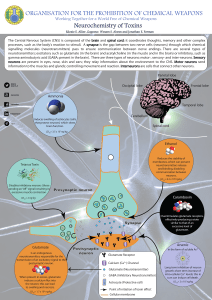
Working Together for a World Free of Chemical Weapons
... Edoxie E. Allier-Gagneur, Wesam S. Alwan and Jonathan E. Forman ...
... Edoxie E. Allier-Gagneur, Wesam S. Alwan and Jonathan E. Forman ...
Glossary of Stem Cell Terms
... marrow are also derived from mesenchymal stem cells. Subculturing The process of growing and replating cells in tissue culture for many months. Surface markers Surface proteins that are unique to certain cell types and that can be visualized using antibodies or other detection methods. Teratoma A tu ...
... marrow are also derived from mesenchymal stem cells. Subculturing The process of growing and replating cells in tissue culture for many months. Surface markers Surface proteins that are unique to certain cell types and that can be visualized using antibodies or other detection methods. Teratoma A tu ...
Instructor`s Answer Key
... producing a graded depolarization that can lead to action potentials. Information from olfactory receptors is transmitted directly to the cerebral cortex instead of being relayed through the thalamus. 5. As the head accelerates in one direction, inertia causes structures in the vestibular apparatus ...
... producing a graded depolarization that can lead to action potentials. Information from olfactory receptors is transmitted directly to the cerebral cortex instead of being relayed through the thalamus. 5. As the head accelerates in one direction, inertia causes structures in the vestibular apparatus ...
NS Outline
... 4. Neuroglia: (nerve glue) support cells in CNS provide support, protection & access to nutrients, & other valuable services for the NS. {nonexcitable} a. Astrocytes: “nurse cells” made up of neuroglia cells that nurish & protect neurons. Star shaped cells in CNS. i. Most abundant neural cells. Form ...
... 4. Neuroglia: (nerve glue) support cells in CNS provide support, protection & access to nutrients, & other valuable services for the NS. {nonexcitable} a. Astrocytes: “nurse cells” made up of neuroglia cells that nurish & protect neurons. Star shaped cells in CNS. i. Most abundant neural cells. Form ...
FUN FACTS ABOUT YOUR BRAIN - the human Central Nervous
... that collects information from other cells Dendritic spine: Small protrusions on dendrites phat increase surface area Nucleus: Central structure containing the chromosome and genes Nuclear membrane: Membrane surrounding the nucleus ...
... that collects information from other cells Dendritic spine: Small protrusions on dendrites phat increase surface area Nucleus: Central structure containing the chromosome and genes Nuclear membrane: Membrane surrounding the nucleus ...
FUN FACTS ABOUT YOUR BRAIN - the human Central Nervous
... that collects information from other cells Dendritic spine: Small protrusions on dendrites phat increase surface area Nucleus: Central structure containing the chromosome and genes Nuclear membrane: Membrane surrounding the nucleus ...
... that collects information from other cells Dendritic spine: Small protrusions on dendrites phat increase surface area Nucleus: Central structure containing the chromosome and genes Nuclear membrane: Membrane surrounding the nucleus ...
the neural crest cells
... Each of the three germ layers gives rise to specific tissues and organs: • Ectoderm forms the outer layer. Ectoderm forms skin, hair, sweat glands, epithelium, brain and nervous system. • Endoderm forms the inner layer. The endoderm forms digestive, respiratory systems, liver, pancreas, all bladder ...
... Each of the three germ layers gives rise to specific tissues and organs: • Ectoderm forms the outer layer. Ectoderm forms skin, hair, sweat glands, epithelium, brain and nervous system. • Endoderm forms the inner layer. The endoderm forms digestive, respiratory systems, liver, pancreas, all bladder ...
Nervous System Exam.tst
... 3) The term central nervous system refers to the: A) brain and cranial nerves B) spinal cord and spinal nerves C) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves D) brain and spinal cord E) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems ...
... 3) The term central nervous system refers to the: A) brain and cranial nerves B) spinal cord and spinal nerves C) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves D) brain and spinal cord E) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems ...
Chapter 15 Marieb
... o Bipolar neurons, they have hairlike extensions into the nuclei called OLFACTORY CILIA. They are non-motile! o Axons converge to form filaments of olfactory nerve (CNI) o They are able to generate action potentials o They are able to regenerate (this is a unique feature!) o SUPPORTING CELLS o Colum ...
... o Bipolar neurons, they have hairlike extensions into the nuclei called OLFACTORY CILIA. They are non-motile! o Axons converge to form filaments of olfactory nerve (CNI) o They are able to generate action potentials o They are able to regenerate (this is a unique feature!) o SUPPORTING CELLS o Colum ...
Nervous tissues (NS)
... acquired their myelin from the activities of oligodendrocytes rather than from Sch. cells). The myelin that surrounds the fibers of tracts gives the tracts a whitish color (they are recognized as white matter of the CNS). Cell bodies and dendrites lack myelin and these areas are recognized as gray m ...
... acquired their myelin from the activities of oligodendrocytes rather than from Sch. cells). The myelin that surrounds the fibers of tracts gives the tracts a whitish color (they are recognized as white matter of the CNS). Cell bodies and dendrites lack myelin and these areas are recognized as gray m ...
Preception of stimuli - IB
... The head of the photoreceptor cell contains the light sensitive pigments The Bipolar cell (named after its 2 processes at either side of the cell body) responds by changing rate of neurotransmitter released to the Ganglion cell The ganglion cell generates the impulse which will travel along the axon ...
