Document
... insights into basic cellular activities [2]. Cryo-electron tomography has likewise stunned the scientific community with seemingly complete maps of the cellular interior, and at a yet unknown degree of ‘morphological’ resolution [3,4] (Figure 1a). With those experimental images at hand, we are begin ...
... insights into basic cellular activities [2]. Cryo-electron tomography has likewise stunned the scientific community with seemingly complete maps of the cellular interior, and at a yet unknown degree of ‘morphological’ resolution [3,4] (Figure 1a). With those experimental images at hand, we are begin ...
Streptomyces roseoverticillatus produces two different poly(amino
... spectrometry and other analyses revealed that the gPGA is a mixture of oligomers consisting of 10–13 L-glutamic acid residues linked by isopeptide bonds. In contrast to the known Bacillus gPGA, the glutamic acid oligomers have a cyclodehydrated structure in each molecule. We previously reported that ...
... spectrometry and other analyses revealed that the gPGA is a mixture of oligomers consisting of 10–13 L-glutamic acid residues linked by isopeptide bonds. In contrast to the known Bacillus gPGA, the glutamic acid oligomers have a cyclodehydrated structure in each molecule. We previously reported that ...
Hitting the Target: Emerging Technologies in the Search for Kinase
... immunoprecipitate and identify specific PI3K-dependent phosphoproteins from insulin-stimulated adipocytes (19). One problem with this method is that phospho-motif antibodies are generated against peptides and, hence, will often not be able to bind and immunoprecipitate proteins in their native folde ...
... immunoprecipitate and identify specific PI3K-dependent phosphoproteins from insulin-stimulated adipocytes (19). One problem with this method is that phospho-motif antibodies are generated against peptides and, hence, will often not be able to bind and immunoprecipitate proteins in their native folde ...
Boron in plants: deficiency and toxicity
... concentrations in comparison to control plants (Camacho-Cristóbal and GonzálezFontes 1999). More recently it has been shown that short-term B deficiency led to a decline in root and, especially, leaf nitrate contents without affecting NR activity (Camacho-Cristóbal and González-Fontes 2007) or the c ...
... concentrations in comparison to control plants (Camacho-Cristóbal and GonzálezFontes 1999). More recently it has been shown that short-term B deficiency led to a decline in root and, especially, leaf nitrate contents without affecting NR activity (Camacho-Cristóbal and González-Fontes 2007) or the c ...
Distribution of Fucose-Containing Xyloglucans in Cell Walls of the
... that CCRC-M1 labels the walls of all cells located within the meristematic zone (Dolan et al., 1993), approximately 200 m from the apex (Fig. 3), in contrast to the absence of labeling in this region observed in intact seedlings (Fig. 1). The absence of surface labeling at the tip of intact seedlin ...
... that CCRC-M1 labels the walls of all cells located within the meristematic zone (Dolan et al., 1993), approximately 200 m from the apex (Fig. 3), in contrast to the absence of labeling in this region observed in intact seedlings (Fig. 1). The absence of surface labeling at the tip of intact seedlin ...
Powerpoint
... Provides information on disappearance of substrate only. May see very little change associated with oxidation in vivo. ...
... Provides information on disappearance of substrate only. May see very little change associated with oxidation in vivo. ...
as a PDF
... Cloning of CYP2S1 cDNA. A full-length CYP2S1 cDNA was amplified from the human lung first-strand cDNA library by a reported nested PCR method with the same outer primers (Rylander et al., 2001). The nested PCR primers were designed using the RightPrimer 1.2.5 software (BioDisk, San Francisco, CA), a ...
... Cloning of CYP2S1 cDNA. A full-length CYP2S1 cDNA was amplified from the human lung first-strand cDNA library by a reported nested PCR method with the same outer primers (Rylander et al., 2001). The nested PCR primers were designed using the RightPrimer 1.2.5 software (BioDisk, San Francisco, CA), a ...
- PMAS-Arid Agriculture University Rawalpindi
... • Nano particles are designed to avoid the body's defense mechanisms can be used to improve drug delivery. • New, complex drug delivery mechanisms are being developed, which can get drugs through cell membranes and into cell cytoplasm, thereby increasing efficiency. • Triggered response is one way f ...
... • Nano particles are designed to avoid the body's defense mechanisms can be used to improve drug delivery. • New, complex drug delivery mechanisms are being developed, which can get drugs through cell membranes and into cell cytoplasm, thereby increasing efficiency. • Triggered response is one way f ...
Model Description Sheet
... is a G-protein coupled receptor which binds to light sensitive retinal. When light enters the cell, the retinal isomerizes from the cis form to the trans form, and opsin is activated; nerves then signal the brain. The opsin complex, sensitive to specific wavelengths of light, is identified by the wa ...
