Cardiomyopathy
... rhythm can get off beat. CMP can lead to heart failure, arrhythmias, and heart valve problems ...
... rhythm can get off beat. CMP can lead to heart failure, arrhythmias, and heart valve problems ...
Third Degree Atrioventricular Block - e
... The location of third-degree atrioventricular block is the AV node itself or lower. In patients with third-degree heart block, the atria are beating at 60 to 100 beats per minute with normal impulses (unless there is also sinus node dysfunction or another disorder present). The problem arises when t ...
... The location of third-degree atrioventricular block is the AV node itself or lower. In patients with third-degree heart block, the atria are beating at 60 to 100 beats per minute with normal impulses (unless there is also sinus node dysfunction or another disorder present). The problem arises when t ...
Effects on Heart Rate and Cardiac Output on Model Heart When
... This represented the plaque buildup in a living heart because the amount of blood flow was restricted. The third experiment represented valve disease and here the clamp was placed on the valve that would represent the mitral valve in real life. Because of the equipment used, the data that was collec ...
... This represented the plaque buildup in a living heart because the amount of blood flow was restricted. The third experiment represented valve disease and here the clamp was placed on the valve that would represent the mitral valve in real life. Because of the equipment used, the data that was collec ...
A / PROF JULIE MCMULLEN CARDIAC HYPERTROPHY CELL SIGNALLING & METABOLISM
... USA, Japan Keywords Cardiac hypertrophy Heart failure Atrial fibrillation Signalling Bio-resources Genetic mouse models Adeno-associated virus ...
... USA, Japan Keywords Cardiac hypertrophy Heart failure Atrial fibrillation Signalling Bio-resources Genetic mouse models Adeno-associated virus ...
Chapter 20
... benefit of ACE inhibitors in the treatment of heart failure with decreased left ventricular function? a. ACE inhibitors block catecholamines and decrease blood pressure. b. ACE inhibitors block the renin–angiotensin system. c. ACE inhibitors block the effect of prostaglandins. d. ACE inhibitors bloc ...
... benefit of ACE inhibitors in the treatment of heart failure with decreased left ventricular function? a. ACE inhibitors block catecholamines and decrease blood pressure. b. ACE inhibitors block the renin–angiotensin system. c. ACE inhibitors block the effect of prostaglandins. d. ACE inhibitors bloc ...
The Heart
... The heart is situated between the lungs and behind the sternum. About 2/3 of it lies to the left of the body’s midline. The heart is the size of a clenched fist. Structure of the Heart Pericardium = Outer double layered membrane of the heart – it reduces friction to maintain the hearts shape. Myocar ...
... The heart is situated between the lungs and behind the sternum. About 2/3 of it lies to the left of the body’s midline. The heart is the size of a clenched fist. Structure of the Heart Pericardium = Outer double layered membrane of the heart – it reduces friction to maintain the hearts shape. Myocar ...
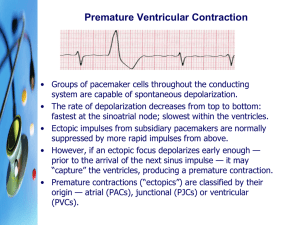
Premature Ventricular Contraction
... • Groups of pacemaker cells throughout the conducting system are capable of spontaneous depolarization. • The rate of depolarization decreases from top to bottom: fastest at the sinoatrial node; slowest within the ventricles. • Ectopic impulses from subsidiary pacemakers are normally suppressed by m ...
... • Groups of pacemaker cells throughout the conducting system are capable of spontaneous depolarization. • The rate of depolarization decreases from top to bottom: fastest at the sinoatrial node; slowest within the ventricles. • Ectopic impulses from subsidiary pacemakers are normally suppressed by m ...
EKG KEY - Belle Vernon Area
... Heart rhythm disorder (arrhythmia) in which the ventricles beat too fast. ...
... Heart rhythm disorder (arrhythmia) in which the ventricles beat too fast. ...
PHYSICAL FITNESS AND CARDIOVASCULAR ENDURANCE
... TARGET HEART RATE • Exercise within your target heart rate to get maximum benefits of exercise • Maintain range for at least 15-30 continuous minutes • Maximum heart rate = 220 – age – Fastest your heart can beat without collapse ...
... TARGET HEART RATE • Exercise within your target heart rate to get maximum benefits of exercise • Maintain range for at least 15-30 continuous minutes • Maximum heart rate = 220 – age – Fastest your heart can beat without collapse ...
Case
... appropriate initial recommendation at this time? A. Obtain an echocardiogram to evaluate for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy B. Perform cardiac MRI to evaluate for arrhythmogenic right ventricular dyplasia C. Transfer patient to a telemetry unit to evaluate for supraventricular arrythmias D. Perform til ...
... appropriate initial recommendation at this time? A. Obtain an echocardiogram to evaluate for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy B. Perform cardiac MRI to evaluate for arrhythmogenic right ventricular dyplasia C. Transfer patient to a telemetry unit to evaluate for supraventricular arrythmias D. Perform til ...
Cardiology
... appropriate initial recommendation at this time? A. Obtain an echocardiogram to evaluate for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy B. Perform cardiac MRI to evaluate for arrhythmogenic right ventricular dyplasia C. Transfer patient to a telemetry unit to evaluate for supraventricular arrythmias D. Perform til ...
