DNA plasmid minipreps - How it works: Solution I: 50 mM glucose
... - The lower pH neutralizes the alkali in Solution II and causes the chromosomal DNA to form an insoluble complex that precipitates in high salt. - The positively charged potassium ions are used in ethanol precipitation to shield the negative charge on the phosphate backbone of the DNA. As a result, ...
... - The lower pH neutralizes the alkali in Solution II and causes the chromosomal DNA to form an insoluble complex that precipitates in high salt. - The positively charged potassium ions are used in ethanol precipitation to shield the negative charge on the phosphate backbone of the DNA. As a result, ...
Prof. Dr. Harry F. Noller Prof. Dr. Ada Yonath
... synthesis is done in the ribosomes, a large number of which act simultaneously on the same mRNA synthesizing different proteins. These ribosomes, which are the focus of the Prize today, are giant cellular assemblies, each composed of two subunits comprising mainly RNA, in which more than 50 proteins ...
... synthesis is done in the ribosomes, a large number of which act simultaneously on the same mRNA synthesizing different proteins. These ribosomes, which are the focus of the Prize today, are giant cellular assemblies, each composed of two subunits comprising mainly RNA, in which more than 50 proteins ...
Study guide for exam 2 Spring 2017
... What are the major phases of the cell cycle? What happens during those stages? Remember the importance of the S-phase. Be familiar with the major stages of mitosis. What occurs during each of these stages? How many daughter cells result from mitosis? Understand the significance of mitosis. How does ...
... What are the major phases of the cell cycle? What happens during those stages? Remember the importance of the S-phase. Be familiar with the major stages of mitosis. What occurs during each of these stages? How many daughter cells result from mitosis? Understand the significance of mitosis. How does ...
Biological Molecules
... amino acids together according to the types of functional characteristics they exhibit. These groups include the charged, or ionizable, amino acids; the non-polar amino acids; the polar, uncharged, amino acids; and those with unique structural properties. The amino acids can be categorized in many d ...
... amino acids together according to the types of functional characteristics they exhibit. These groups include the charged, or ionizable, amino acids; the non-polar amino acids; the polar, uncharged, amino acids; and those with unique structural properties. The amino acids can be categorized in many d ...
Cell Growth and Division Digital Guide
... leads to diseases such as cancer 6A Identify components of DNA and describe how information for specifying the traits of an organism is carried in the DNA 10C Analyze levels of organization in biological systems and relate the levels to each other and to the whole system ...
... leads to diseases such as cancer 6A Identify components of DNA and describe how information for specifying the traits of an organism is carried in the DNA 10C Analyze levels of organization in biological systems and relate the levels to each other and to the whole system ...
were performed essentially as described previously (Witt et al
... Interaction of between nebulin and titin. To survey for the residues in titin mediating binding to nebulin, we used a SPOTS blot membrane (JPT, Berlin) that displays exon 4 – exon 7 of titin (see also EMBL data library, accession AJ277892) as a series of 31 overlapping residues (peptides were acetyl ...
... Interaction of between nebulin and titin. To survey for the residues in titin mediating binding to nebulin, we used a SPOTS blot membrane (JPT, Berlin) that displays exon 4 – exon 7 of titin (see also EMBL data library, accession AJ277892) as a series of 31 overlapping residues (peptides were acetyl ...
8th Grade Sixth Six Weeks Vocabulary
... an organic compound that is made of one or more chains of amino acids and that is a principal component of all cells Teacher Information: Teach chains of a.a. = protein. any one of twenty different organic molecules that contain a carboxyl and an amino group and that combine to form proteins an orga ...
... an organic compound that is made of one or more chains of amino acids and that is a principal component of all cells Teacher Information: Teach chains of a.a. = protein. any one of twenty different organic molecules that contain a carboxyl and an amino group and that combine to form proteins an orga ...
Secondary structure
... With the information already obtained such as ; The rigid and planer nature of peptide bond, Allowed conformations using torsion angles and X-ray result of keratin protein obtained by Willium Astbury, who observed that a regular structure was occurring in keratin that reapeated everu 5.15 to 5.2 Ao. ...
... With the information already obtained such as ; The rigid and planer nature of peptide bond, Allowed conformations using torsion angles and X-ray result of keratin protein obtained by Willium Astbury, who observed that a regular structure was occurring in keratin that reapeated everu 5.15 to 5.2 Ao. ...
cloze 1 - Uplift Education
... __________________________ cells are cells that do not contain a nucleus or other type of membrane-bound organelle. These cells contain ______________________, but this genetic material is not found in a nucleus. Prokaryotic cells are much ________________________ than eukaryotic cells. Bacteria are ...
