Lindsay Kinyon
... the octahedrally coordinated platinum family analogs, [Pt(N-N)3]4+ & [Pd(N-N)3]4+, most likely due to the difficulty of solvating the high charge density of the platinum (4+) & palladium (4+) ions. Early in the summer of 1996, Dr. Robert Granger developed a new, versatile scheme for the synthesis of ...
... the octahedrally coordinated platinum family analogs, [Pt(N-N)3]4+ & [Pd(N-N)3]4+, most likely due to the difficulty of solvating the high charge density of the platinum (4+) & palladium (4+) ions. Early in the summer of 1996, Dr. Robert Granger developed a new, versatile scheme for the synthesis of ...
Name: Cell Biology Test #1: 50 points
... [S] 63) What is the Fluid Mosaic Model of a cell membrane? What are the characteristics of membrane lipids and proteins that make this model work? (20-40 words with diagrams if this helps) 64) With respect to glycolysis, many of the chemical reactions have a positive ∆G’o value. Describe three thing ...
... [S] 63) What is the Fluid Mosaic Model of a cell membrane? What are the characteristics of membrane lipids and proteins that make this model work? (20-40 words with diagrams if this helps) 64) With respect to glycolysis, many of the chemical reactions have a positive ∆G’o value. Describe three thing ...
Practice Test - Cardinal Newman High School
... Asexual reproduction can occur by mitosis. Binary fission is a form of sexual reproduction in bacteria. Human sperm and egg cells have 23 chromosomes. Trisomy is the addition or removal of a single nitrogen-containing base. During telophase, a nuclear envelope usually surrounds each new set of chrom ...
... Asexual reproduction can occur by mitosis. Binary fission is a form of sexual reproduction in bacteria. Human sperm and egg cells have 23 chromosomes. Trisomy is the addition or removal of a single nitrogen-containing base. During telophase, a nuclear envelope usually surrounds each new set of chrom ...
Purification and Characterization of a DNA Plasmid Part A
... Midiprep resin. Mix by swirling. This allows the DNA to bind to the resin in batch mode. Discard the pellet. 5. Place the column tip (labeled with your initials) into the vacuum manifold. Pour the DNAresin slurry into the column. Apply vacuum to pack the slurry into the column. Once the "flow-throug ...
... Midiprep resin. Mix by swirling. This allows the DNA to bind to the resin in batch mode. Discard the pellet. 5. Place the column tip (labeled with your initials) into the vacuum manifold. Pour the DNAresin slurry into the column. Apply vacuum to pack the slurry into the column. Once the "flow-throug ...
Genetics Review Questions
... 8. A hybrid gene pair is also referred to as heterozygous. 9. Offspring inherit one gene from each parent. 10. Pp has genes that are different and represent a hybrid organism. 11. The likelihood that an event may or may not take place is called probability. 12. What is the probability that a child w ...
... 8. A hybrid gene pair is also referred to as heterozygous. 9. Offspring inherit one gene from each parent. 10. Pp has genes that are different and represent a hybrid organism. 11. The likelihood that an event may or may not take place is called probability. 12. What is the probability that a child w ...
CHAPTER 3 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
... An amino acid contains: 1. Amino group 2. Carboxyl group 3. Side chain/ “R group” ...
... An amino acid contains: 1. Amino group 2. Carboxyl group 3. Side chain/ “R group” ...
Restriction enzyme
... Methylase Enzymes Restriction enzymes usually occur in combination with one or two modification enzymes (DNAmethyltransferases) Protect the cell’s own DNA from cleavage by the restriction enzyme. Modification enzymes recognize the same DNA sequence as the restriction enzyme that they accompany, Ins ...
... Methylase Enzymes Restriction enzymes usually occur in combination with one or two modification enzymes (DNAmethyltransferases) Protect the cell’s own DNA from cleavage by the restriction enzyme. Modification enzymes recognize the same DNA sequence as the restriction enzyme that they accompany, Ins ...
Molecular Biology of the Cell
... • What would happen if ddCTP were added to a DNA replication reaction in large excess over dCTP • What would happen if ddCTP were added to 10% of the concentration of dCTP? • What would happen if ddCMP were added to 10% of the concentration of dCTP or in large excess? ...
... • What would happen if ddCTP were added to a DNA replication reaction in large excess over dCTP • What would happen if ddCTP were added to 10% of the concentration of dCTP? • What would happen if ddCMP were added to 10% of the concentration of dCTP or in large excess? ...
Taxonomy of Life • Three domains: Eukaryotes, Bacteria (Eubacteria
... to ions and small molecules, and can actively transport such molecules into and out of the interior of the cell. • Eukaryotic cells are generally highly compartmentalized. The interior can be partitioned into nucleus + cytoplasm. The nucleus contains the genome (DNA). The cytoplasm contains various ...
... to ions and small molecules, and can actively transport such molecules into and out of the interior of the cell. • Eukaryotic cells are generally highly compartmentalized. The interior can be partitioned into nucleus + cytoplasm. The nucleus contains the genome (DNA). The cytoplasm contains various ...
genetic ppt melanie - IB
... human development • It helps identify genetic diseases • It allows the production of new drugs based on DNA base sequences of genes or the structure of proteins coded for by these genes • It will give us more information on the origins, evolution and migration of humans ...
... human development • It helps identify genetic diseases • It allows the production of new drugs based on DNA base sequences of genes or the structure of proteins coded for by these genes • It will give us more information on the origins, evolution and migration of humans ...
Unit 3 Review Guide Key Concepts Sickle cell disease is caused by
... Amino Acid- An organic monomer which serves as a building block of proteins. Anticodon- A triplet of nucleotide bases in transfer RNA that identifies the amino acid carried and binds to a complementary codon in messenger RNA during protein synthesis at a ribosome. Codon- A three-nucleotide sequence ...
