- Wiley Online Library
... A related way of PPi formation can be found in the oxidation of the phosphide mineral schreibersite (Fe,Ni)3P. This mineral is normally referred to as a component of iron meteorites (Pasek, 2008), but it is also known to occur in terrestrial basalts (Pauly, 1969; Ulff-Møller, 1985), as well as an in ...
... A related way of PPi formation can be found in the oxidation of the phosphide mineral schreibersite (Fe,Ni)3P. This mineral is normally referred to as a component of iron meteorites (Pasek, 2008), but it is also known to occur in terrestrial basalts (Pauly, 1969; Ulff-Møller, 1985), as well as an in ...
GFP - Bio-Rad
... the right conditions, these bacteria can make authentic human insulin. When allowed to multiply in gigantic vats (fermenters) these bacteria can be used to mass produce the human insulin protein. This genetically engineered insulin is purified using protein chromatography and used to treat patients ...
... the right conditions, these bacteria can make authentic human insulin. When allowed to multiply in gigantic vats (fermenters) these bacteria can be used to mass produce the human insulin protein. This genetically engineered insulin is purified using protein chromatography and used to treat patients ...
Chapter Nineteen
... reaction, or specific type of reaction. ► The enzyme papain from papaya fruit catalyzes the hydrolysis of peptide bonds in many locations. ► Thrombin is specific for catalyzing hydrolysis of a peptide bond adjacent to arginine and does so primarily in a protein essential to blood clotting. ► Catalas ...
... reaction, or specific type of reaction. ► The enzyme papain from papaya fruit catalyzes the hydrolysis of peptide bonds in many locations. ► Thrombin is specific for catalyzing hydrolysis of a peptide bond adjacent to arginine and does so primarily in a protein essential to blood clotting. ► Catalas ...
Glycolysis 2
... high affinity for substrate (Km for glucose is ~0.1mM) expressed in all tissues phosphorylates a variety of hexose sugars inhibited by the product of the reaction, glucose-6-P ...
... high affinity for substrate (Km for glucose is ~0.1mM) expressed in all tissues phosphorylates a variety of hexose sugars inhibited by the product of the reaction, glucose-6-P ...
Mutation Types - CK
... Any form of reproduction of this book in any format or medium, in whole or in sections must include the referral attribution link http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (placed in a visible location) in addition to the following terms. Except as otherwise noted, all CK-12 Content (including CK-12 Curriculum ...
... Any form of reproduction of this book in any format or medium, in whole or in sections must include the referral attribution link http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (placed in a visible location) in addition to the following terms. Except as otherwise noted, all CK-12 Content (including CK-12 Curriculum ...
Determination of the entire sequence of turtle CR1: the first open
... and Eickbush 1995). In the case of R2Bm, the R2 protein makes a specific nick in one of the DNA strands at the insertion site in the 28s rRNA gene and uses the 3’ hydroxyl group exposed by this nick to prime reverse transcription of its RNA transcript. Furthermore, the recent finding that the revers ...
... and Eickbush 1995). In the case of R2Bm, the R2 protein makes a specific nick in one of the DNA strands at the insertion site in the 28s rRNA gene and uses the 3’ hydroxyl group exposed by this nick to prime reverse transcription of its RNA transcript. Furthermore, the recent finding that the revers ...
Intelligent Icons: Integrating Lite-Weight Data Mining
... The three files in the example are ASCII text files, each of which contains approximately 16,000 base pairs of mitochondrial DNA. Here we used string edit distance as suggested in [15] to measure the distance between file names, and Euclidean distance to measure the distance between the file icons ( ...
... The three files in the example are ASCII text files, each of which contains approximately 16,000 base pairs of mitochondrial DNA. Here we used string edit distance as suggested in [15] to measure the distance between file names, and Euclidean distance to measure the distance between the file icons ( ...
Chapter 6 – Exam style questions Q1. Bk Ch6 Exam MQ1 What is
... Comparative embryology of the vertebrates shown clearly indicates similarities between the different organisms in the early stages of development. Such similarities suggest an evolutionary relationship between the organisms such that at some point in the history of their development they shared a co ...
... Comparative embryology of the vertebrates shown clearly indicates similarities between the different organisms in the early stages of development. Such similarities suggest an evolutionary relationship between the organisms such that at some point in the history of their development they shared a co ...
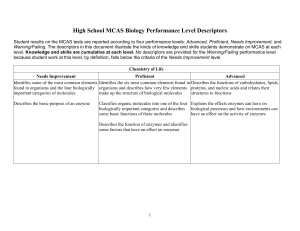
High School Biology MCAS Performance Level Descriptors
... Explains how viruses differ from cellular used in growth/repair of cells; describes how the organisms in structure, function, and purpose of meiosis is to produce sex cells with Identifies examples of mitosis and meiosis; ...
... Explains how viruses differ from cellular used in growth/repair of cells; describes how the organisms in structure, function, and purpose of meiosis is to produce sex cells with Identifies examples of mitosis and meiosis; ...