... The head of the photoreceptor cell contains the light sensitive pigments The Bipolar cell (named after its 2 processes at either side of the cell body) responds by changing rate of neurotransmitter released to the Ganglion cell The ganglion cell generates the impulse which will travel along the axon ...
Answers
... Return to “BRAIN BASICS,” scroll down and click on “Compare the Brains of 9 Species.” Take the test to see how many brains you can identify. 1. How many did you answer correctly? _____________ 2. Which animal has the smallest brain of those pictured? ___LEAST WEASEL___________ 3. Which animal has th ...
... Return to “BRAIN BASICS,” scroll down and click on “Compare the Brains of 9 Species.” Take the test to see how many brains you can identify. 1. How many did you answer correctly? _____________ 2. Which animal has the smallest brain of those pictured? ___LEAST WEASEL___________ 3. Which animal has th ...
Nervous tissue is composed of two types of cells, neurons and glial
... Nervous tissue is composed of two types of cells, neurons and glial cells. Neurons are the primary type of cell that most anyone associates with the nervous system. They are responsible for the computation and communication that the nervous system provides. They are electrically active and release c ...
... Nervous tissue is composed of two types of cells, neurons and glial cells. Neurons are the primary type of cell that most anyone associates with the nervous system. They are responsible for the computation and communication that the nervous system provides. They are electrically active and release c ...
The Nervous System
... But when you sniff, air swirls up into the top of the cavity. Here is a small patch of about 10 million specialized olfactory (smelling) cells. They have long microhairs, or cilia, sticking out from them. ...
... But when you sniff, air swirls up into the top of the cavity. Here is a small patch of about 10 million specialized olfactory (smelling) cells. They have long microhairs, or cilia, sticking out from them. ...
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 7
... 10. A self-propagating wave of electrical negativity that travels along the surface of the neuron membrane is called a/an ___action potential_______. 11. Indentations between the Schwann cells/myelin sheaths are called the __Nodes_ of _Ranvier__. 12. Nerve cells are also known as ______neurons_____. ...
... 10. A self-propagating wave of electrical negativity that travels along the surface of the neuron membrane is called a/an ___action potential_______. 11. Indentations between the Schwann cells/myelin sheaths are called the __Nodes_ of _Ranvier__. 12. Nerve cells are also known as ______neurons_____. ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 3.1 Typical morphology of projection
... FIGURE 3.12 Radial glia perform support and guidance functions for migrating neurons. In early development, radial glia span the thickness of the expanding brain parenchyma. (Inset) Defined layers of the neural tube from the ventricular to the outer surface: VZ, ventricular zone; IZ, intermediate zo ...
... FIGURE 3.12 Radial glia perform support and guidance functions for migrating neurons. In early development, radial glia span the thickness of the expanding brain parenchyma. (Inset) Defined layers of the neural tube from the ventricular to the outer surface: VZ, ventricular zone; IZ, intermediate zo ...
PSY 437 Sensation and Perception Knapp Study Guide 11 Primary
... 12. Ok, the following concept will be important repeatedly throughout the semester. What is selective adaptation? 13. What happens to a person’s sensitivity for a particular feature that has been selectively adaptive? 14. What is neural plasticity? 15. What can selective rearing teach us about featu ...
... 12. Ok, the following concept will be important repeatedly throughout the semester. What is selective adaptation? 13. What happens to a person’s sensitivity for a particular feature that has been selectively adaptive? 14. What is neural plasticity? 15. What can selective rearing teach us about featu ...
doi:10
... the adult SGZ, GCL and hilus ( Fig. 4a–d). The average fraction of BrdU-labeled cells that were also calbindin-positive in the granule cell layer was 7.9 2.2% among the BrdUtreated patients. The dentate gyrus from all individuals contained a fraction of BrdU-positive cells that were also GFAP-positi ...
... the adult SGZ, GCL and hilus ( Fig. 4a–d). The average fraction of BrdU-labeled cells that were also calbindin-positive in the granule cell layer was 7.9 2.2% among the BrdUtreated patients. The dentate gyrus from all individuals contained a fraction of BrdU-positive cells that were also GFAP-positi ...
Application Six - Sheila Tooker Impey
... neurons are no longer communicating with the motor neuron. In simpler terms, the phone works but no one is calling anymore. The patient is an adult. Adult mammals no longer produce the chemical and molecular conditions that stimulate and guide neural growth (Garrett, 2011). Although axons do not reg ...
... neurons are no longer communicating with the motor neuron. In simpler terms, the phone works but no one is calling anymore. The patient is an adult. Adult mammals no longer produce the chemical and molecular conditions that stimulate and guide neural growth (Garrett, 2011). Although axons do not reg ...
Exam 5 Objectives Bio241
... 7. Describe the events at a synapse during neurotransmission including how a neurotransmitter is released from the presynaptic cell (calcium triggers exocytosis), what determines the effect that a neurotransmitter will have on the postsynaptic cell, and how the signal is terminated. What is the mech ...
... 7. Describe the events at a synapse during neurotransmission including how a neurotransmitter is released from the presynaptic cell (calcium triggers exocytosis), what determines the effect that a neurotransmitter will have on the postsynaptic cell, and how the signal is terminated. What is the mech ...
Subventricular zone

The subventricular zone (SVZ) is a paired brain structure situated throughout the lateral walls of the lateral ventricles. It is composed of four distinct layers of variable thickness and cell density, as well as cellular composition. Along with the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus, the SVZ is one of two places where neurogenesis has been found to occur in the adult mammalian brain.