ANTH 2301 Midterm Review Sheet Spring 2016
... 1) Imagine there is a locus with two alleles, H and h, where H is dominant and is the “hairy nose” allele. If a man with genotype HH mates with a woman with genotype hh, the proportion of offspring expected to have the “hairy nose” phenotype is… 2) The ABO blood group has three alleles (A, B, O). If ...
... 1) Imagine there is a locus with two alleles, H and h, where H is dominant and is the “hairy nose” allele. If a man with genotype HH mates with a woman with genotype hh, the proportion of offspring expected to have the “hairy nose” phenotype is… 2) The ABO blood group has three alleles (A, B, O). If ...
growth regulators
... in Britain and the U.S. during World War II. This discovery revolutionized modern agriculture. Since the synthesis of 2,4-D, a number of other synthetic auxins have become commercially available. Although these products are referred to as growth regulators or phytohormones (previously known as plant ...
... in Britain and the U.S. during World War II. This discovery revolutionized modern agriculture. Since the synthesis of 2,4-D, a number of other synthetic auxins have become commercially available. Although these products are referred to as growth regulators or phytohormones (previously known as plant ...
Origin of life - River Dell Regional School District
... – Natural selection acted on these errors to improve the function of these early ribozymes – With increased speed and accuracy of replication, these variant ribozymes reproduced, copying themselves and displacing less efficient molecules ...
... – Natural selection acted on these errors to improve the function of these early ribozymes – With increased speed and accuracy of replication, these variant ribozymes reproduced, copying themselves and displacing less efficient molecules ...
FUNCTION IN PHYSARUM POLYCEPHALUM mitochondria of
... 1 b). In addition, the central matrix between the cristae is occupied by an electron-dense rod-shaped structure (long arrows in Fig. I b, c). Fig. 2 a illustrates several b u m p y b r a n c h - s h a p e d structures, averaging a b o u t 500 600 A in diameter, and a centrally located electron-dense ...
... 1 b). In addition, the central matrix between the cristae is occupied by an electron-dense rod-shaped structure (long arrows in Fig. I b, c). Fig. 2 a illustrates several b u m p y b r a n c h - s h a p e d structures, averaging a b o u t 500 600 A in diameter, and a centrally located electron-dense ...
THE LAC OPERON
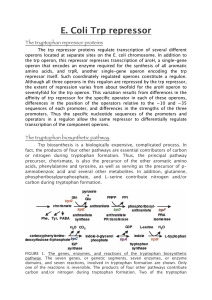
... present and this bonds to the repressor (tryptophanrepressor complex) changing its shape ( an allosteric change) and causing it to bind to the operator(active repressor). It is a repressible operon because if typtophan is not present, the gene will be on. The repressor is not the right shape to bond ...
... present and this bonds to the repressor (tryptophanrepressor complex) changing its shape ( an allosteric change) and causing it to bind to the operator(active repressor). It is a repressible operon because if typtophan is not present, the gene will be on. The repressor is not the right shape to bond ...
Analysis of the glycoside hydrolase family 8 catalytic core in
... The glycoside hydrolase family 8 (GH-8) consists of bifunctional cellulase-chitosanases many of which are produced by species of Bacillus. Chitosanolytic enzymes can be useful in producing low molecular weight chitooligosaccharides which have several applications. In addition, a bifunctional enzyme ...
... The glycoside hydrolase family 8 (GH-8) consists of bifunctional cellulase-chitosanases many of which are produced by species of Bacillus. Chitosanolytic enzymes can be useful in producing low molecular weight chitooligosaccharides which have several applications. In addition, a bifunctional enzyme ...
The tryptophan biosynthetic pathway
... trpL mRNA stalls at one of its two Trp codons. This permits the RNA antiterminator structure to form, which prevents formation of the terminator. Transcription then continues into the operon’s structural genes. An attenuator site, in effect, is a DNA sequence where a choice is made by RNA polymerase ...
... trpL mRNA stalls at one of its two Trp codons. This permits the RNA antiterminator structure to form, which prevents formation of the terminator. Transcription then continues into the operon’s structural genes. An attenuator site, in effect, is a DNA sequence where a choice is made by RNA polymerase ...
