13-1 The Genetic Material
... 13-1 The Genetic Material How was DNA discovered to be the chemical unit of heredity? Frederick Griffith's Experiment - the discovery of transformation Using two varieties of streptococcus, he originally searched for a vaccine. One variety of bacteria had a capsule (like a cell wall) the other did n ...
... 13-1 The Genetic Material How was DNA discovered to be the chemical unit of heredity? Frederick Griffith's Experiment - the discovery of transformation Using two varieties of streptococcus, he originally searched for a vaccine. One variety of bacteria had a capsule (like a cell wall) the other did n ...
Exercise 5
... In the winter of 1982, I had the good fortune to work as part of Eric Davidson’s molecular biology research group at Caltech. Through the subsequent months, under the tutelage of one of the postdocs in the group, Howard Jacobs (now Director of the Institute of Biotechnology in Helsinki), I was able ...
... In the winter of 1982, I had the good fortune to work as part of Eric Davidson’s molecular biology research group at Caltech. Through the subsequent months, under the tutelage of one of the postdocs in the group, Howard Jacobs (now Director of the Institute of Biotechnology in Helsinki), I was able ...
Biochemistry Presentation Notes Pre-AP 14-15
... F. 20 different amino acids combine in different ways to make up thousands of different proteins ...
... F. 20 different amino acids combine in different ways to make up thousands of different proteins ...
What is a chromosome?
... Without histones, the unwound DNA in chromosomes would be very long (a length to width ratio of more than 10 million to 1 in human DNA). For example, each human cell has about 1.8 meters of DNA, but wound on the histones it has about 90 micrometers (0.09 mm) of chromatin, which, when duplicated and ...
... Without histones, the unwound DNA in chromosomes would be very long (a length to width ratio of more than 10 million to 1 in human DNA). For example, each human cell has about 1.8 meters of DNA, but wound on the histones it has about 90 micrometers (0.09 mm) of chromatin, which, when duplicated and ...
1BIOLOGY 220W - Lecture Notes Packet
... are of different sizes, or they are all the same size. If they are different sizes, then we can detect the difference in size by separating the fragments on an electrophoretic gel. An example of a kind of polymorphism where there are many differences in length is called a microsatellite, also calle ...
... are of different sizes, or they are all the same size. If they are different sizes, then we can detect the difference in size by separating the fragments on an electrophoretic gel. An example of a kind of polymorphism where there are many differences in length is called a microsatellite, also calle ...
Syllabus Notes - Southwest High School
... – They are catalysts. (They speed up reactions that would normally happen anyway.) – They do not use energy to work. – They do not get used up. They do not change – Substrates are what the enzymes work on. ...
... – They are catalysts. (They speed up reactions that would normally happen anyway.) – They do not use energy to work. – They do not get used up. They do not change – Substrates are what the enzymes work on. ...
PCR - Michigan State University
... to answer questions of interest to the legal system. This may be in relation to a crime or to a civil action. • It is often of interest in forensic science to identify individuals genetically. In these cases, one is interested in looking at variable regions of the genome as opposed to highly-conserv ...
... to answer questions of interest to the legal system. This may be in relation to a crime or to a civil action. • It is often of interest in forensic science to identify individuals genetically. In these cases, one is interested in looking at variable regions of the genome as opposed to highly-conserv ...
Medical School Biochemistry
... Sugar residues are bound to collagen through hydroxylysine residues Procollagen contains N- and C-terminal globular regions ...
... Sugar residues are bound to collagen through hydroxylysine residues Procollagen contains N- and C-terminal globular regions ...
BIOL 112 – Principles of Zoology
... GAL80 encodes a protein that negatively regulates transcription. The repressor protein binds to an Activator protein, rendering it inactive. GAL4 encodes an activator w/zinc finger motif that activates transcription of the three GAL genes ...
... GAL80 encodes a protein that negatively regulates transcription. The repressor protein binds to an Activator protein, rendering it inactive. GAL4 encodes an activator w/zinc finger motif that activates transcription of the three GAL genes ...
Notes - Humble ISD
... A mutation is a change in the DNA sequence. The mutation may be classified as: ______________________ or _____________ mutations. Most mutations are harmful, but a few can be beneficial or silent. A. Chromosomal Mutation 1. Chromosomal mutations involve the______________________ or _________________ ...
... A mutation is a change in the DNA sequence. The mutation may be classified as: ______________________ or _____________ mutations. Most mutations are harmful, but a few can be beneficial or silent. A. Chromosomal Mutation 1. Chromosomal mutations involve the______________________ or _________________ ...
Modeling Transcription and Translation
... Why is it important for the cell to correct any errors that occur during replication? (If errors were not corrected, one of the new cells that form during cell division would have DNA with incorrect genetic information.) How much of the cell's DNA is copied during replication? (all of it; in humans, ...
... Why is it important for the cell to correct any errors that occur during replication? (If errors were not corrected, one of the new cells that form during cell division would have DNA with incorrect genetic information.) How much of the cell's DNA is copied during replication? (all of it; in humans, ...
Gene Technology PowerPoint
... Manipulating Genes Recombinant DNA - molecules are DNA molecules formed by laboratory methods of genetic recombination (such as molecular cloning) to bring together genetic material from multiple sources, creating sequences that would not otherwise be found in biological organisms. ...
... Manipulating Genes Recombinant DNA - molecules are DNA molecules formed by laboratory methods of genetic recombination (such as molecular cloning) to bring together genetic material from multiple sources, creating sequences that would not otherwise be found in biological organisms. ...
