BIOLOGY 12 MUTATIONS FRAMESHIFT MUTATIONS
... • Missense mutations are point mutations that result in a single amino acid change within the protein. UAC – CAC – this leads to a change in shape of protein and its function. The fat cat. – The rat cat. • Nonsense mutations are point mutations that create a premature "translation stop signal" (or " ...
... • Missense mutations are point mutations that result in a single amino acid change within the protein. UAC – CAC – this leads to a change in shape of protein and its function. The fat cat. – The rat cat. • Nonsense mutations are point mutations that create a premature "translation stop signal" (or " ...
3.1 Class Notes Powerpoint
... • There are also three nucleotides on the bottom of the tRNA called an anti-codon. • Anti-codons complementary base pair with the codons on mRNA. (this is to make sure they are bringing the correct amino acidIf the anti-codon doesn’t base pair with the codon, then the wrong amino acid was brought) ...
... • There are also three nucleotides on the bottom of the tRNA called an anti-codon. • Anti-codons complementary base pair with the codons on mRNA. (this is to make sure they are bringing the correct amino acidIf the anti-codon doesn’t base pair with the codon, then the wrong amino acid was brought) ...
Is the process of manipulating genes and genomes Biotechnology
... -Is the process of manipulating organisms or their components for the purpose of making useful products ...
... -Is the process of manipulating organisms or their components for the purpose of making useful products ...
LabChip GX/GXII Automated Electrophoresis Systems
... LabChip electrophoresis is performed on a small, microfluidic chip. Prior to RNA, DNA, or protein analysis, reagents are loaded into the individual wells of the chip. These wells are connected to small plates of quartz etched with tiny microchannels about the size of a human hair. When the chip is l ...
... LabChip electrophoresis is performed on a small, microfluidic chip. Prior to RNA, DNA, or protein analysis, reagents are loaded into the individual wells of the chip. These wells are connected to small plates of quartz etched with tiny microchannels about the size of a human hair. When the chip is l ...
From DNA to Protein
... cell hair proteins. The linear polymer DNA with all the information about proteins can be easily duplicated in cell division. How does it work? To make new proteins, the living cell uses the genetic code of the macromolecule DNA, which stores all the information about the sequence of amino acids in ...
... cell hair proteins. The linear polymer DNA with all the information about proteins can be easily duplicated in cell division. How does it work? To make new proteins, the living cell uses the genetic code of the macromolecule DNA, which stores all the information about the sequence of amino acids in ...
Transformations, Cloning
... fewest errors, we should use the DNA from that colony for future steps ...
... fewest errors, we should use the DNA from that colony for future steps ...
Document
... to explore the roles, relationships, and actions of the various types of molecules that make up the cells of an organism. technologies include: Genomics, “the study of genes and their function” (Human Genome Project (HGP), 2003) Proteomics, the study of proteins. ...
... to explore the roles, relationships, and actions of the various types of molecules that make up the cells of an organism. technologies include: Genomics, “the study of genes and their function” (Human Genome Project (HGP), 2003) Proteomics, the study of proteins. ...
Activities 3
... breaking of chemical bonds • Atoms shift from one molecule to another without any change in number or identity of atoms • Reactants = original molecules • Products = molecules resulting from reaction ...
... breaking of chemical bonds • Atoms shift from one molecule to another without any change in number or identity of atoms • Reactants = original molecules • Products = molecules resulting from reaction ...
VII. Molecular Biology Techniques
... When process is complete 2 identical DNA molecules are formed. ...
... When process is complete 2 identical DNA molecules are formed. ...
Flumequine 50% Water Soluble Powder for Veterinary
... Flumequine is one of the first generation quinolones , a synthetic antibacterial agent, bactericide in action inhibit DNA - gyras lead to inhibiting the production of DNA. It is active against gram negative bacteria as E. Coli, Klebsiella and some limited activity against pseudomonas, Salmonella ...
... Flumequine is one of the first generation quinolones , a synthetic antibacterial agent, bactericide in action inhibit DNA - gyras lead to inhibiting the production of DNA. It is active against gram negative bacteria as E. Coli, Klebsiella and some limited activity against pseudomonas, Salmonella ...
3.4 A: Structure of DNA and RNA Quiz PROCTOR VERSION
... (D) A water molecule is split via hydrolysis, and the phosphate group and the deoxyribose sugar are covalently linked. Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the student may understand that a water molecule is involved in the synthesis of a polymer, but does not understand that water is a produc ...
... (D) A water molecule is split via hydrolysis, and the phosphate group and the deoxyribose sugar are covalently linked. Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the student may understand that a water molecule is involved in the synthesis of a polymer, but does not understand that water is a produc ...
biotechnology
... 2 things you need to understand better 1 thing you do not understand at all ...
