CHAPTER 27
... washing over them. There is a gradual hardening of the sediments to form rocks. Thus the oldest sedimentary rocks are usually those on the bottom of any strata. Bits and pieces of plants and animals washed down in the sediments quickly become covered and were protected from decay by the rapid burial ...
... washing over them. There is a gradual hardening of the sediments to form rocks. Thus the oldest sedimentary rocks are usually those on the bottom of any strata. Bits and pieces of plants and animals washed down in the sediments quickly become covered and were protected from decay by the rapid burial ...
powerpoint
... 1. Information Storage - these nucleic acids are recipes for proteins... the linear sequence of A, T, C, and G's in these molecules determines the linear sequence of amino acids that will be linked together to form a protein. ...
... 1. Information Storage - these nucleic acids are recipes for proteins... the linear sequence of A, T, C, and G's in these molecules determines the linear sequence of amino acids that will be linked together to form a protein. ...
Standard Operating Procedure for the Determination of Tissue
... necessary to conduct real time QPCR in assessing fungal tissue burden of secondary tissue homogenates from organs harvested from laboratory animals infected with experimental pulmonary aspergillosis at the molecular level. Additional information is provided to encompass additional processing such as ...
... necessary to conduct real time QPCR in assessing fungal tissue burden of secondary tissue homogenates from organs harvested from laboratory animals infected with experimental pulmonary aspergillosis at the molecular level. Additional information is provided to encompass additional processing such as ...
2015 Midterm Study Guide
... Why are there multiple points of gene regulation? Why is it essential that multicellular organisms have tightly regulated gene expression **Enables cells to remain specialized and carry out their specific functions and save energy DNA Packing Histones - Nucleosomes Euchromatin Heterochromatin Methyl ...
... Why are there multiple points of gene regulation? Why is it essential that multicellular organisms have tightly regulated gene expression **Enables cells to remain specialized and carry out their specific functions and save energy DNA Packing Histones - Nucleosomes Euchromatin Heterochromatin Methyl ...
Molecular-aided identification of woody plants in a tropical forest of
... of assignment into MOTUs, we found that DOTUR had a poor performance for all the ...
... of assignment into MOTUs, we found that DOTUR had a poor performance for all the ...
Lecture#5 - Introduction to gene regulation and operons in
... First understanding of gene regulation comes from the work of Jacob and Monod in the 1950's and ‘60's -> Nobel prize in 1965. Inducers - specific substrates that induced the appearance of specific enzymes (new synthesis of the enzymes). beta-galactosidase could be induced with several types of beta- ...
... First understanding of gene regulation comes from the work of Jacob and Monod in the 1950's and ‘60's -> Nobel prize in 1965. Inducers - specific substrates that induced the appearance of specific enzymes (new synthesis of the enzymes). beta-galactosidase could be induced with several types of beta- ...
Key concepts_chromatin
... The genomes of all organisms are compacted by interaction with specific proteins. These often play roles in gene regulation. In bacteria, a large circular chromosome is complexed by proteins in a dynamic manner that compacts it and yet makes it accessible for transcription. Eukaryotes utilize a set ...
... The genomes of all organisms are compacted by interaction with specific proteins. These often play roles in gene regulation. In bacteria, a large circular chromosome is complexed by proteins in a dynamic manner that compacts it and yet makes it accessible for transcription. Eukaryotes utilize a set ...
14 - Lab Times
... must have been reducing, since oxygen prevents the synthesis of some of life’s key organic building blocks. Contemporary observations of Jupiter and Saturn had shown that they contained ammonia, methane and large amounts of hydrogen. These reducing atmospheres were regarded as captured remnants of t ...
... must have been reducing, since oxygen prevents the synthesis of some of life’s key organic building blocks. Contemporary observations of Jupiter and Saturn had shown that they contained ammonia, methane and large amounts of hydrogen. These reducing atmospheres were regarded as captured remnants of t ...
Exam 2 question possibility for 2008
... two DNA’s. This time you denature the mix by heating it, and then cool it down. You separate the ds (double stranded) DNA molecules that you have at the end on the basis of density. (Assume there are no single stranded molecules left.) B-1. How many types of ds DNA (with different densities) will yo ...