... __________________________ cells are cells that do not contain a nucleus or other type of membrane-bound organelle. These cells contain ______________________, but this genetic material is not found in a nucleus. Prokaryotic cells are much ________________________ than eukaryotic cells. Bacteria are ...
Bio A
... Carbon, however, can make special bonds where they share multiple electrons with the same molecule o These are called double or triple bonds In addition to these special bonds, carbon can bond in different arrangements o Carbon can make long straight chains, carbon can make long branched chains, ...
... Carbon, however, can make special bonds where they share multiple electrons with the same molecule o These are called double or triple bonds In addition to these special bonds, carbon can bond in different arrangements o Carbon can make long straight chains, carbon can make long branched chains, ...
CHAPTER NINE: MITOSIS NOTES PT. 1 What Happens When A
... Chromosomes contain all of our DNA Our DNA is coiled up extremely tight and wrapped around proteins (called histones) so that it is able to fit into the cell Each one of our cells contains over 3 billion Nitrogen bases (GCAT) DNA can replicate itself DNA encodes for proteins ...
... Chromosomes contain all of our DNA Our DNA is coiled up extremely tight and wrapped around proteins (called histones) so that it is able to fit into the cell Each one of our cells contains over 3 billion Nitrogen bases (GCAT) DNA can replicate itself DNA encodes for proteins ...
Biological Molecules - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... 1. Many biological molecules are polymers A. ...
... 1. Many biological molecules are polymers A. ...
Name: Honors Biology Midterm Review Packet Mrs. Sands Chapter
... A cell has a defect that results in the loss of its ability to regulate the passage of food, water and waste into and out of the cell. In which of the following cell structures is this defect most likely to be located? a. Ribosomes c. Plasma (Cell) Membrane b. Chloroplasts d. Endoplasmic Reticulum ...
... A cell has a defect that results in the loss of its ability to regulate the passage of food, water and waste into and out of the cell. In which of the following cell structures is this defect most likely to be located? a. Ribosomes c. Plasma (Cell) Membrane b. Chloroplasts d. Endoplasmic Reticulum ...
cell wall - SCHOOLinSITES
... Eukaryotic Cells and Eukaryotes • Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and other membranebound organelles. Most eukaryotic cells are microscopic, but are about 10 times larger than bacterial cells. • All living things that are not bacteria or archaea are made of one or more eukaryotic cells. Organisms ma ...
... Eukaryotic Cells and Eukaryotes • Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and other membranebound organelles. Most eukaryotic cells are microscopic, but are about 10 times larger than bacterial cells. • All living things that are not bacteria or archaea are made of one or more eukaryotic cells. Organisms ma ...
Document
... Q2. (8pts) Sanger sequencing is a rather simple technique. 1. It takes advantage of inhibiting replication with _____________________________. 2. And the coupling of what to the above answer? ________________________. 3. Finally, fragments are run on a size fractionation matrix. Are those fragments ...
... Q2. (8pts) Sanger sequencing is a rather simple technique. 1. It takes advantage of inhibiting replication with _____________________________. 2. And the coupling of what to the above answer? ________________________. 3. Finally, fragments are run on a size fractionation matrix. Are those fragments ...
Getting things where they need to go: Protein Targeting
... deform PM for clathrin coated vesicles. May suggest that using a helix to deform membrane is common mechanism for budding/fission ...
... deform PM for clathrin coated vesicles. May suggest that using a helix to deform membrane is common mechanism for budding/fission ...
paramedics - anatomy and physiology.indb
... external environment from the cytoplasm and controlling what enters and leaves the cell. Cell membranes are comprised of a double layer of phospholipid molecules tightly packed together.The membrane is partially permeable and has protein molecules embedded in it that allow transport of substances in ...
... external environment from the cytoplasm and controlling what enters and leaves the cell. Cell membranes are comprised of a double layer of phospholipid molecules tightly packed together.The membrane is partially permeable and has protein molecules embedded in it that allow transport of substances in ...
Macro-molecules short 2014
... There are 20 different amino acids found in nature This allows for very diverse combinations of proteins to be formed with diverse functions See figure 2-16 on p.47 in textbook 3 basic roles of proteins: 1) Structure (muscle and bone) 2) Control chemical reactions and regulate cell processes (enzyme ...
... There are 20 different amino acids found in nature This allows for very diverse combinations of proteins to be formed with diverse functions See figure 2-16 on p.47 in textbook 3 basic roles of proteins: 1) Structure (muscle and bone) 2) Control chemical reactions and regulate cell processes (enzyme ...