Brooker Chapter 15
... Transcription factor proteins contain regions, called domains, that have specific functions ...
... Transcription factor proteins contain regions, called domains, that have specific functions ...
enzymes
... The allosteric site • The allosteric site is not at the active site or substrate binding site, but is somewhere else on the molecule • The allosteric site is the site where small molecules bind and affect a change in the active site or the substrate binding site • The binding of this specific molecu ...
... The allosteric site • The allosteric site is not at the active site or substrate binding site, but is somewhere else on the molecule • The allosteric site is the site where small molecules bind and affect a change in the active site or the substrate binding site • The binding of this specific molecu ...
Replicators and Vehicles by Richard Dawkins he theory of natural
... selection bias equal to several or many times its rate of endogenous change" (p. 25). It is clear that we are never going to sell this kind of definition to a generation brought up on the "one gene–one protein" doctrine, which is one reason why I (Dawkins, 1978) have advocated using the word "replic ...
... selection bias equal to several or many times its rate of endogenous change" (p. 25). It is clear that we are never going to sell this kind of definition to a generation brought up on the "one gene–one protein" doctrine, which is one reason why I (Dawkins, 1978) have advocated using the word "replic ...
transcription factor binding site
... transcription factor (TF) binding sites To understand transcriptional regulation in general, we would like to analyze/predict TF binding sites in any cell type/biological condition/. . . A critical limitation of most of the standard TFBS prediction methods is that they are condition independent That ...
... transcription factor (TF) binding sites To understand transcriptional regulation in general, we would like to analyze/predict TF binding sites in any cell type/biological condition/. . . A critical limitation of most of the standard TFBS prediction methods is that they are condition independent That ...
The science of replacing mitochondrial DNA and
... vast majority of his mitochondrial DNA from the donor, will go on to do very well. How might MRT fail and what are some ideas to make MRT more successful? MRT can provide a wonderful benefit to families carrying such mutations, and the only major concern is that an individual application might fail, ...
... vast majority of his mitochondrial DNA from the donor, will go on to do very well. How might MRT fail and what are some ideas to make MRT more successful? MRT can provide a wonderful benefit to families carrying such mutations, and the only major concern is that an individual application might fail, ...
Chap. 5 "Properties of Enzymes" Reading Assignment: pp. 130
... A. Regulation of allosteric enzymes by noncovalent binding of effectors. The activity of allosteric enzymes can be controlled by reversible binding of negative effectors (inhibitors) and positive effectors (activators), which usually don't resemble the structure of the substrate, to separate regulat ...
... A. Regulation of allosteric enzymes by noncovalent binding of effectors. The activity of allosteric enzymes can be controlled by reversible binding of negative effectors (inhibitors) and positive effectors (activators), which usually don't resemble the structure of the substrate, to separate regulat ...
Genetics of Bitter I - Buffalo State College Faculty and Staff Web Server
... is termed a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP). One specific combination of the three SNPs, termed a haplotype, correlates most strongly with tasting ability. Analogous changes in other cell-surface molecules influence the activity of many drugs. For example, SNPs in serotonin transporter and rece ...
... is termed a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP). One specific combination of the three SNPs, termed a haplotype, correlates most strongly with tasting ability. Analogous changes in other cell-surface molecules influence the activity of many drugs. For example, SNPs in serotonin transporter and rece ...
The Science of Ampelography - Fred Dex, Master Sommelier
... made clear that Plavac Mali was not Zinfandel, but was most likely related. In 2001, another Croatian variety, Dobričić, was found to be related to Zinfandel, but was still not an exact link. Later that year, during one last expedition around the island coasts of Dalmatia near Split, a tiny planting ...
... made clear that Plavac Mali was not Zinfandel, but was most likely related. In 2001, another Croatian variety, Dobričić, was found to be related to Zinfandel, but was still not an exact link. Later that year, during one last expedition around the island coasts of Dalmatia near Split, a tiny planting ...
- Circle of Docs
... urea produced in the liver and excreted in the kidney hidden in blood, urine, or cell find where elevated and where sample came from any liver problem will cause the bund to decrease – since liver can not produce urea any kidney problem will cause the bund to increase – since kidney is not functioni ...
... urea produced in the liver and excreted in the kidney hidden in blood, urine, or cell find where elevated and where sample came from any liver problem will cause the bund to decrease – since liver can not produce urea any kidney problem will cause the bund to increase – since kidney is not functioni ...
Coordination of replication and transcription along a Drosophila
... a gene increased markedly with detectable mRNA expression levels. The blue and red lines represent the modeled probability and 95% confidence levels, respectively. For comparison, each sequence on the array was ordered by mRNA expression levels and sorted into bins of 200 (gray bars). The height of ...
... a gene increased markedly with detectable mRNA expression levels. The blue and red lines represent the modeled probability and 95% confidence levels, respectively. For comparison, each sequence on the array was ordered by mRNA expression levels and sorted into bins of 200 (gray bars). The height of ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.