Section 12.2 - CPO Science
... 12.2 Bohr model of the atom Danish physicist Neils Bohr proposed the concept of energy levels to explain the spectrum of hydrogen. When an electron moves from a higher energy level to a lower one, the atom gives up the energy difference between the two levels. The energy comes out as differen ...
... 12.2 Bohr model of the atom Danish physicist Neils Bohr proposed the concept of energy levels to explain the spectrum of hydrogen. When an electron moves from a higher energy level to a lower one, the atom gives up the energy difference between the two levels. The energy comes out as differen ...
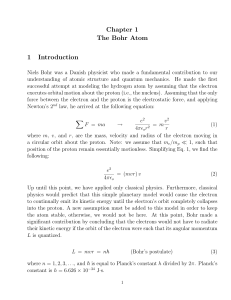
Chapter 1 The Bohr Atom 1 Introduction
... physics would predict that this simple planetary model would cause the electron to continually emit its kinetic energy until the electron’s orbit completely collapses into the proton. A new assumption must be added to this model in order to keep the atom stable, otherwise, we would not be here. At t ...
... physics would predict that this simple planetary model would cause the electron to continually emit its kinetic energy until the electron’s orbit completely collapses into the proton. A new assumption must be added to this model in order to keep the atom stable, otherwise, we would not be here. At t ...
Multi-electron atoms have interactions between electrons, not just
... this WAVEFUNCTION ... without doing the actual math. - There are FOUR of these parameters. (the Bohr model had only one!) - The parameters are called "quantum numbers" Principal quantum number Angular momentum quantum number Magnetic quantum number Spin quantum number ...
... this WAVEFUNCTION ... without doing the actual math. - There are FOUR of these parameters. (the Bohr model had only one!) - The parameters are called "quantum numbers" Principal quantum number Angular momentum quantum number Magnetic quantum number Spin quantum number ...
Transcript - the Cassiopeia Project
... But of course, the atom is not always found in this lowest energy state. As there are other orbits allowed in the Bohr model, there are other, higher energy states in the quantum mechanical hydrogen atom. These states are defined primarily by the quantum number “n” that we talked about earlier. And ...
... But of course, the atom is not always found in this lowest energy state. As there are other orbits allowed in the Bohr model, there are other, higher energy states in the quantum mechanical hydrogen atom. These states are defined primarily by the quantum number “n” that we talked about earlier. And ...
(Bohr Model And X-Rays) Part-1
... Bohr gave following postulates for electron in hydrogen atom :• An electron in an atom could resolve in certain stable orbits without the emission of radiant energy. • An electron resolves around the nucleus only in those orbits for which the angular momentum is some integral multiple of L= ...
... Bohr gave following postulates for electron in hydrogen atom :• An electron in an atom could resolve in certain stable orbits without the emission of radiant energy. • An electron resolves around the nucleus only in those orbits for which the angular momentum is some integral multiple of L= ...
Prof. Knut W. Urban
... Research Centre Jülich, Jülich, Germany Picometer Electron Microscopy - An expedition into the world of atoms by aberration-corrected electron optics The realization of aberration-corrected lenses has triggered a quantum jump in electron optics. The recent generation of transmission electron microsc ...
... Research Centre Jülich, Jülich, Germany Picometer Electron Microscopy - An expedition into the world of atoms by aberration-corrected electron optics The realization of aberration-corrected lenses has triggered a quantum jump in electron optics. The recent generation of transmission electron microsc ...
Chem 1st Sem Rev Ch2
... c. father of the modern atomic theory, everything made of atoms d. planetary model of the atom, electrons move around the nucleus like planets around sun. e. plum pudding model of the atom: atom looks like chocolate chip cookie f. gold foil experiment – atoms have a dense core called nucleus g. he g ...
... c. father of the modern atomic theory, everything made of atoms d. planetary model of the atom, electrons move around the nucleus like planets around sun. e. plum pudding model of the atom: atom looks like chocolate chip cookie f. gold foil experiment – atoms have a dense core called nucleus g. he g ...