Rate and Equilibrium
... State shows the activation energy and the rate is also the slowest. It is called rate-determining step. ...
... State shows the activation energy and the rate is also the slowest. It is called rate-determining step. ...
Milestone2
... The GC content of a genome is the percentage of nucleotides in the genome that are either guanines or cytosines. Different genomes have widely varying GC contents. For example, the genomes of the bacteria Anaeromyxobacter have a GC content of about 75%, whereas the genomes of the bacteria Buchnera h ...
... The GC content of a genome is the percentage of nucleotides in the genome that are either guanines or cytosines. Different genomes have widely varying GC contents. For example, the genomes of the bacteria Anaeromyxobacter have a GC content of about 75%, whereas the genomes of the bacteria Buchnera h ...
NMEICT PROJECT
... Vmax, and Ki. Enzyme assays can also disclose information on the substrates and inhibitors that may affect the enzyme. In order to assay an enzyme, the overall equation of the reaction should be known. An analytical technique must be on hand for determining either the loss of substrate or the format ...
... Vmax, and Ki. Enzyme assays can also disclose information on the substrates and inhibitors that may affect the enzyme. In order to assay an enzyme, the overall equation of the reaction should be known. An analytical technique must be on hand for determining either the loss of substrate or the format ...
Slide 1
... from a limited set of small molecules The four classes of biological molecules contain very large molecules. – They are often called macromolecules because of their large size. – They are also called polymers because they are made from identical building blocks strung together. – The building bloc ...
... from a limited set of small molecules The four classes of biological molecules contain very large molecules. – They are often called macromolecules because of their large size. – They are also called polymers because they are made from identical building blocks strung together. – The building bloc ...
p19 siRNA Binding Protein | NEB
... p19 siRNA Binding Protein contains no detectable DNases, RNases and phosphatases. The purified protein contains no detectable DNA or RNA as determined by ethidium bromide staining of an agarose gel. Quality Control Assays The following Quality Control Tests are performed on each new lot and meet the ...
... p19 siRNA Binding Protein contains no detectable DNases, RNases and phosphatases. The purified protein contains no detectable DNA or RNA as determined by ethidium bromide staining of an agarose gel. Quality Control Assays The following Quality Control Tests are performed on each new lot and meet the ...
Supplementary Methods Tables
... coverage) whole genome sequencing (Illumina HiSeq 2000) to detect chromosome and subchromosomal copy number changes and translocations, microarray (Agilent) and RNA-Seq (Illumina) for mRNA expression profiling, Illumina Infinium HumanMethylation27 arrays to profile DNA methylation at gene promoters, ...
... coverage) whole genome sequencing (Illumina HiSeq 2000) to detect chromosome and subchromosomal copy number changes and translocations, microarray (Agilent) and RNA-Seq (Illumina) for mRNA expression profiling, Illumina Infinium HumanMethylation27 arrays to profile DNA methylation at gene promoters, ...
Lehninger-Principles-of-Biochemistry-Nelson-5th-Edition-1
... The free-energy change for the formation of a protein from the individual amino acids is positive and is thus an endergonic reaction. How, then, do cells accomplish this process? Ans: The endergonic (thermodynamically unfavorable) reaction is coupled to an exergonic (thermodynamically favorable) rea ...
... The free-energy change for the formation of a protein from the individual amino acids is positive and is thus an endergonic reaction. How, then, do cells accomplish this process? Ans: The endergonic (thermodynamically unfavorable) reaction is coupled to an exergonic (thermodynamically favorable) rea ...
are mRNA
... 3) Redundant, redundancy of genetic code: more than one code specify one amino acid. (61 codon, 40 tRNA, 20 amino acid). 4) Reads as a series of nucleotide. - No comma between the codon - The start codon determines the ...
... 3) Redundant, redundancy of genetic code: more than one code specify one amino acid. (61 codon, 40 tRNA, 20 amino acid). 4) Reads as a series of nucleotide. - No comma between the codon - The start codon determines the ...
