Barnegat Township School District
... that affect a gene or a gene control region (Note: not all of our DNA is genes, lots of 'filler' DNA) • Mutations can occur spontaneously (very rare) or can be caused by exposure to certain agents (UV rays, radiation, chemicals) • Different types of mutations: insertions, deletions, substitutions. ...
... that affect a gene or a gene control region (Note: not all of our DNA is genes, lots of 'filler' DNA) • Mutations can occur spontaneously (very rare) or can be caused by exposure to certain agents (UV rays, radiation, chemicals) • Different types of mutations: insertions, deletions, substitutions. ...
The P53-Mdm2 Network: From Oscillations To Apoptosis
... Abstract. The p53 tumour suppressor gene, often characterized as the “guardian of the genome” plays a central role in protecting cells from malignant transformation. It is the most frequently mutated of genes in human cancer. The gene constitutes a highly connected node in a network of signaling pat ...
... Abstract. The p53 tumour suppressor gene, often characterized as the “guardian of the genome” plays a central role in protecting cells from malignant transformation. It is the most frequently mutated of genes in human cancer. The gene constitutes a highly connected node in a network of signaling pat ...
HIGHLIGHTS FOR 7TH GRADE SCIENCE CURRICULUM Cells
... HIGHLIGHTS FOR 7TH GRADE SCIENCE CURRICULUM ...
... HIGHLIGHTS FOR 7TH GRADE SCIENCE CURRICULUM ...
Module 1 (Practice Test)
... 18) A sodium-potassium pump within a cell membrane requires energy to move a sodium and potassium ions into or out of a cell. The movement of glucose into or out of a cell does not require energy. Which statement BEST describes the movement of these materials across a cell membrane? A. B. C. D. ...
... 18) A sodium-potassium pump within a cell membrane requires energy to move a sodium and potassium ions into or out of a cell. The movement of glucose into or out of a cell does not require energy. Which statement BEST describes the movement of these materials across a cell membrane? A. B. C. D. ...
Membrane Protein : Integral/Peripheral
... • Open or closed by changes in voltage across the membrane or by binding molecules • Eg. Muscle contractions ...
... • Open or closed by changes in voltage across the membrane or by binding molecules • Eg. Muscle contractions ...
Biology Quick Notes
... Protects cells and acts as a boundary between what’s inside and outside the cell Phospholipid Bilayer- two layers of phospholipids o Hydrophilic Head- likes water (point out toward water in/out of cell) o Hydrophobic Head- hates water (point toward each other) Diffusion- small molecules moving acros ...
... Protects cells and acts as a boundary between what’s inside and outside the cell Phospholipid Bilayer- two layers of phospholipids o Hydrophilic Head- likes water (point out toward water in/out of cell) o Hydrophobic Head- hates water (point toward each other) Diffusion- small molecules moving acros ...
Click here
... Apart from the macroelements, all organism requires several other nutrients in vary minute quantity. These are known as micronutrients or trace elements and are manganese, zinc, cobalt, molybdenum, nickel, and copper. Either they are part of enzymes and cofactors or they play an important role in ca ...
... Apart from the macroelements, all organism requires several other nutrients in vary minute quantity. These are known as micronutrients or trace elements and are manganese, zinc, cobalt, molybdenum, nickel, and copper. Either they are part of enzymes and cofactors or they play an important role in ca ...
Cell-penetrating peptide

Cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) are short peptides that facilitate cellular uptake of various molecular cargo (from nanosize particles to small chemical molecules and large fragments of DNA). The ""cargo"" is associated with the peptides either through chemical linkage via covalent bonds or through non-covalent interactions. The function of the CPPs are to deliver the cargo into cells, a process that commonly occurs through endocytosis with the cargo delivered to the endosomes of living mammalian cells.CPPs hold great potential as in vitro and in vivo delivery vectors for use in research and medicine. Current use is limited by a lack of cell specificity in CPP-mediated cargo delivery and insufficient understanding of the modes of their uptake.CPPs typically have an amino acid composition that either contains a high relative abundance of positively charged amino acids such as lysine or arginine or has sequences that contain an alternating pattern of polar/charged amino acids and non-polar, hydrophobic amino acids. These two types of structures are referred to as polycationic or amphipathic, respectively. A third class of CPPs are the hydrophobic peptides, containing only apolar residues, with low net chargeor have hydrophobic amino acid groups that are crucial for cellular uptake.The first CPP was discovered independently by two laboratories in 1988, when it was found that the trans-activating transcriptional activator (TAT) from human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1) could be efficiently taken up from the surrounding media by numerous cell types in culture. Since then, the number of known CPPs has expanded considerably and small molecule synthetic analogues with more effective protein transduction properties have been generated.