In Silico Mapping of Complex Disease
... a single base pair (the smallest building block of DNA) and are shared by many people. Such single base pair differences are called "single nucleotide polymorphisms", or SNPs for short. Nonetheless many SNPs, perhaps the majority, do not produce physical changes in people with affected DNA. Why then ...
... a single base pair (the smallest building block of DNA) and are shared by many people. Such single base pair differences are called "single nucleotide polymorphisms", or SNPs for short. Nonetheless many SNPs, perhaps the majority, do not produce physical changes in people with affected DNA. Why then ...
The bond in the bacteriophage 4x174 gene A protein
... The results indicate that gene A protein and A* protein are linked via a tyrosyl residue to the 5 ’ -phosphate of the adenylic residue at position 8 of the octadecamer {fig. 1). It was shown in (71 that cleavage of the hexadecamer CAACTTGATATTAATA by the gene A protein or A* protein produced the hep ...
... The results indicate that gene A protein and A* protein are linked via a tyrosyl residue to the 5 ’ -phosphate of the adenylic residue at position 8 of the octadecamer {fig. 1). It was shown in (71 that cleavage of the hexadecamer CAACTTGATATTAATA by the gene A protein or A* protein produced the hep ...
Novel DNA Polymerase Increases Efficiency of Multiple PCR
... that specializes in amplifying long DNA fragments — generally 8 kb or more. However, it is known that the longer the amplified sequence is, the less efficient the PCR reaction is, and conventional polymerases such as Taq and Tth are unsuitable for the method. Because SD polymerase's strand displacem ...
... that specializes in amplifying long DNA fragments — generally 8 kb or more. However, it is known that the longer the amplified sequence is, the less efficient the PCR reaction is, and conventional polymerases such as Taq and Tth are unsuitable for the method. Because SD polymerase's strand displacem ...
Advanced primer design
... alignment of the wild type and the mutant type. In the entire length of 510 bp there are seven mutations. The region containing these mutations is the target region for amplification. Figure 2- 2 shows an example of primer selection. Under default, primers have been designed for the wild type strain ...
... alignment of the wild type and the mutant type. In the entire length of 510 bp there are seven mutations. The region containing these mutations is the target region for amplification. Figure 2- 2 shows an example of primer selection. Under default, primers have been designed for the wild type strain ...
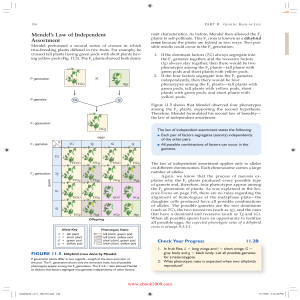
! Mendel`s Law of Independent Assortment
... they are placed off a horizontal line.) Which pattern of inheritance (I or II) do you suppose represents an autosomal dominant characteristic, and which represents an autosomal recessive characteristic? In pattern I, the child is affected, but neither parent is; this can happen if the condition is r ...
... they are placed off a horizontal line.) Which pattern of inheritance (I or II) do you suppose represents an autosomal dominant characteristic, and which represents an autosomal recessive characteristic? In pattern I, the child is affected, but neither parent is; this can happen if the condition is r ...
Les métaux ou les non-métaux
... It is therapeutic cloning because the aim of the technique is not to produce a new individual but rather to generate genetically compatible tissues for a person in need of a transplant. ...
... It is therapeutic cloning because the aim of the technique is not to produce a new individual but rather to generate genetically compatible tissues for a person in need of a transplant. ...
2nd Lecture
... sequence. As such, it is part of the epigenetic code and is also the most well characterized epigenetic mechanism ...
... sequence. As such, it is part of the epigenetic code and is also the most well characterized epigenetic mechanism ...
DNA Recombination Mechanisms
... structure is formed If the recombined plasmids are cut with a restriction enzyme a c (chi) is formed ...
... structure is formed If the recombined plasmids are cut with a restriction enzyme a c (chi) is formed ...
BIO 1301 notes - Faulkner University
... Genetic expression – cells exert control over selves and each other the phenotype cell type and function cell environment – chemicals, signals and outside factors development adaptation programmed cell death control systems concept regulatory proteins – interactions operon concept: promoter, repress ...
... Genetic expression – cells exert control over selves and each other the phenotype cell type and function cell environment – chemicals, signals and outside factors development adaptation programmed cell death control systems concept regulatory proteins – interactions operon concept: promoter, repress ...
