PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... i. Gene = a segment of DNA coding for a RNA segment. These RNA segments will be used to produce a polypeptide (structural or enzymatic protein) ii. Each strand of DNA can contain thousands of genes iii. Each gene has a beginning and an end b. DNA is used as the blueprint to direct the production of ...
... i. Gene = a segment of DNA coding for a RNA segment. These RNA segments will be used to produce a polypeptide (structural or enzymatic protein) ii. Each strand of DNA can contain thousands of genes iii. Each gene has a beginning and an end b. DNA is used as the blueprint to direct the production of ...
Biology 218 Microbial Metabolism and Genetics Chapter Six
... Prokaryotic Genetics Review Vocabulary Phenotype: physical traits Genotype: genetic make-up Mutations: replication errors, single base pairs Recombination: rearranging or acquiring genes ...
... Prokaryotic Genetics Review Vocabulary Phenotype: physical traits Genotype: genetic make-up Mutations: replication errors, single base pairs Recombination: rearranging or acquiring genes ...
DNA Lab Techniques
... • Restriction enzymes cut DNA at specific sequences • Useful to divide DNA into manageable fragments ...
... • Restriction enzymes cut DNA at specific sequences • Useful to divide DNA into manageable fragments ...
Chapter 18 – Gene Mutations and DNA Repair
... • DNA strand is separated; singlestrand binding proteins stabilize • Large section is removed • DNA polymerase fills in; DNA ligase seals nicks ...
... • DNA strand is separated; singlestrand binding proteins stabilize • Large section is removed • DNA polymerase fills in; DNA ligase seals nicks ...
Chapter 18 – Gene Mutations and DNA Repair
... • DNA strand is separated; single-strand binding proteins stabilize • Large section is removed • DNA polymerase fills in; DNA ligase seals nicks ...
... • DNA strand is separated; single-strand binding proteins stabilize • Large section is removed • DNA polymerase fills in; DNA ligase seals nicks ...
Genetics
... 2.3 DNA • DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid • DNA is a double helix consisting of paired nucleotides • The order of nucleotides determines the sequence of amino acids in a protein • DNA is self replicating using a semiconservative process ...
... 2.3 DNA • DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid • DNA is a double helix consisting of paired nucleotides • The order of nucleotides determines the sequence of amino acids in a protein • DNA is self replicating using a semiconservative process ...
Investigating the effects of different types of mutations
... The sequence of DNA that encodes for a protein is called a gene. Genes encode for all proteinsfrom the enzymes needed in respiration to the tough keratin protein that makes up your fingernails. The first step in the production of a protein is creating a messenger that can pass from the DNA in the nu ...
... The sequence of DNA that encodes for a protein is called a gene. Genes encode for all proteinsfrom the enzymes needed in respiration to the tough keratin protein that makes up your fingernails. The first step in the production of a protein is creating a messenger that can pass from the DNA in the nu ...
Prostate cancer stem cells Ongoing Projects 3
... sequences. This can lead to genes being gained or lost or being under the control of the wrong elements. Increased expression of oncogenes or decreseed expression of tumour suppressor genes can lead to cancer. We use a method called FISH (fluorescent in situ hybridisa-on) ...
... sequences. This can lead to genes being gained or lost or being under the control of the wrong elements. Increased expression of oncogenes or decreseed expression of tumour suppressor genes can lead to cancer. We use a method called FISH (fluorescent in situ hybridisa-on) ...
Document
... DNA Microarrays Data from multiple microarray experiment can be grouped and analyzed to identify genes that are coordinately regulated. E.g. Part of the transcriptional pattern of genes in a fibroblast responding to serum stimulation: ...
... DNA Microarrays Data from multiple microarray experiment can be grouped and analyzed to identify genes that are coordinately regulated. E.g. Part of the transcriptional pattern of genes in a fibroblast responding to serum stimulation: ...
HEREDITY: INHERITANCE and TRENDS Unit Cover Page Topic
... particular segment of the DNA. The instructions for forming species characteristics are carried in DNA. All cells in an organism have the same genetic content, but the genes expressed by the cell may be regulated in different ways. Not all DNA codes for a protein; some segments of DNA are involved i ...
... particular segment of the DNA. The instructions for forming species characteristics are carried in DNA. All cells in an organism have the same genetic content, but the genes expressed by the cell may be regulated in different ways. Not all DNA codes for a protein; some segments of DNA are involved i ...
Problem 3: Why do pre-mRNAs get smaller during RNA processing?
... Promoters for eukaryotic mRNA genes: A. are more complex than prokaryotic promoters B. can require binding of multiple transcription factors to form a transcription complex C. have specific DNA sequences such as the "TATA" box that are recognized by proteins D. are the stretches of DNA to which RNA ...