... two DNA’s. This time you denature the mix by heating it, and then cool it down. You separate the ds (double stranded) DNA molecules that you have at the end on the basis of density. (Assume there are no single stranded molecules left.) B-1. How many types of ds DNA (with different densities) will yo ...
SBI4U: Molecular Genetics Unit Review
... 33. A polypeptide sequence is composed of 45 amino acids. How many bases are read by the ribosome to produce this polypeptide? 45 amino acids x 3 (bases/amino acid) = 135 bases – this of course assumes you do not count the stop codon, which would add another 3 bases on to your total 34. Describe t ...
... 33. A polypeptide sequence is composed of 45 amino acids. How many bases are read by the ribosome to produce this polypeptide? 45 amino acids x 3 (bases/amino acid) = 135 bases – this of course assumes you do not count the stop codon, which would add another 3 bases on to your total 34. Describe t ...
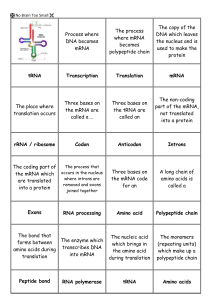
Gene expression flash cards
... The view that nucleic acids / DNA determines protein structure is known as The Central Dogma ...
... The view that nucleic acids / DNA determines protein structure is known as The Central Dogma ...
Gene Testing: What Does It Mean for Producers?
... simply identify a sequence of DNA just as ear tags identify individual calves.” Marker-assisted selection can be used to increase the frequency of desirable forms of a gene within a population by selection ...
... simply identify a sequence of DNA just as ear tags identify individual calves.” Marker-assisted selection can be used to increase the frequency of desirable forms of a gene within a population by selection ...
16Discovery Of DNA
... Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Pre-Lab: Molecular Biology
... replication. 1. Draw a segment of DNA undergoing replication (refer to text pages 190-191). Have your DNA contain 14 base pairs with half of the molecule unzipped and replicated. Label parental strands and daughter strands, the replication fork, the enzymes DNA polymerase and DNA ligase. Be sure tha ...
... replication. 1. Draw a segment of DNA undergoing replication (refer to text pages 190-191). Have your DNA contain 14 base pairs with half of the molecule unzipped and replicated. Label parental strands and daughter strands, the replication fork, the enzymes DNA polymerase and DNA ligase. Be sure tha ...
Biology and the Body Final Review 2014
... When cancer cells come in contact with other cells, they are not signaled by ___________________, and they (stop growing/grow uncontrollably). ...
... When cancer cells come in contact with other cells, they are not signaled by ___________________, and they (stop growing/grow uncontrollably). ...
Gene mutations and their effects
... bases occur next to each other along one of the two DNA strands, they can become linked to form a thymine dimer. The dimer can be replicated as a single base, which results in a frameshift, possibly mutation, possibly resulting in skin cancer. • Chemicals – there are hundreds of chemical mutagens ...
... bases occur next to each other along one of the two DNA strands, they can become linked to form a thymine dimer. The dimer can be replicated as a single base, which results in a frameshift, possibly mutation, possibly resulting in skin cancer. • Chemicals – there are hundreds of chemical mutagens ...
DNA (Gene) Mutations
... more) missing, added, or incorrect A mistake in the genetic code Wrong instructions wrong building materials wrong structure. ...
... more) missing, added, or incorrect A mistake in the genetic code Wrong instructions wrong building materials wrong structure. ...
DNA Mutations ppt
... more) missing, added, or incorrect A mistake in the genetic code Wrong instructions wrong building materials wrong structure. ...
... more) missing, added, or incorrect A mistake in the genetic code Wrong instructions wrong building materials wrong structure. ...
DNA (Gene) Mutations
... more) missing, added, or incorrect A mistake in the genetic code Wrong instructions wrong building materials wrong structure. ...
... more) missing, added, or incorrect A mistake in the genetic code Wrong instructions wrong building materials wrong structure. ...
File - NCEA Level 3 Biology
... • Biotechnology means using biological technology to produce useful organisms such as plants, animals and microorganisms. • The organisms themselves or the products which they produce may be useful. • To do this we use Gene technology to modify the DNA of these organisms. • We alter genes, remove ge ...
... • Biotechnology means using biological technology to produce useful organisms such as plants, animals and microorganisms. • The organisms themselves or the products which they produce may be useful. • To do this we use Gene technology to modify the DNA of these organisms. • We alter genes, remove ge ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.