Mendelian Genetics in Populations – 1
... • When C(2) is common (> 0.90), most matings are between C(2) homozygotes, which produce 25% viable offspring, and C(2) increases toward fixation • When C(2) is less common (< 0.80), enough matings occur between N(2) homozygotes, which produce 100% viable offspring, that N(2) chromosomes can increas ...
... • When C(2) is common (> 0.90), most matings are between C(2) homozygotes, which produce 25% viable offspring, and C(2) increases toward fixation • When C(2) is less common (< 0.80), enough matings occur between N(2) homozygotes, which produce 100% viable offspring, that N(2) chromosomes can increas ...
C2005/F2401 `09
... isolated from the digest. Also suppose the original plasmid used as a cloning vector had one site each for Bit1 and Bit2. The two enzymes produce different sticky ends. The vector also has one gene for resistance to the drug bubimycin, and the site for Bit1 is in that gene. C-1. To make the final pl ...
... isolated from the digest. Also suppose the original plasmid used as a cloning vector had one site each for Bit1 and Bit2. The two enzymes produce different sticky ends. The vector also has one gene for resistance to the drug bubimycin, and the site for Bit1 is in that gene. C-1. To make the final pl ...
CHAPTER 4 - HCC Learning Web
... A polymer of glucose, stored by plants as granules within cellular structure known as PLASTIDS. Human and most animals can hydrolyze starch, making glucose available as a nutrient for cells. Most of the glucose molecules are joined by alpha 1-4linkage The simplest form of starch is unbranche ...
... A polymer of glucose, stored by plants as granules within cellular structure known as PLASTIDS. Human and most animals can hydrolyze starch, making glucose available as a nutrient for cells. Most of the glucose molecules are joined by alpha 1-4linkage The simplest form of starch is unbranche ...
The Symbiotic Relationship of Science and Technology in the 21st
... and genetic engineering must include the instrument makers such as Janssen, Huygens, Leeuvenhoek, and Hooke who, in the 16th and 17th centuries, developed the early models of the light microscope and other laboratory equipment so necessary for examination and discovery. These technologies were cruci ...
... and genetic engineering must include the instrument makers such as Janssen, Huygens, Leeuvenhoek, and Hooke who, in the 16th and 17th centuries, developed the early models of the light microscope and other laboratory equipment so necessary for examination and discovery. These technologies were cruci ...
Lab exam 1 V DONE
... same location, but four of them map to chromosome 4 and the remaining six map to chromosome 6. Other scientists get the same data as well (for the same species) and even confirm these loci encode for mRNA. Select the answer that explains these results. Select either D or E if you think there are two ...
... same location, but four of them map to chromosome 4 and the remaining six map to chromosome 6. Other scientists get the same data as well (for the same species) and even confirm these loci encode for mRNA. Select the answer that explains these results. Select either D or E if you think there are two ...
1. Introduction - diss.fu
... chromosomes. Genetic crosses revealed that the mobilization of such element is dependent on a protein product of another element that she named "Activator", or Ac, which itself was able to move by using its own protein product. This transposable element system is called Ac/Ds, and is considered to b ...
... chromosomes. Genetic crosses revealed that the mobilization of such element is dependent on a protein product of another element that she named "Activator", or Ac, which itself was able to move by using its own protein product. This transposable element system is called Ac/Ds, and is considered to b ...
university of calcutta
... (aromatic amino (–NH2), Amido (–CONH2, including imide), aromatic nitro (–NO2), Phenolic –OH, Carboxylic acid (–COOH), Carbonyl (>C= O); only one test for each functional group is to be reported) [6×1½=9M] 6. *Each student, during laboratory session, is required to carry out qualitative chemical tes ...
... (aromatic amino (–NH2), Amido (–CONH2, including imide), aromatic nitro (–NO2), Phenolic –OH, Carboxylic acid (–COOH), Carbonyl (>C= O); only one test for each functional group is to be reported) [6×1½=9M] 6. *Each student, during laboratory session, is required to carry out qualitative chemical tes ...
Biology 393 Midterm Review
... nitrogen-base that RNA has and DNA does not is called Uracil Describe each type of RNA: -tRNA (Transfer RNA)- transfers amino acids to the ribosome, matches amino acids to mRNA -rRNA (ribosomal RNA)- makes up the structure of a ribosome -mRNA (messenger RNA)- carries information from DNA to ribosome ...