... is a G-protein coupled receptor which binds to light sensitive retinal. When light enters the cell, the retinal isomerizes from the cis form to the trans form, and opsin is activated; nerves then signal the brain. The opsin complex, sensitive to specific wavelengths of light, is identified by the wa ...
PROTEIN-LIPID AND PROTEIN-CARBOHYDRATE INTERACTIONS
... characteristic of the majority of glycoproteins. Theoretically ionic bonding may not be excluded between oxidized derivatives of carbohydrates and ionic groups of the polypeptide chain. Fractionation and reconstitution studies have shown that starch tailings fraction, although contributing to water ...
... characteristic of the majority of glycoproteins. Theoretically ionic bonding may not be excluded between oxidized derivatives of carbohydrates and ionic groups of the polypeptide chain. Fractionation and reconstitution studies have shown that starch tailings fraction, although contributing to water ...
Biology Textbook - South Sevier High School
... Have you ever asked yourself questions about your surroundings and wondered how or why they are happening? This is science. Science works best when driven by curiosity and innovation. In order for you to experience science in its fullest sense you must take it beyond the textbook and into your every ...
... Have you ever asked yourself questions about your surroundings and wondered how or why they are happening? This is science. Science works best when driven by curiosity and innovation. In order for you to experience science in its fullest sense you must take it beyond the textbook and into your every ...
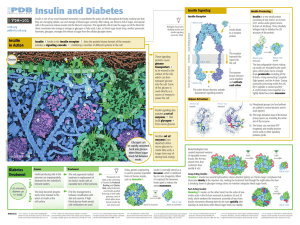
poster PDF
... Insulin is one of our most important hormones. It coordinates the action of cells throughout the body, making sure that they are managing uptake, use and storage of blood sugar correctly. After eating, our blood is full of sugar, and special cells in the pancreas release insulin into the blood in re ...
... Insulin is one of our most important hormones. It coordinates the action of cells throughout the body, making sure that they are managing uptake, use and storage of blood sugar correctly. After eating, our blood is full of sugar, and special cells in the pancreas release insulin into the blood in re ...
The Cytoskeleton
... GTPases: cdc42: its activation triggers actin polymerization and bundling at ...
... GTPases: cdc42: its activation triggers actin polymerization and bundling at ...
GEFs: master regulators of G
... GEFs are the recipients of the regulatory signals that trigger G-protein-coupled pathways. Regulation of GEFs might involve their specific localization, as well as direct activation by protein–protein interactions. Information gleaned from studies of Ras-directed GEFs is instructive for our understa ...
... GEFs are the recipients of the regulatory signals that trigger G-protein-coupled pathways. Regulation of GEFs might involve their specific localization, as well as direct activation by protein–protein interactions. Information gleaned from studies of Ras-directed GEFs is instructive for our understa ...
Table II presents the enzyme activity as well as the... bers of an ordered tetrad. The strains were grown...
... and the analog sensitivity of the individual components against 3AT or para-fluorophenylalanine (pFPA) was complemented (test B). The control heterokaryons no 1, 2, 4 and 5 (Table 1) demonstrated that under each condition, the mutant alleles were recessive to their respective wild-type alleles. Grow ...
... and the analog sensitivity of the individual components against 3AT or para-fluorophenylalanine (pFPA) was complemented (test B). The control heterokaryons no 1, 2, 4 and 5 (Table 1) demonstrated that under each condition, the mutant alleles were recessive to their respective wild-type alleles. Grow ...
1. Pam matrices
... substituted in these 2 sequences eventually will being represented in the substitution matrix and is being used to determine the percentage similar between them and Besides, amino acid substitution matrix was based upon 2 important concepts. These concepts are being introduced by Dayhoff and co-work ...
... substituted in these 2 sequences eventually will being represented in the substitution matrix and is being used to determine the percentage similar between them and Besides, amino acid substitution matrix was based upon 2 important concepts. These concepts are being introduced by Dayhoff and co-work ...
Free amino acids and proteins dynamics in somatic embryogenesis
... acids represent the first step in nitrogen assimilation (Ortiz-Lopez et al., 2000). In MS/2 medium, free amino acids contents was low in embryogenic calli and then increased significantly during globular and bipolar embryos formation. These results are similar to those obtained in Pinus patula (Mala ...
... acids represent the first step in nitrogen assimilation (Ortiz-Lopez et al., 2000). In MS/2 medium, free amino acids contents was low in embryogenic calli and then increased significantly during globular and bipolar embryos formation. These results are similar to those obtained in Pinus patula (Mala ...