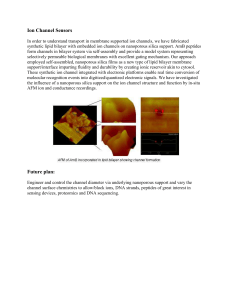
Ion Channel Sensors
... synthetic lipid bilayer with embedded ion channels on nanoporous silica support. AmB peptides form channels in bilayer system via self-assembly and provide a model system representing selectively permeable biological membranes with excellent gating mechanism. Our approach employed self-assembled, na ...
... synthetic lipid bilayer with embedded ion channels on nanoporous silica support. AmB peptides form channels in bilayer system via self-assembly and provide a model system representing selectively permeable biological membranes with excellent gating mechanism. Our approach employed self-assembled, na ...
Standard Growth Conditions and Measurement of Growth
... 2. Water activity—most bacteria require a water activity between 0.9 and 1.0 3. Osmolarity—The osmolarity of the bacterial cell cytoplasm must be greater than that of its environment for cell growth— turgor pressure 4. Oxygen—bacteria have a great variety of specifications with respect to the amount ...
... 2. Water activity—most bacteria require a water activity between 0.9 and 1.0 3. Osmolarity—The osmolarity of the bacterial cell cytoplasm must be greater than that of its environment for cell growth— turgor pressure 4. Oxygen—bacteria have a great variety of specifications with respect to the amount ...
LECTURE #10: Cancer- A Deeper Look
... – normally inhibits (turns “off”) cell division – if switched “OFF” can cause cancer – example: p53 gene ...
... – normally inhibits (turns “off”) cell division – if switched “OFF” can cause cancer – example: p53 gene ...
Cell identification using Monoclonal Antibodies
... Technology: The first step in the production of MAbs is to immunize a mouse with an antigen. When the mouse begins to produce antibodies to the antigen, its spleen is removed. Antibody-producing cells from the spleen are then fused with a selected myeloma cell line, one which is not Ab-producing and ...
... Technology: The first step in the production of MAbs is to immunize a mouse with an antigen. When the mouse begins to produce antibodies to the antigen, its spleen is removed. Antibody-producing cells from the spleen are then fused with a selected myeloma cell line, one which is not Ab-producing and ...
Novel in vivo Metal Clusters with
... Unfolding and subsequent aggregation of proteins is a common phenomenon linked to many human disorders. In investigating a possible mechanism by which excess hemoglobin release may be controlled in blood plasma in the disease state, it was discovered that human blood contains particles (“proteons”) ...
... Unfolding and subsequent aggregation of proteins is a common phenomenon linked to many human disorders. In investigating a possible mechanism by which excess hemoglobin release may be controlled in blood plasma in the disease state, it was discovered that human blood contains particles (“proteons”) ...
SYLLABUS Advanced Cell Biology BIOL 3301 (3
... Fundamental knowledge in cell biology will be discussed. Topics include DNAs, RNAs, proteins, cell structure, cell motility, bio-membrane, endocytosis, exocytosis, nucleocytoplasmic transport, vesicular transport, cancers, visualizing macromolecular trafficking in cells with advanced microscopy imag ...
... Fundamental knowledge in cell biology will be discussed. Topics include DNAs, RNAs, proteins, cell structure, cell motility, bio-membrane, endocytosis, exocytosis, nucleocytoplasmic transport, vesicular transport, cancers, visualizing macromolecular trafficking in cells with advanced microscopy imag ...
Cell-penetrating peptide

Cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) are short peptides that facilitate cellular uptake of various molecular cargo (from nanosize particles to small chemical molecules and large fragments of DNA). The ""cargo"" is associated with the peptides either through chemical linkage via covalent bonds or through non-covalent interactions. The function of the CPPs are to deliver the cargo into cells, a process that commonly occurs through endocytosis with the cargo delivered to the endosomes of living mammalian cells.CPPs hold great potential as in vitro and in vivo delivery vectors for use in research and medicine. Current use is limited by a lack of cell specificity in CPP-mediated cargo delivery and insufficient understanding of the modes of their uptake.CPPs typically have an amino acid composition that either contains a high relative abundance of positively charged amino acids such as lysine or arginine or has sequences that contain an alternating pattern of polar/charged amino acids and non-polar, hydrophobic amino acids. These two types of structures are referred to as polycationic or amphipathic, respectively. A third class of CPPs are the hydrophobic peptides, containing only apolar residues, with low net chargeor have hydrophobic amino acid groups that are crucial for cellular uptake.The first CPP was discovered independently by two laboratories in 1988, when it was found that the trans-activating transcriptional activator (TAT) from human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1) could be efficiently taken up from the surrounding media by numerous cell types in culture. Since then, the number of known CPPs has expanded considerably and small molecule synthetic analogues with more effective protein transduction properties have been generated.