... nitrogen-base that RNA has and DNA does not is called Uracil Describe each type of RNA: -tRNA (Transfer RNA)- transfers amino acids to the ribosome, matches amino acids to mRNA -rRNA (ribosomal RNA)- makes up the structure of a ribosome -mRNA (messenger RNA)- carries information from DNA to ribosome ...
Biochemistry - Austin Community College
... • Enzymes are proteins that carry out most catalysis in living organisms. • Unlike heat, enzymes are highly specific. Each enzyme typically speeds up only one or a few chemical reactions. • Unique three-dimensional shape enables an enzyme to stabilize a temporary association between substrates. • Be ...
... • Enzymes are proteins that carry out most catalysis in living organisms. • Unlike heat, enzymes are highly specific. Each enzyme typically speeds up only one or a few chemical reactions. • Unique three-dimensional shape enables an enzyme to stabilize a temporary association between substrates. • Be ...
LETTER Insertion DNA Promotes Ectopic Recombination during
... asymmetric DNAs such as insertion sequences affect heritable characters of adjacent nonindel sequences. Heritable effects of insertions on adjacent symmetric DNA have been demonstrated. However, little is known about these genetic effects of insertion sequences on their own, during meiosis. For exam ...
... asymmetric DNAs such as insertion sequences affect heritable characters of adjacent nonindel sequences. Heritable effects of insertions on adjacent symmetric DNA have been demonstrated. However, little is known about these genetic effects of insertion sequences on their own, during meiosis. For exam ...
Curriculum for UG
... 4. Iron deficiency anemia 5. Wilson’s disease 6. Tetany 7. PUFA and risk factors for IHD 8. Cholera/ gastroenteritis 1. Haem Metabolism:Formation and catabolism of haem, bile pigments. Tests for liver function Clinical correlations: 1. Porphyrias 2. Jaundice i.Metabolism of Xenobiotics Cyctochrome P ...
... 4. Iron deficiency anemia 5. Wilson’s disease 6. Tetany 7. PUFA and risk factors for IHD 8. Cholera/ gastroenteritis 1. Haem Metabolism:Formation and catabolism of haem, bile pigments. Tests for liver function Clinical correlations: 1. Porphyrias 2. Jaundice i.Metabolism of Xenobiotics Cyctochrome P ...
Measuring the Rates of Transcriptional Elongation in the Female
... kinase) and 5 μl of [α-32P]UTP (6000 Ci/mmol, 40 μCi/μl; MP Biomedicals, Irvine, California). After incubation for 30 minutes at 23°C, the reaction was stopped by adding 25 μl of RNase-free DNase (RQ1, Promega) and incubating for 5 minutes at 37°C. Proteins were digested by adding 20 μl of 15x prote ...
... kinase) and 5 μl of [α-32P]UTP (6000 Ci/mmol, 40 μCi/μl; MP Biomedicals, Irvine, California). After incubation for 30 minutes at 23°C, the reaction was stopped by adding 25 μl of RNase-free DNase (RQ1, Promega) and incubating for 5 minutes at 37°C. Proteins were digested by adding 20 μl of 15x prote ...
Evidence from the gnarly New Zealand snails for and against the red
... 18. Describe the process of shifting balance. What are the three phases? What was the theory meant to explain? How does Wright’s shifting-balance view of evolution compare with Fisher’s thinking on evolution? 29. Write your own question on aspects of the material covered in this section of the cours ...
... 18. Describe the process of shifting balance. What are the three phases? What was the theory meant to explain? How does Wright’s shifting-balance view of evolution compare with Fisher’s thinking on evolution? 29. Write your own question on aspects of the material covered in this section of the cours ...
Welcome to Comp 665 - UNC Computational Genetics
... Sequence Organization • The DNA sequence is broken into several independent segments organized into structures called chromosomes • Chromosomes vary between different organisms. The DNA molecule may be circular or linear, and can contain from 10,000 to 1,000,000,000 nucleotides. • Simple single-cel ...
... Sequence Organization • The DNA sequence is broken into several independent segments organized into structures called chromosomes • Chromosomes vary between different organisms. The DNA molecule may be circular or linear, and can contain from 10,000 to 1,000,000,000 nucleotides. • Simple single-cel ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.