... appropriate initial recommendation at this time? A. Obtain an echocardiogram to evaluate for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy B. Perform cardiac MRI to evaluate for arrhythmogenic right ventricular dyplasia C. Transfer patient to a telemetry unit to evaluate for supraventricular arrythmias D. Perform til ...
Heart Failure Devices: Staying Connected
... • ICDs prevent premature death from dangerous heart rhythms • ICD will not make you feel better • Important to continue heart medications and lifestyle recommendations • Important to keep follow-up with you heart failure and device provider ...
... • ICDs prevent premature death from dangerous heart rhythms • ICD will not make you feel better • Important to continue heart medications and lifestyle recommendations • Important to keep follow-up with you heart failure and device provider ...
Anesthetic Considerations in Patient with Wolff
... The goal of anesthetic management in these patients include: avoidance of sympathetic stimulation such as pain, anxiety, stress response to intubation and hypovolemia. Regional anesthesia is preferred technique over general anesthesia to avoid poly pharmacy and sympathetic stimulation during intubat ...
... The goal of anesthetic management in these patients include: avoidance of sympathetic stimulation such as pain, anxiety, stress response to intubation and hypovolemia. Regional anesthesia is preferred technique over general anesthesia to avoid poly pharmacy and sympathetic stimulation during intubat ...
heart - eSSUIR
... • This brings the cell to threshold in usually slightly less than a second • Rate of depolarization determines the rate of cardiac contraction • After AP - potassium conductance drops which ultimately activates sodium and calcium channels • Cycle completed by the Hodgkin cycle • High impedance cells ...
... • This brings the cell to threshold in usually slightly less than a second • Rate of depolarization determines the rate of cardiac contraction • After AP - potassium conductance drops which ultimately activates sodium and calcium channels • Cycle completed by the Hodgkin cycle • High impedance cells ...
Chapter 37
... Describe the structures of the four-chambered heart. Differentiate between the pulmonary and systemic circulation paths. Trace the path of blood through both circulatory paths. Discuss specializations and advantages of this heart design. Describe the structure and function of the various b ...
... Describe the structures of the four-chambered heart. Differentiate between the pulmonary and systemic circulation paths. Trace the path of blood through both circulatory paths. Discuss specializations and advantages of this heart design. Describe the structure and function of the various b ...
Heart
... Small "ear-shaped" pouches projecting from the upper anterior portion of each atrium of the heart, increasing slightly the atrial volume http://faculty.ucc.edu/biology-potter/Fetal_Blood_Vessels ...
... Small "ear-shaped" pouches projecting from the upper anterior portion of each atrium of the heart, increasing slightly the atrial volume http://faculty.ucc.edu/biology-potter/Fetal_Blood_Vessels ...
Cardiac Arrhythmias and Their Electrocardiographic Interpretation
... cardiac arrest. This results from cessation of all electrical control signals in the heart. That is, no spontaneous rhythm remains. Cardiac arrest may occur during deep anesthesia, when many patients develop severe hypoxia because of inadequate respiration. The hypoxia prevents the muscle fibers and ...
... cardiac arrest. This results from cessation of all electrical control signals in the heart. That is, no spontaneous rhythm remains. Cardiac arrest may occur during deep anesthesia, when many patients develop severe hypoxia because of inadequate respiration. The hypoxia prevents the muscle fibers and ...
Arrhythmias 101
... pattern. Usually a 2:1 conduction pattern; if it is 3:1 or higher, there is AV node damage • Treatment is to slow AV node conduction with amiodarone, propafenone or sotalol • DC cardiovert if <48 hours or unstable ...
... pattern. Usually a 2:1 conduction pattern; if it is 3:1 or higher, there is AV node damage • Treatment is to slow AV node conduction with amiodarone, propafenone or sotalol • DC cardiovert if <48 hours or unstable ...
Week 25 Feb. 13-17 - Tipp City Schools
... O – TSW Describe the location of the heart in the body, and identify its major anatomical areas on an appropriate model or diagram. Trace the pathway of blood through the heart. Compare the pulmonary and systemic circuits. Explain the operation of the heart valves, name the functional blood supply o ...
... O – TSW Describe the location of the heart in the body, and identify its major anatomical areas on an appropriate model or diagram. Trace the pathway of blood through the heart. Compare the pulmonary and systemic circuits. Explain the operation of the heart valves, name the functional blood supply o ...
Biol 155 Human Physiology - University of British Columbia
... as valves close at beginning of ventricular systole Results from closure of aortic and pulmonary semilunar valves at beginning of ventricular diastole, lasts longer ...
... as valves close at beginning of ventricular systole Results from closure of aortic and pulmonary semilunar valves at beginning of ventricular diastole, lasts longer ...
Atrial Fibrillation in Dogs
... several electrical wires to the dog in strategic locations. The electrical impulses of the heart are then recorded and examined. Atrial fibrillation has a very unique rhythmic pattern on an ECG. How is atrial fibrillation in dogs treated? The treatment of atrial fibrillation involves re-establishing ...
... several electrical wires to the dog in strategic locations. The electrical impulses of the heart are then recorded and examined. Atrial fibrillation has a very unique rhythmic pattern on an ECG. How is atrial fibrillation in dogs treated? The treatment of atrial fibrillation involves re-establishing ...
Chapter # 5 Irregular Heartbeats
... minute this is known as bradycardia. This may occur if you have a heart block. ...
... minute this is known as bradycardia. This may occur if you have a heart block. ...