Textbook PowerPoint
... Hearing begins when sound waves strike the eardrum and cause it to vibrate. This vibration, in turn, makes three bones in the middle ear—the hammer, the anvil, and the stirrup—vibrate in sequence ...
... Hearing begins when sound waves strike the eardrum and cause it to vibrate. This vibration, in turn, makes three bones in the middle ear—the hammer, the anvil, and the stirrup—vibrate in sequence ...
A1985AUW1100002
... thought that, memory aside, the hippocampus offered several advantages. It has a cellular architecture that is remarkably conserved throughout mammals, and the main cetts, catted the pyramidal cells, are clustered in a discrete layer, an easy target for microelectrodes. These cells send their axons ...
... thought that, memory aside, the hippocampus offered several advantages. It has a cellular architecture that is remarkably conserved throughout mammals, and the main cetts, catted the pyramidal cells, are clustered in a discrete layer, an easy target for microelectrodes. These cells send their axons ...
The human brain is a 3 pound mass of fatty tissue that controls all
... excitable output fiber, the axon. Most axons also give rise to many smaller branches before ending at nerve terminals. Synapses, from the Greek word meaning “to clasp together,” are the contact points where one neuron communicates with another. Other structures, dendrites, Greek for “tree branches,” ...
... excitable output fiber, the axon. Most axons also give rise to many smaller branches before ending at nerve terminals. Synapses, from the Greek word meaning “to clasp together,” are the contact points where one neuron communicates with another. Other structures, dendrites, Greek for “tree branches,” ...
A Compressing Auto-encoder as a Developmental Model of Grid Cells
... Although the mechanisms through which these multiple spatially scaled modules emerge are still unknown, existing neural models attribute this modular behaviour to odometry such that the change of the triangular tessellating grid cell ring is in uenced by the animal's velocity and direction inputs. ...
... Although the mechanisms through which these multiple spatially scaled modules emerge are still unknown, existing neural models attribute this modular behaviour to odometry such that the change of the triangular tessellating grid cell ring is in uenced by the animal's velocity and direction inputs. ...
Neocortex Cell Types
... There may be a tendency for cells in the infragranular layers to send local axonal collaterals to the supragranular layers, and conversely; but some collaterals also occur in the same layers as the cell bodies of their origin. These collaterals generally ramify in the immediate horizontal vicinity o ...
... There may be a tendency for cells in the infragranular layers to send local axonal collaterals to the supragranular layers, and conversely; but some collaterals also occur in the same layers as the cell bodies of their origin. These collaterals generally ramify in the immediate horizontal vicinity o ...
Spontaneous fluctuations in cells support chemotaxis
... environments. In the multicellular body, this process plays a central role in directing immune responses by white blood cells and the formation of nervous system tissues. For more primitive eukaryotes, such as the slime mold Dictyostelium, chemotaxis plays what is perhaps an even more fascinating ro ...
... environments. In the multicellular body, this process plays a central role in directing immune responses by white blood cells and the formation of nervous system tissues. For more primitive eukaryotes, such as the slime mold Dictyostelium, chemotaxis plays what is perhaps an even more fascinating ro ...
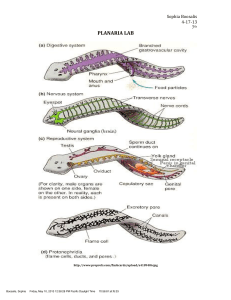
planaria lab report
... One of them is for treating people with Stargardt’s Macular Dystrophy, which is a genetic eye disorder. This disorder is most common among children in the ages 6-‐20. It’s caused by mutations in the ...
... One of them is for treating people with Stargardt’s Macular Dystrophy, which is a genetic eye disorder. This disorder is most common among children in the ages 6-‐20. It’s caused by mutations in the ...
Part 1 - Kirkwood Community College
... – Sensory afferent fibers – carry impulses from skin, skeletal muscles, and joints to the brain – Visceral afferent fibers – transmit impulses from visceral organs to the brain ...