... Promoters for eukaryotic mRNA genes: A. are more complex than prokaryotic promoters B. can require binding of multiple transcription factors to form a transcription complex C. have specific DNA sequences such as the "TATA" box that are recognized by proteins D. are the stretches of DNA to which RNA ...
Protein Synthesis and Mutations Review Explain the differences and
... needed) to create the final mRNA strand that is then taken out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm where the small ribosomal subunit will bind with it. The small ribosomal subunit (with the mRNA strand) will then bind with the large ribosomal subunit. The ribosome will then scan the mRNA strand lookin ...
... needed) to create the final mRNA strand that is then taken out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm where the small ribosomal subunit will bind with it. The small ribosomal subunit (with the mRNA strand) will then bind with the large ribosomal subunit. The ribosome will then scan the mRNA strand lookin ...
Slajd 1
... Applications of the PCR 1 – Detection of the polymorphisms 2 – Diagnostics of hereditary diseases 3 – Sequencing (detection of mutations, paternity tests) 4 – Detection of viruses, parasites and bacteria 5 – Detection of GMOs 6 – In situ PCR (detection of given sequences in given subcellular localiz ...
... Applications of the PCR 1 – Detection of the polymorphisms 2 – Diagnostics of hereditary diseases 3 – Sequencing (detection of mutations, paternity tests) 4 – Detection of viruses, parasites and bacteria 5 – Detection of GMOs 6 – In situ PCR (detection of given sequences in given subcellular localiz ...
Restriction Enzymes - Solon City Schools
... Once the gene is isolated, how do we join it with the organism’s DNA? 1. Cut the organism’s DNA with the same restriction enzyme…why? ...
... Once the gene is isolated, how do we join it with the organism’s DNA? 1. Cut the organism’s DNA with the same restriction enzyme…why? ...
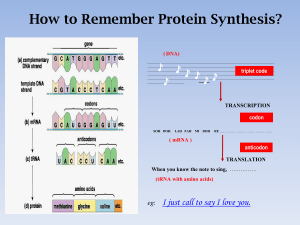
How to remember Protein Synthesis
... ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ ...
... ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ ...
Chapter 13 – Genetic Engineering
... in meiosis have been used to create plants that have more than two sets of chromosomes (2n). These are called polyploid plants. – Ex – bananas, citrus fruit, strawberries, many ornamental flowers Diploid corn Tetraploid corn ...
... in meiosis have been used to create plants that have more than two sets of chromosomes (2n). These are called polyploid plants. – Ex – bananas, citrus fruit, strawberries, many ornamental flowers Diploid corn Tetraploid corn ...
Chapter 13 – Genetic Engineering
... in meiosis have been used to create plants that have more than two sets of chromosomes (2n). These are called polyploid plants. – Ex – bananas, citrus fruit, strawberries, many ornamental flowers Diploid corn Tetraploid corn ...
... in meiosis have been used to create plants that have more than two sets of chromosomes (2n). These are called polyploid plants. – Ex – bananas, citrus fruit, strawberries, many ornamental flowers Diploid corn Tetraploid corn ...
Chapter 13 – Genetic Engineering
... – Also used to locate and identify one particular gene out of an individual’s genome. ...
... – Also used to locate and identify one particular gene out of an individual’s genome. ...
MBLG2x71 Course Information for mmb web site
... DNA Fingerprinting II & Plasmid Gel electrophoresis analysis of PCR products and Isolation miniprep isolation of plasmid DNA. Plasmid Analysis ...
... DNA Fingerprinting II & Plasmid Gel electrophoresis analysis of PCR products and Isolation miniprep isolation of plasmid DNA. Plasmid Analysis ...
Topic 6 – Making Recombinant DNA Recombinant DNA – fragment
... http://highered.mcgraw‐hill.com/sites/0072556781/student_view0/chapter14/animation_quiz_6.html ...
... http://highered.mcgraw‐hill.com/sites/0072556781/student_view0/chapter14/animation_quiz_6.html ...
Lab Module 8 - philipdarrenjones.com
... Figure. Transcription: from DNA to mRNA In the first of the two stages of making protein from DNA, a gene on the DNA molecule is transcribed into a complementary mRNA molecule. From RNA to Protein: Translation Like translating a book from one language into another, the codons on a strand of mRNA mus ...
... Figure. Transcription: from DNA to mRNA In the first of the two stages of making protein from DNA, a gene on the DNA molecule is transcribed into a complementary mRNA molecule. From RNA to Protein: Translation Like translating a book from one language into another, the codons on a strand of mRNA mus ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.