May_08FL - Wichita State University
... Endocrine disruptors (EDs) represent an expanding group of environmental compounds that can markedly affect biological processes in animals and humans. These include pesticides, herbicides, solvents, plasticizers, prescription drugs, and naturally occurring compounds such as isoflavones. Whereas EDs ...
... Endocrine disruptors (EDs) represent an expanding group of environmental compounds that can markedly affect biological processes in animals and humans. These include pesticides, herbicides, solvents, plasticizers, prescription drugs, and naturally occurring compounds such as isoflavones. Whereas EDs ...
Cells - Deer Creek Schools
... • Storage of water & other nutrients • Breakdown wastes to be disposed of • Hydrolysis of macromolecules • Enlargement of vacuole is major mechanism in plant growth • Can act as a pump to rid the plant of excess water ...
... • Storage of water & other nutrients • Breakdown wastes to be disposed of • Hydrolysis of macromolecules • Enlargement of vacuole is major mechanism in plant growth • Can act as a pump to rid the plant of excess water ...
Chapter 17 and 19: Review Questions
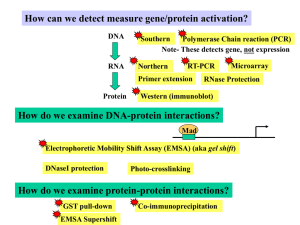
... specific enzyme. Their experiments demonstrated that _____. genes carry information for making proteins mutations are changes in genetic information genes are made of DNA enzymes are required to repair damaged DNA information cells need specific enzymes in order to function 2. The flow of informatio ...
... specific enzyme. Their experiments demonstrated that _____. genes carry information for making proteins mutations are changes in genetic information genes are made of DNA enzymes are required to repair damaged DNA information cells need specific enzymes in order to function 2. The flow of informatio ...
DNA to Protein Name____________ Period______ DNA Location
... Location of Translation_______________________________________________________________________ Name 5 Amino Acids (p298)___________________________________________________________________ Names of 5 Proteins_________________________________________________________________________ OVERVEIW OF THE PRO ...
... Location of Translation_______________________________________________________________________ Name 5 Amino Acids (p298)___________________________________________________________________ Names of 5 Proteins_________________________________________________________________________ OVERVEIW OF THE PRO ...
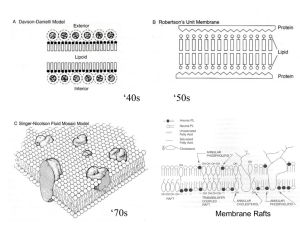
The Fluid Mosaic Model of the Cell Membrane
... and would only follow many years after the publication of the model. What was the biochemical structure of these proteins predicted to be? Consider the energetic principles and molecular interactions on which Singer and Nicolson's model is based. Use your understanding of how these principles in uen ...
... and would only follow many years after the publication of the model. What was the biochemical structure of these proteins predicted to be? Consider the energetic principles and molecular interactions on which Singer and Nicolson's model is based. Use your understanding of how these principles in uen ...
Cells - TeacherWeb
... perform a common function are referred to as a system or organ system. The blood vessels, blood, and the heart are organs which work together to form the circulatory system. Many different systems function together to allow a complex organism to function. ...
... perform a common function are referred to as a system or organ system. The blood vessels, blood, and the heart are organs which work together to form the circulatory system. Many different systems function together to allow a complex organism to function. ...
File
... different amino acids found in nature Amino acids are joined by covalent bonds The instructions for arranging amino acids into many different proteins are stored in DNA ...
... different amino acids found in nature Amino acids are joined by covalent bonds The instructions for arranging amino acids into many different proteins are stored in DNA ...
Control of Cell Division
... – The rungs of the ladder are made up of four different bases, arranged in different orders and sequences – These sequences are the genetic code – The DNA of our 46 chromosomes is the genome which contains 20,000 to 30,000 genes ...