Evolving Insights into the Laws of Nature for Biological Evolution
... animals and humans. They have resided in genomes possibly since the early times of biological evolution, as have housekeeping genes. We come therefore to the novel insight of a principal duality of the genome (8). It is well known that many genes in the genome work for the immediate benefit of the i ...
... animals and humans. They have resided in genomes possibly since the early times of biological evolution, as have housekeeping genes. We come therefore to the novel insight of a principal duality of the genome (8). It is well known that many genes in the genome work for the immediate benefit of the i ...
Sten_Ilmjärv_Different Aspects of Gene Regulation
... The genetic code of the DNA is made up of three letter nucleic acids which are overall named as codon. In the end every codon is opposed by an amino acid. But one amino acid can be formed by different codons which differ by their nucleic acid sequence. ...
... The genetic code of the DNA is made up of three letter nucleic acids which are overall named as codon. In the end every codon is opposed by an amino acid. But one amino acid can be formed by different codons which differ by their nucleic acid sequence. ...
File - prepareforchemistry
... The primary structure of protein refers to the specific sequence in which various amino acids are present in it, i.e., the sequence of linkages between amino acids in a polypeptide chain. The sequence in which amino acids are arranged is different in each protein. A change in the sequence creates a ...
... The primary structure of protein refers to the specific sequence in which various amino acids are present in it, i.e., the sequence of linkages between amino acids in a polypeptide chain. The sequence in which amino acids are arranged is different in each protein. A change in the sequence creates a ...
2. In a double helix a region along one DNA strand
... 23. With the exception of identical twins, siblings who have the same two biological parents are likely to look similar, but not identical to each other because a. b. c. d. e. ...
... 23. With the exception of identical twins, siblings who have the same two biological parents are likely to look similar, but not identical to each other because a. b. c. d. e. ...
2 Weeks Unit Essential Question
... Why can bacteria recognize a human gene and then produce a human protein? A. B. * C. D. ...
... Why can bacteria recognize a human gene and then produce a human protein? A. B. * C. D. ...
Cha. 3 Cell structure
... Rough ER contains ribosomes for protein synthesis Smooth ER contains enzymes for steroid synthesis and inactivation; Ca+ storage ...
... Rough ER contains ribosomes for protein synthesis Smooth ER contains enzymes for steroid synthesis and inactivation; Ca+ storage ...
AIMS Review Packet
... 84) If an mRNA had 12 codons, how many amino acids would it code for? 85) Where does transcription occur in the cell? 86) Where does translation occur in the cell? 87) The mRNA codon AUG codes for the amino acid 88) The mRNA codon CCA codes for the amino acid ...
... 84) If an mRNA had 12 codons, how many amino acids would it code for? 85) Where does transcription occur in the cell? 86) Where does translation occur in the cell? 87) The mRNA codon AUG codes for the amino acid 88) The mRNA codon CCA codes for the amino acid ...
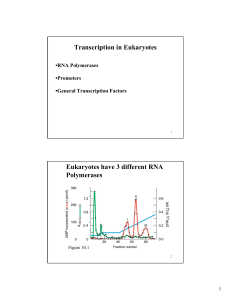
Transcription in Eukaryotes Eukaryotes have 3 different RNA
... binding to promoters and a basal level of transcription. •Gene-specific factors stimulate transcription further (or repress it) and allow fine regulatory control. ...
... binding to promoters and a basal level of transcription. •Gene-specific factors stimulate transcription further (or repress it) and allow fine regulatory control. ...
Chapter 10
... • Therefore we use mRNA to identify active regions of DNA • Use mRNA sequence and base pairing rules to identify DNA original sequence ...
... • Therefore we use mRNA to identify active regions of DNA • Use mRNA sequence and base pairing rules to identify DNA original sequence ...
PREVIEW_on_Ng_etal_STRUCTURE-MK
... attachment to the host plasma membrane and a single catalytic A subunit, which subverts cellular functions once the toxin complex has been internalized (Merritt & Hol, 1995). Four AB5 families have been reported based on the function of the catalytic subunit: the Shiga toxins, which interfere with p ...
... attachment to the host plasma membrane and a single catalytic A subunit, which subverts cellular functions once the toxin complex has been internalized (Merritt & Hol, 1995). Four AB5 families have been reported based on the function of the catalytic subunit: the Shiga toxins, which interfere with p ...
BIO PLACEMENT TEST REVIEW QUESTIONS Review 1: Answer
... cells have ___ chromosomes. A) 6 B) 10 C) 12 D) 18 E) 24 36) The haploid number of chromosomes for humans is *A) 23 B) 24 C) 26 D) 46 E) 48 37) Which represents the correct sequence of stages in the cell cycle? A) G1, G2, S, M B) G1, G2, M, S C) M, S, G1, G2 D) G1, S, G2, M E) G1, M, G2, S 38) Which ...
... cells have ___ chromosomes. A) 6 B) 10 C) 12 D) 18 E) 24 36) The haploid number of chromosomes for humans is *A) 23 B) 24 C) 26 D) 46 E) 48 37) Which represents the correct sequence of stages in the cell cycle? A) G1, G2, S, M B) G1, G2, M, S C) M, S, G1, G2 D) G1, S, G2, M E) G1, M, G2, S 38) Which ...
here
... amino acids may give rise to different shapes, therefore different functionalities. The shape of protein depends on the sequence of amino acids, the nature of the primary solvent (water or lipid), the concentration of salts, the temperature, and etc. Raswin (Software to study of the protein structur ...
... amino acids may give rise to different shapes, therefore different functionalities. The shape of protein depends on the sequence of amino acids, the nature of the primary solvent (water or lipid), the concentration of salts, the temperature, and etc. Raswin (Software to study of the protein structur ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.