Topic 5 – Mutations and Genetic Variation PreClass Reading
... o Occur as a result of DNA replication o Usually an enzyme checks the new DNA strands for errors in the replication process (but it can miss some) Induced mutations o Arise from exposure to mutagenic agents (something that causes a mutation) o Eg. UV radiation, Xrays, certain chemicals ...
... o Occur as a result of DNA replication o Usually an enzyme checks the new DNA strands for errors in the replication process (but it can miss some) Induced mutations o Arise from exposure to mutagenic agents (something that causes a mutation) o Eg. UV radiation, Xrays, certain chemicals ...
Chapt 16: Other RNA Processing 16.1 Ribosomal RNA Processing
... • Explain how tRNA precursors are trimmed, modified • Describe how trans-splicing and RNA editing occur in some protists or parasitic worms • Describe how RNA interference (RNAi) uses ds RNA to degrade specific mRNA • Figures: 1, 2*, 3, 4*, 5*, 7, 10, 13, 14, 17, 20, 29, 31, 33*, 36*, ...
... • Explain how tRNA precursors are trimmed, modified • Describe how trans-splicing and RNA editing occur in some protists or parasitic worms • Describe how RNA interference (RNAi) uses ds RNA to degrade specific mRNA • Figures: 1, 2*, 3, 4*, 5*, 7, 10, 13, 14, 17, 20, 29, 31, 33*, 36*, ...
No Slide Title
... • 3 promoters: 2 on H strand, one on L • pL transcribes entire light strand; later processed into tRNA & ND6 • pH1 transcribes entire H strand • pH2 may transcribe 12S & 16S rRNA • In vitro only need TFAM & TFB2M to transcribe pL & pH1 • Uncertain if pH2 is used ...
... • 3 promoters: 2 on H strand, one on L • pL transcribes entire light strand; later processed into tRNA & ND6 • pH1 transcribes entire H strand • pH2 may transcribe 12S & 16S rRNA • In vitro only need TFAM & TFB2M to transcribe pL & pH1 • Uncertain if pH2 is used ...
MARKER GENE TECHNOLOGIES, Inc
... We do not recommend reusing RedView precast gels as signal decreases with ...
... We do not recommend reusing RedView precast gels as signal decreases with ...
Document
... If a multiple of 3 are lost (3,6,9,etc…), then only those amino acids are lost from the polypeptide. However, if any other number are lost, all the amino acids change (called a reading frame shift or a frame shift mutation). ...
... If a multiple of 3 are lost (3,6,9,etc…), then only those amino acids are lost from the polypeptide. However, if any other number are lost, all the amino acids change (called a reading frame shift or a frame shift mutation). ...
Leukaemia Section t(11;19)(q23;p13.1) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... Contains a Lysin rich domain (basic motif); nuclear localisation; transcription factor (RNA polymerase elongation factor). ...
... Contains a Lysin rich domain (basic motif); nuclear localisation; transcription factor (RNA polymerase elongation factor). ...
Exam 3a - web.biosci.utexas.edu
... 12. (6 points) An E. coli cell lacking the fertility factor is referred to as a(n) F - / F ’ / F + / Hfr cell, where as one in which the factor is integrated into the chromosome is referred to as a(n) F - / F ’ / F + / Hfr cell. Circle the correct answer for each. 13. (4 points) True / False ...
... 12. (6 points) An E. coli cell lacking the fertility factor is referred to as a(n) F - / F ’ / F + / Hfr cell, where as one in which the factor is integrated into the chromosome is referred to as a(n) F - / F ’ / F + / Hfr cell. Circle the correct answer for each. 13. (4 points) True / False ...
박사님 별 연구주제 및 인턴으로서 하게 될 일 Dr. Ben Tall: I work with
... DNA to low levels, but cannot eliminate these altogether. For this reason, to develop molecular epidemiological methods for Cyclospora, alternative approaches to WGS of Cyclospora are needed. The sequencing of Cyclospora genomes will be done using a metagenomics approach on Illumina’s MiSeq and Nex ...
... DNA to low levels, but cannot eliminate these altogether. For this reason, to develop molecular epidemiological methods for Cyclospora, alternative approaches to WGS of Cyclospora are needed. The sequencing of Cyclospora genomes will be done using a metagenomics approach on Illumina’s MiSeq and Nex ...
C:\BOB\HSC\Exams 05\Supps\Biology 3201 August 2005.wpd
... Instructions: Complete all questions in this section. Your responses must be clearly presented in a well-organized manner. Value ...
... Instructions: Complete all questions in this section. Your responses must be clearly presented in a well-organized manner. Value ...
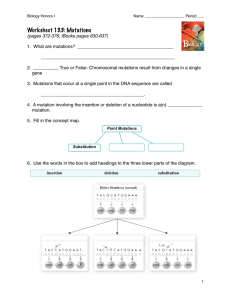
GENE MUTATION = POINT MUTATION at the DNA level: at the level
... p.Tyr495Cys, in conserved amino acid in exon 20 of DNMT1 so WHAT? All mutations are within the targeting-sequence domain of DNMT1. These mutations cause premature degradation of mutant proteins, reduced methyltransferase activity and impaired heterochromatin binding during the G2 cell cycle phase l ...