... 2 things you need to understand better 1 thing you do not understand at all ...
Polymerase Chain Reaction
... disease, diabetes, and some cancers). Although such disorders are inherited, they depend on the simultaneous presence of several alleles; thus the hereditary patterns are usually more complex than those of single-gene disorders. Compare singlegene disorders. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR): A method ...
... disease, diabetes, and some cancers). Although such disorders are inherited, they depend on the simultaneous presence of several alleles; thus the hereditary patterns are usually more complex than those of single-gene disorders. Compare singlegene disorders. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR): A method ...
3.5 billion years ago.
... b. If lipids are included in the solution, they form selectively permeable membranes similar to those of cells Lab experiments cannot prove that the sequence above is how life began. They only show that such events could have taken place. Debates still go on about the beginning of life. ...
... b. If lipids are included in the solution, they form selectively permeable membranes similar to those of cells Lab experiments cannot prove that the sequence above is how life began. They only show that such events could have taken place. Debates still go on about the beginning of life. ...
DNA, RNA and Protein
... We hope we were able to… • Provide necessary knowledge to foster comprehension of the research literature • Provide necessary knowledge to understand the translation of the methodology to clinical applications ...
... We hope we were able to… • Provide necessary knowledge to foster comprehension of the research literature • Provide necessary knowledge to understand the translation of the methodology to clinical applications ...
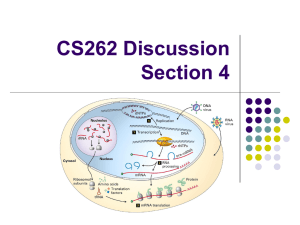
CS262 Discussion Section 4
... regions are classified according to their effect on the protein synthesized. ...
... regions are classified according to their effect on the protein synthesized. ...
mutations - Université d`Ottawa
... 1. Relatively high rate of amino acid sequence evolution - variable among proteins, but in many cases about 0.5 – 1.5 x 10-9 changes per non-synonymous (ie. amino acid-altering) site per year (Table 4.1) 2. Relatively constant rate of evolution for given protein over time - based on pairwise compari ...
... 1. Relatively high rate of amino acid sequence evolution - variable among proteins, but in many cases about 0.5 – 1.5 x 10-9 changes per non-synonymous (ie. amino acid-altering) site per year (Table 4.1) 2. Relatively constant rate of evolution for given protein over time - based on pairwise compari ...
What Is Gene cloning and How Is It Used? 1. Explain what is meant
... Indicate the purpose of the vector and name the two types of vectors used. ...
... Indicate the purpose of the vector and name the two types of vectors used. ...
Controlling the Code: molecules at work
... compacted and almost entirely inactive. This X chromosome inactivation occurs during early embryonic development. One of the two X chromosomes in each cell is inactivated at random. The inactivation is inherited by all of a cell’s descendents. The tortoiseshell gene in cats is located on the X chrom ...
... compacted and almost entirely inactive. This X chromosome inactivation occurs during early embryonic development. One of the two X chromosomes in each cell is inactivated at random. The inactivation is inherited by all of a cell’s descendents. The tortoiseshell gene in cats is located on the X chrom ...
Concepts in Biochemistry 3/e
... biologists have been interested in learning how biological information is transferred from one generation to another. DNA, RNA, proteins and even some carbohydrates are information-rich molecules that carry instructions for cellular processes. Biochemists work with the molecules, cell components and ...
... biologists have been interested in learning how biological information is transferred from one generation to another. DNA, RNA, proteins and even some carbohydrates are information-rich molecules that carry instructions for cellular processes. Biochemists work with the molecules, cell components and ...
Ligation and Transformation
... 1. The plasmid vector must be cut with a restriction endonuclease (aka: restriction enzyme) 2. DNA ligase joins the DNA fragment & vector DNA 3. Host cell is made competent so can plasmid can enter 4. Transformed cells are grown on selection media ...
... 1. The plasmid vector must be cut with a restriction endonuclease (aka: restriction enzyme) 2. DNA ligase joins the DNA fragment & vector DNA 3. Host cell is made competent so can plasmid can enter 4. Transformed cells are grown on selection media ...
DNA Extraction from Strawberries
... contain large amounts of DNA. Each cell in a strawberry contains 8 copies of its genetic information (octaploid), while human cells only contain 2 copies (diploid). The DNA being visualized in this lab is clumps of many copies of DNA from many different cells throughout the strawberries. Each materi ...
... contain large amounts of DNA. Each cell in a strawberry contains 8 copies of its genetic information (octaploid), while human cells only contain 2 copies (diploid). The DNA being visualized in this lab is clumps of many copies of DNA from many different cells throughout the strawberries. Each materi ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.