... – The rungs of the ladder are made up of four different bases, arranged in different orders and sequences – These sequences are the genetic code – The DNA of our 46 chromosomes is the genome which contains 20,000 to 30,000 genes ...
lecture 11
... Bio significance: in GOLGI, proteins with short TMDs reside in non raft regions, whereas proteins with longer TMDs reside in raft regions destined to the plasma membrane (rich in cholesterol and SPM). Length of TMD has been indicated to be an important factor in controlling protein trafficing. ...
... Bio significance: in GOLGI, proteins with short TMDs reside in non raft regions, whereas proteins with longer TMDs reside in raft regions destined to the plasma membrane (rich in cholesterol and SPM). Length of TMD has been indicated to be an important factor in controlling protein trafficing. ...
1 Cells Cells -Cells are the building blocks of living things
... -makes proteins for the membrane -modifies proteins: folds amino acids into polypeptide chains -forms tubes and channels: amino acids made in ribosomes get folded and glucose chain is added as receptors/cell markers -carries proteins and other out of cells through these channels -makes materials for ...
... -makes proteins for the membrane -modifies proteins: folds amino acids into polypeptide chains -forms tubes and channels: amino acids made in ribosomes get folded and glucose chain is added as receptors/cell markers -carries proteins and other out of cells through these channels -makes materials for ...
Cells Cells -Cells are the building blocks of living things
... -makes proteins for the membrane -modifies proteins: folds amino acids into polypeptide chains -forms tubes and channels: amino acids made in ribosomes get folded and glucose chain is added as receptors/cell markers -carries proteins and other out of cells through these channels -makes materials for ...
... -makes proteins for the membrane -modifies proteins: folds amino acids into polypeptide chains -forms tubes and channels: amino acids made in ribosomes get folded and glucose chain is added as receptors/cell markers -carries proteins and other out of cells through these channels -makes materials for ...
Y12 Biology Year 1 AS LOs Student Teacher 1
... The basic structure of all cell membranes, including cell-surface membranes and the membranes around the cell organelles of eukaryotes, is the same. The arrangement and any movement of phospholipids, proteins, glycoproteins and glycolipids in the fluid-mosaic model of membrane structure. Cholesterol ...
... The basic structure of all cell membranes, including cell-surface membranes and the membranes around the cell organelles of eukaryotes, is the same. The arrangement and any movement of phospholipids, proteins, glycoproteins and glycolipids in the fluid-mosaic model of membrane structure. Cholesterol ...
AB205Abstract_proteomics_conference
... sustainable agricultural production and food security. Studying plant responses to these adverse conditions can help in determining the strategies to combat them. A proteomic approach was used to compare protein expression between Arachis hypogaea callus cell lines adapted to salinity stressand cont ...
... sustainable agricultural production and food security. Studying plant responses to these adverse conditions can help in determining the strategies to combat them. A proteomic approach was used to compare protein expression between Arachis hypogaea callus cell lines adapted to salinity stressand cont ...
Science Notes
... -They are non-living cells, as they do not have nuclei, cell membranes or cytoplasm (no organelles) -Have protein coats/capsids that help to attach them to a host cell; surrounded by a coat of protein units. -Classified by the type of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) and the shapes of their protein coats. ...
... -They are non-living cells, as they do not have nuclei, cell membranes or cytoplasm (no organelles) -Have protein coats/capsids that help to attach them to a host cell; surrounded by a coat of protein units. -Classified by the type of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) and the shapes of their protein coats. ...
Characteristics of Life: • Living things have cells. o Cell:
... Living things have cells. o Cell: __________________________________ ______________________________________ o Some organisms have ______ cell, some are made up of ___________________ of cells. Living things sense and respond to change. o _____________________: maintenance of a stable internal en ...
... Living things have cells. o Cell: __________________________________ ______________________________________ o Some organisms have ______ cell, some are made up of ___________________ of cells. Living things sense and respond to change. o _____________________: maintenance of a stable internal en ...
charged
... The information encoded in DNA is transcribed into RNA and finally translated into the sequence of proteins. The genetic unit coding for one single amino acid is a codon. One gene codes for one proteins, one cistron for one polypeptide chain. As many proteins consist of only one polypeptide chain, m ...