... p.Tyr495Cys, in conserved amino acid in exon 20 of DNMT1 so WHAT? All mutations are within the targeting-sequence domain of DNMT1. These mutations cause premature degradation of mutant proteins, reduced methyltransferase activity and impaired heterochromatin binding during the G2 cell cycle phase l ...
Restriction Enzyme digestion of DNA
... • A special class of endonucleases from a bacteria has been isolated for this experiment. These special enzymes, termed restriction endonucleases (RE), digest DNA by breaking bonds only within a specific short sequence of bases. These base sequences usually ran in size from 48 base pairs but can be ...
... • A special class of endonucleases from a bacteria has been isolated for this experiment. These special enzymes, termed restriction endonucleases (RE), digest DNA by breaking bonds only within a specific short sequence of bases. These base sequences usually ran in size from 48 base pairs but can be ...
Biological Sequence Data Formats
... include spaces or non-letter or number characters. Avoid (1) Names longer than 15 character; (2) Spaces; and (3) Characters other than letters or numbers. FASTA Format: Multiple Entries Sometimes you need to input many sequences at the same time to a program, such as a multiple sequence alignment pr ...
... include spaces or non-letter or number characters. Avoid (1) Names longer than 15 character; (2) Spaces; and (3) Characters other than letters or numbers. FASTA Format: Multiple Entries Sometimes you need to input many sequences at the same time to a program, such as a multiple sequence alignment pr ...
Chapter 5- Enzymes State Standard Standard 1.b. – Enzymes
... 1. Which of the following is not true of enzymes? A. Are proteins B. Act as a biological catalyst C. Supplies energy to start a chemical reaction D. Is specific E. Lowers the energy of activation 2. An enzyme is specific, this means A. It has a certain amino acid sequence B. It is found only in a ce ...
... 1. Which of the following is not true of enzymes? A. Are proteins B. Act as a biological catalyst C. Supplies energy to start a chemical reaction D. Is specific E. Lowers the energy of activation 2. An enzyme is specific, this means A. It has a certain amino acid sequence B. It is found only in a ce ...
Stabilization of carbanions
... so that a significant fraction of the alcohol is in the ionized (alkoxide)! form at physiological pH.! ...
... so that a significant fraction of the alcohol is in the ionized (alkoxide)! form at physiological pH.! ...
Characterization of two rice DNA methyltransferases
... libraries. OsMET1-1 has an open reading frame of 4,566 nucleotides with twelve exons and eleven introns while OsMET1-2 has an open reading frame of 4,452 nucleotides with eleven exons and ten introns. Although OsMET1-1 and OsMET1-2 have high sequence similarity overall, they share only 24% identity ...
... libraries. OsMET1-1 has an open reading frame of 4,566 nucleotides with twelve exons and eleven introns while OsMET1-2 has an open reading frame of 4,452 nucleotides with eleven exons and ten introns. Although OsMET1-1 and OsMET1-2 have high sequence similarity overall, they share only 24% identity ...
8-7 Power Point
... Mutations can be caused by several factors. • Replication errors can cause mutations. • Mutagens, such as UV ray and chemicals, can cause mutations. • Some cancer drugs use mutagenic properties to kill ...
... Mutations can be caused by several factors. • Replication errors can cause mutations. • Mutagens, such as UV ray and chemicals, can cause mutations. • Some cancer drugs use mutagenic properties to kill ...
FREE Sample Here
... Yes, these molecules are just strings of glucose, but it is how the glucose units are actually connected to one another that gives each molecule its particular properties. In particular, they differ in length of the chains and degree of branching, but the major difference lies in which particular ca ...
... Yes, these molecules are just strings of glucose, but it is how the glucose units are actually connected to one another that gives each molecule its particular properties. In particular, they differ in length of the chains and degree of branching, but the major difference lies in which particular ca ...
NAME :Abubakar Aisha MATRIC NO:14/sci05/001 DEPT
... mutation alters a protein that plays a critical role in the body, a medical condition can result. A condition caused by mutations in one or more genes is called a genetic disorder. Some mutations alter a gene's DNA base sequence but do not change the function of the protein made by the gene. One stu ...
... mutation alters a protein that plays a critical role in the body, a medical condition can result. A condition caused by mutations in one or more genes is called a genetic disorder. Some mutations alter a gene's DNA base sequence but do not change the function of the protein made by the gene. One stu ...
Evolution Notes Part 2 - Mercer Island School District
... Eliminates average individuals, but favors individuals at either extreme of the spectrum of variation. Results in a __________ distribution, with fewer of the average form and more of the extremes. ...
... Eliminates average individuals, but favors individuals at either extreme of the spectrum of variation. Results in a __________ distribution, with fewer of the average form and more of the extremes. ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.