UNIT I - Net Start Class
... is another example. Carbon has six electrons: 1s2, 2s2, 2p2. The carbon shares its four electrons of its outer shell with 4 Hydrogen atoms to get CH4 = Methane. If atoms share one pair of electrons, one electron from each atom, then they form one covalent bond (single bond). If two atoms share two ...
... is another example. Carbon has six electrons: 1s2, 2s2, 2p2. The carbon shares its four electrons of its outer shell with 4 Hydrogen atoms to get CH4 = Methane. If atoms share one pair of electrons, one electron from each atom, then they form one covalent bond (single bond). If two atoms share two ...
b. non-vascular plants - Mrs. Harter
... If atoms share one pair of electrons, one electron from each atom, then they form one covalent bond (single bond). If two atoms share two pairs of atoms, two from each atom, they form two covalent bonds (double bond). If two atoms share three pairs of electrons, three from each atom, they form three ...
... If atoms share one pair of electrons, one electron from each atom, then they form one covalent bond (single bond). If two atoms share two pairs of atoms, two from each atom, they form two covalent bonds (double bond). If two atoms share three pairs of electrons, three from each atom, they form three ...
... In accordance with another aspect of the present In such a diagnostic assay, a nucleic acid sequence in a invention, there is also provided nucleic acid probes comsample derived from a tissue other than the prostate is prising nucleic acid molecules of sufficient length to speamplified and detected. ...
AP Study Guide
... sharing electrons. In fact, atoms give up little by sharing. For example, 2 Hydrogen atoms share their electron to have two electrons in their shell. Oxygen (1s2, 2s2, 2p4) shares two electrons to form O2. Methane is another example. Carbon has six electrons: 1s2, 2s2, 2p2. The carbon shares its fou ...
... sharing electrons. In fact, atoms give up little by sharing. For example, 2 Hydrogen atoms share their electron to have two electrons in their shell. Oxygen (1s2, 2s2, 2p4) shares two electrons to form O2. Methane is another example. Carbon has six electrons: 1s2, 2s2, 2p2. The carbon shares its fou ...
Structural Analysis of Type III Collagen Using Two Dimensional
... where G is glycine and X and Y are often proline and proline-modified amino acids, such as 4hydroxyproline or 3-hydroxyproline for example [2]. Although proline and hydroxyproline make up nearly thirty percent of collagen residues, the modification of proline to hydroxyproline does not occur until a ...
... where G is glycine and X and Y are often proline and proline-modified amino acids, such as 4hydroxyproline or 3-hydroxyproline for example [2]. Although proline and hydroxyproline make up nearly thirty percent of collagen residues, the modification of proline to hydroxyproline does not occur until a ...
Lecture 21: Structure of Prokaryotic Cells
... membrane known as matrix. The proteins present in intermembrane space have a role in executing “programmed cell death” or “apoptosis”. Matrix is the liquid part present in the inner most of mitochondria and it contains ribosome, DNA, RNA, enzymes to run kreb cycle and other proteins. Mitochondrial D ...
... membrane known as matrix. The proteins present in intermembrane space have a role in executing “programmed cell death” or “apoptosis”. Matrix is the liquid part present in the inner most of mitochondria and it contains ribosome, DNA, RNA, enzymes to run kreb cycle and other proteins. Mitochondrial D ...
Cell-penetrating peptide

Cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) are short peptides that facilitate cellular uptake of various molecular cargo (from nanosize particles to small chemical molecules and large fragments of DNA). The ""cargo"" is associated with the peptides either through chemical linkage via covalent bonds or through non-covalent interactions. The function of the CPPs are to deliver the cargo into cells, a process that commonly occurs through endocytosis with the cargo delivered to the endosomes of living mammalian cells.CPPs hold great potential as in vitro and in vivo delivery vectors for use in research and medicine. Current use is limited by a lack of cell specificity in CPP-mediated cargo delivery and insufficient understanding of the modes of their uptake.CPPs typically have an amino acid composition that either contains a high relative abundance of positively charged amino acids such as lysine or arginine or has sequences that contain an alternating pattern of polar/charged amino acids and non-polar, hydrophobic amino acids. These two types of structures are referred to as polycationic or amphipathic, respectively. A third class of CPPs are the hydrophobic peptides, containing only apolar residues, with low net chargeor have hydrophobic amino acid groups that are crucial for cellular uptake.The first CPP was discovered independently by two laboratories in 1988, when it was found that the trans-activating transcriptional activator (TAT) from human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1) could be efficiently taken up from the surrounding media by numerous cell types in culture. Since then, the number of known CPPs has expanded considerably and small molecule synthetic analogues with more effective protein transduction properties have been generated.