... Amino Acid- An organic monomer which serves as a building block of proteins. Anticodon- A triplet of nucleotide bases in transfer RNA that identifies the amino acid carried and binds to a complementary codon in messenger RNA during protein synthesis at a ribosome. Codon- A three-nucleotide sequence ...
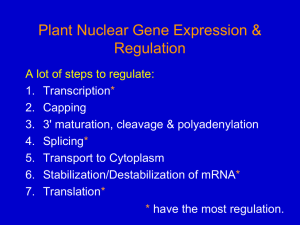
Nuclear gene expression 1
... 2. Can have > 1 of each type of module 3. Many factors also have a dimerization domain (some can form heterodimers). ...
... 2. Can have > 1 of each type of module 3. Many factors also have a dimerization domain (some can form heterodimers). ...
Gene Cloning
... This is done by using an oligo dT column or oligo dT magnetic beads to isolated mRNA which is polyadenylated. cDNA synthesis then relies upon the enzyme Reverse transcriptase and a primer, usually an oligo dT primer for first strand synthesis and then a self-priming or specific primer plus a DNA pol ...
... This is done by using an oligo dT column or oligo dT magnetic beads to isolated mRNA which is polyadenylated. cDNA synthesis then relies upon the enzyme Reverse transcriptase and a primer, usually an oligo dT primer for first strand synthesis and then a self-priming or specific primer plus a DNA pol ...
Mammoth Reconstruction
... decomposing the mammoth’s body. By using the analysis of an elephant’s DNA (preferably that of an Indian elephant), we can fill in any suspicious gaps or check for the number of repeats. We can also note the differences between the mammoth’s and elephant’s DNA. This will help us make hypotheses on ...
... decomposing the mammoth’s body. By using the analysis of an elephant’s DNA (preferably that of an Indian elephant), we can fill in any suspicious gaps or check for the number of repeats. We can also note the differences between the mammoth’s and elephant’s DNA. This will help us make hypotheses on ...
RNA is synthesized by a DNA-dependent RNA polymerase (uses
... Transcription and RNA Processing The first stage in the expression of genetic information is transcription of the information in the base sequence of a double-stranded DNA molecule to form the base sequence of a single-stranded molecule of RNA. For any particular gene, only one strand of the DNA mol ...
... Transcription and RNA Processing The first stage in the expression of genetic information is transcription of the information in the base sequence of a double-stranded DNA molecule to form the base sequence of a single-stranded molecule of RNA. For any particular gene, only one strand of the DNA mol ...
Genomic sequencing
... 1. Use of restriction endonucleases to cut up the same extract of DNA, since each recognise different restriction sites on the DNA they cut it at different points. 2. Take each fragment produced and sequence it to establish the order of its bases. Many of the fragments may overlap. ...
... 1. Use of restriction endonucleases to cut up the same extract of DNA, since each recognise different restriction sites on the DNA they cut it at different points. 2. Take each fragment produced and sequence it to establish the order of its bases. Many of the fragments may overlap. ...
zChap00_Front_140901
... excerpts derived from this work. Non-commercial. You may not use this work for commercial purposes. Share Alike. If you alter, transform, or build upon this work, you may distribute the resulting work only under the same or similar licence to this one. For any reuse or distribution, you must m ...
... excerpts derived from this work. Non-commercial. You may not use this work for commercial purposes. Share Alike. If you alter, transform, or build upon this work, you may distribute the resulting work only under the same or similar licence to this one. For any reuse or distribution, you must m ...
6th Year Biology Higher Level Wesley Hammond DNA and RNA
... DNA and RNA can be worth 5% if asked as a short question in Section A. DNA and RNA can be worth 7.5% if asked as an experiment in Section B. DNA and RNA can be worth 15% if asked as a long question in Section C. Note: DNA and RNA question has been asked every year since 2004 except for ...
... DNA and RNA can be worth 5% if asked as a short question in Section A. DNA and RNA can be worth 7.5% if asked as an experiment in Section B. DNA and RNA can be worth 15% if asked as a long question in Section C. Note: DNA and RNA question has been asked every year since 2004 except for ...
Genetics Outcomes
... forensic investigations. 40. Analyze DNA profiles to draw conclusions about paternity or forensic investigations. To do this, complete the Murder Mystery by using DNA profiling. (Will be handed out) 41. Outline three outcomes of the sequencing of the complete human genome. 42. State that, when genes ...
... forensic investigations. 40. Analyze DNA profiles to draw conclusions about paternity or forensic investigations. To do this, complete the Murder Mystery by using DNA profiling. (Will be handed out) 41. Outline three outcomes of the sequencing of the complete human genome. 42. State that, when genes ...
Intest Aid IB - SpeechNutrients.eu
... The DNA in a cell consists of a long pattern made up of four different nucleotide bases. ...
... The DNA in a cell consists of a long pattern made up of four different nucleotide bases. ...
dna TRANSCRIPTION AND tRANSLATION
... Pyrimidines: Thymine, Cytosine, and Uracil (note: in RNA, Uracil replaces Thymine) Nucleotide pairing – Also known as base pairing, is the joining of purine to a pyrimidine through a hydrogen bond link (A—T, C—G, or A—U in RNA) Ribonucleic acid (RNA) – Messenger to carry instructions from DNA for co ...
... Pyrimidines: Thymine, Cytosine, and Uracil (note: in RNA, Uracil replaces Thymine) Nucleotide pairing – Also known as base pairing, is the joining of purine to a pyrimidine through a hydrogen bond link (A—T, C—G, or A—U in RNA) Ribonucleic acid (RNA) – Messenger to carry instructions from DNA for co ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.