... – Sensory afferent fibers – carry impulses from skin, skeletal muscles, and joints to the brain – Visceral afferent fibers – transmit impulses from visceral organs to the brain ...
Cell Types and Physiology in the CANS
... (These are the two primary acoustic cues for localizing sounds) ...
... (These are the two primary acoustic cues for localizing sounds) ...
Ch 3
... 18. What is the function of the neurotransmitter? Why are neurotransmitters important in psychological functioning? 19. What is plasticity and for what mental function does it play a particularly important role? ...
... 18. What is the function of the neurotransmitter? Why are neurotransmitters important in psychological functioning? 19. What is plasticity and for what mental function does it play a particularly important role? ...
Embryology • Important as a process, the way the organism
... Movement and enlargement of these. Ectoderm forms the outer part of the animal (part of the skin). Endoderm forms the inner lining of the gut tube. The mesoderm forms everything else. For example, the dermatome (the lateral or outer portion of the epimere) spans underneath the ectoderm and loses its ...
... Movement and enlargement of these. Ectoderm forms the outer part of the animal (part of the skin). Endoderm forms the inner lining of the gut tube. The mesoderm forms everything else. For example, the dermatome (the lateral or outer portion of the epimere) spans underneath the ectoderm and loses its ...
awl review q answers
... as the presence of food and water. Through detectors within the body, it is informed of such internal states as dehydration, body temperature and level of nutrient reserves. The brain monitors its own chemical environment (e.g. level of hydration of brain tissue) and is informed of the physiological ...
... as the presence of food and water. Through detectors within the body, it is informed of such internal states as dehydration, body temperature and level of nutrient reserves. The brain monitors its own chemical environment (e.g. level of hydration of brain tissue) and is informed of the physiological ...
Texts - mistergui
... Just how exercise remakes minds on a molecular level is not yet fully understood, but research suggests that exercise prompts increases in something called brain-derived neurotropic factor, or B.D.N.F., a substance that strengthens cells and axons, fortifies the connections among neurons and sparks ...
... Just how exercise remakes minds on a molecular level is not yet fully understood, but research suggests that exercise prompts increases in something called brain-derived neurotropic factor, or B.D.N.F., a substance that strengthens cells and axons, fortifies the connections among neurons and sparks ...
Stages of Brain Development
... We are born with around 100 billion neurons, and the development of the brain continues long after birth, with dendrites of some neurons in the neocortex continuing to grow well into old age[1]. Pregnancy is a time of great joy and expectation - however, our world and its potential hazards are very ...
... We are born with around 100 billion neurons, and the development of the brain continues long after birth, with dendrites of some neurons in the neocortex continuing to grow well into old age[1]. Pregnancy is a time of great joy and expectation - however, our world and its potential hazards are very ...
Nature Versus Nurture
... Remember that as you interact with others you change the structure of their nervous system and they change yours! § This also includes, yes….. removing and weakening synapses ...
... Remember that as you interact with others you change the structure of their nervous system and they change yours! § This also includes, yes….. removing and weakening synapses ...
The Endocrine System
... Common stains allow the recognition of three cell types in the pars distalis: Chromophobes(Gr. chroma, color, + phobos, fear) Chromophils (Gr. chroma + philein, to love) Two types of chromophils: Basophils according to their affinity for basic dyes Acidophils according to their affinity ...
... Common stains allow the recognition of three cell types in the pars distalis: Chromophobes(Gr. chroma, color, + phobos, fear) Chromophils (Gr. chroma + philein, to love) Two types of chromophils: Basophils according to their affinity for basic dyes Acidophils according to their affinity ...
Subventricular zone

The subventricular zone (SVZ) is a paired brain structure situated throughout the lateral walls of the lateral ventricles. It is composed of four distinct layers of variable thickness and cell density, as well as cellular composition. Along with the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus, the SVZ is one of two places where neurogenesis has been found to occur in the adult mammalian brain.