... The information encoded in DNA is transcribed into RNA and finally translated into the sequence of proteins. The genetic unit coding for one single amino acid is a codon. One gene codes for one proteins, one cistron for one polypeptide chain. As many proteins consist of only one polypeptide chain, m ...
CELLS structure and function
... When a substance is transported from a low concentration to a high concentration i.e. uphill against the concentration gradient, energy has to be used. This is called active transport. Active transport is important in maintaining different concentrations of the ions sodium and potassium on either si ...
... When a substance is transported from a low concentration to a high concentration i.e. uphill against the concentration gradient, energy has to be used. This is called active transport. Active transport is important in maintaining different concentrations of the ions sodium and potassium on either si ...
Hot Topics in Protein Medicinal Chemistry
... David Tirrell, California Institute of Technology “Non-Canonical Amino Acids as Tools for Protein Medicinal Chemistry” ...
... David Tirrell, California Institute of Technology “Non-Canonical Amino Acids as Tools for Protein Medicinal Chemistry” ...
The cellular response to aggregated proteins associated with
... them — the ER-associated degradation (ERAD) pathway. Although this pathway was originally thought to involve a distinct proteolytic mechanism, it now appears to be mediated in large part from the cytoplasmic face of the ER by the ubiquitin system and the proteosome. Substrate-specific and cell type– ...
... them — the ER-associated degradation (ERAD) pathway. Although this pathway was originally thought to involve a distinct proteolytic mechanism, it now appears to be mediated in large part from the cytoplasmic face of the ER by the ubiquitin system and the proteosome. Substrate-specific and cell type– ...
AH summary Unit 1
... hormone signal has bound to the receptor can the transcription factor bind to gene regulatory sequences of DNA for transcription to occur. (c) Hydrophilic signals and transduction Hydrophilic signalling molecules include peptide hormones and neurotransmitters. Hydrophilic signals require receptor mo ...
... hormone signal has bound to the receptor can the transcription factor bind to gene regulatory sequences of DNA for transcription to occur. (c) Hydrophilic signals and transduction Hydrophilic signalling molecules include peptide hormones and neurotransmitters. Hydrophilic signals require receptor mo ...
amino acid
... groups that make up the train? If the necklace is the polymer, what are the monomers that make up the necklace? ...
... groups that make up the train? If the necklace is the polymer, what are the monomers that make up the necklace? ...
Cell-penetrating peptide

Cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) are short peptides that facilitate cellular uptake of various molecular cargo (from nanosize particles to small chemical molecules and large fragments of DNA). The ""cargo"" is associated with the peptides either through chemical linkage via covalent bonds or through non-covalent interactions. The function of the CPPs are to deliver the cargo into cells, a process that commonly occurs through endocytosis with the cargo delivered to the endosomes of living mammalian cells.CPPs hold great potential as in vitro and in vivo delivery vectors for use in research and medicine. Current use is limited by a lack of cell specificity in CPP-mediated cargo delivery and insufficient understanding of the modes of their uptake.CPPs typically have an amino acid composition that either contains a high relative abundance of positively charged amino acids such as lysine or arginine or has sequences that contain an alternating pattern of polar/charged amino acids and non-polar, hydrophobic amino acids. These two types of structures are referred to as polycationic or amphipathic, respectively. A third class of CPPs are the hydrophobic peptides, containing only apolar residues, with low net chargeor have hydrophobic amino acid groups that are crucial for cellular uptake.The first CPP was discovered independently by two laboratories in 1988, when it was found that the trans-activating transcriptional activator (TAT) from human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1) could be efficiently taken up from the surrounding media by numerous cell types in culture. Since then, the number of known CPPs has expanded considerably and small molecule synthetic analogues with more effective protein transduction properties have been generated.