PDF File
... mapping predicted a secondary structure that was quite similar overall to the model derived from phylogeny. The color coding in Figure 2 corresponds to the complementary helical elements now known to be formed, and the performance of each of the models in predicting helices is summarized in Table 1. ...
... mapping predicted a secondary structure that was quite similar overall to the model derived from phylogeny. The color coding in Figure 2 corresponds to the complementary helical elements now known to be formed, and the performance of each of the models in predicting helices is summarized in Table 1. ...
Splicing regulation: a structural biology perspective
... Three chapters have been dedicated to this nuclear macromolecular machinery in human, yeasts and plants. Here, we focus on the large number of splicing factors involved in the regulation of splicing (also referred as alternative-splicing). Recent estimations indicate that nearly 80 to 95% of human m ...
... Three chapters have been dedicated to this nuclear macromolecular machinery in human, yeasts and plants. Here, we focus on the large number of splicing factors involved in the regulation of splicing (also referred as alternative-splicing). Recent estimations indicate that nearly 80 to 95% of human m ...
HILL12_Lecture_16
... oxidized, a (-S-S-) disulfide linkage can form. 4. Dispersion forces: These are attractive forces between two nonpolar side chains. ...
... oxidized, a (-S-S-) disulfide linkage can form. 4. Dispersion forces: These are attractive forces between two nonpolar side chains. ...
Initiation of transcription by Pol II Separate basal and activated
... Activated transcription by Pol II enhancers are sequences 5’ to TATAA transcriptional activators bind them • have distinct DNA binding and activation domains • activation domain interacts with mediator • helps assemble initiation complex on TATAA ...
... Activated transcription by Pol II enhancers are sequences 5’ to TATAA transcriptional activators bind them • have distinct DNA binding and activation domains • activation domain interacts with mediator • helps assemble initiation complex on TATAA ...
Chapter 5 - Hale AP Biology
... • Some microbes use enzymes to digest cellulose • Many herbivores, from cows to termites, have symbiotic relationships with these microbes ...
... • Some microbes use enzymes to digest cellulose • Many herbivores, from cows to termites, have symbiotic relationships with these microbes ...
Diagnostic protocol for
... blotted dry as before. 10 µl of 0.1 mmol l-1 phosphate-buffered glycerine (pH 7.6) with an anti-fadding reagent, is added to each window and covered with a coverslip. The slides are examined with a fluorescence microscope under immersion oil at x 600 or x 1000. The FITC will fluoresce bright green u ...
... blotted dry as before. 10 µl of 0.1 mmol l-1 phosphate-buffered glycerine (pH 7.6) with an anti-fadding reagent, is added to each window and covered with a coverslip. The slides are examined with a fluorescence microscope under immersion oil at x 600 or x 1000. The FITC will fluoresce bright green u ...
Use of molecular markers and major genes in the genetic
... technique allowed the identification of only two alleles per locus and is slow to be used with large genome size in mammals, where about 3 x109 individual nucleotides are present in the total DNA content (Albert et al., 1994; Brash, 1994; Lewin, 1994; Wilmut et al., 1992). The reduced variability ob ...
... technique allowed the identification of only two alleles per locus and is slow to be used with large genome size in mammals, where about 3 x109 individual nucleotides are present in the total DNA content (Albert et al., 1994; Brash, 1994; Lewin, 1994; Wilmut et al., 1992). The reduced variability ob ...
Isolation and characterization of (S)
... plants are derived from the amino acids tyrosine, tryptophan and phenylalanine. They are often basic and contain nitrogen in a heterocyclic ring. The classification of alkaloids is based on their carbon-nitrogen skeletons; common alkaloid ring structures include the pyridines, pyrroles, indoles, pyr ...
... plants are derived from the amino acids tyrosine, tryptophan and phenylalanine. They are often basic and contain nitrogen in a heterocyclic ring. The classification of alkaloids is based on their carbon-nitrogen skeletons; common alkaloid ring structures include the pyridines, pyrroles, indoles, pyr ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.