NASC 1110
... Find the radius of the second orbit, ionization energy from the 2nd orbit, and transition wavelength between the 2nd and 3rd orbit in a singly ionized helium atom. He+, ...
... Find the radius of the second orbit, ionization energy from the 2nd orbit, and transition wavelength between the 2nd and 3rd orbit in a singly ionized helium atom. He+, ...
PPT - Tensors for Tots
... The photoelectric effect deals with electrons that are emitted from a metal surface when struck by radiation of adequately high wave length (light or ultraviolet radiation). Unoxided metal surfaces emit electrons when they are negatively charged and their surface is struck by light. With this, the f ...
... The photoelectric effect deals with electrons that are emitted from a metal surface when struck by radiation of adequately high wave length (light or ultraviolet radiation). Unoxided metal surfaces emit electrons when they are negatively charged and their surface is struck by light. With this, the f ...
Random Laser - Department of Physics
... semiconductor is fully and uniquely characterized by its band structure. At zero temperature, electrons occupy only the lower energy bands, and the highest such occupied band is called valence band. The next highest energy band is termed the conduction band. The two most important and useful quanti ...
... semiconductor is fully and uniquely characterized by its band structure. At zero temperature, electrons occupy only the lower energy bands, and the highest such occupied band is called valence band. The next highest energy band is termed the conduction band. The two most important and useful quanti ...
Chapter 7 - Colby College Wiki
... • Heinrich Hertz (1888) discovered that light striking the surface of certain metals causes ejection of electrons - the photoelectric effect. • Electrons were only ejected if the frequency of the light (v) was above a certain threshold frequency (vo) • The number of electrons ejected were proportion ...
... • Heinrich Hertz (1888) discovered that light striking the surface of certain metals causes ejection of electrons - the photoelectric effect. • Electrons were only ejected if the frequency of the light (v) was above a certain threshold frequency (vo) • The number of electrons ejected were proportion ...
Many-Electron Atoms Thornton and Rex, Ch. 8
... Put first 5 electrons all with spin in same direction. First 2 electrons have ml =-2 and -1, etc. ...
... Put first 5 electrons all with spin in same direction. First 2 electrons have ml =-2 and -1, etc. ...
Chapter 5 Notes
... equation also leads to a mathematical expression called an atomic orbital An atomic orbital is the region of space in which there is a high probability of finding an electron ...
... equation also leads to a mathematical expression called an atomic orbital An atomic orbital is the region of space in which there is a high probability of finding an electron ...
Writing Words on Atoms
... A.B.: Prof. Stroud, this experiment has a long history – five years ago it was proposed in “Nature”. Why did it take so long to realize it? C.R.S.: There were two principal hurdles to overcome. First, we needed an electromagnetic pulse one picosecond [i.e. 0.000 000 000 001 s] in duration that did n ...
... A.B.: Prof. Stroud, this experiment has a long history – five years ago it was proposed in “Nature”. Why did it take so long to realize it? C.R.S.: There were two principal hurdles to overcome. First, we needed an electromagnetic pulse one picosecond [i.e. 0.000 000 000 001 s] in duration that did n ...
Section 3: Modern Atomic Theory Atoms Section 3
... number of electrons. The electrons in an atom’s outer energy level are called valence electrons, which determine the chemical properties of an atom. The diagram below shows how many electrons can be found in each of the first four energy levels of an atom. ...
... number of electrons. The electrons in an atom’s outer energy level are called valence electrons, which determine the chemical properties of an atom. The diagram below shows how many electrons can be found in each of the first four energy levels of an atom. ...
Atomic Structure Zumdahl Chemistry Chapter 7
... Wolfgang Pauli (1900-1958)discovered that in a given atom no two electrons can have the same set of four quantum numbers Since electrons in the same orbital have the same value of the first three, this postulate says that they must have different values of spin. An orbital can only hold two electron ...
... Wolfgang Pauli (1900-1958)discovered that in a given atom no two electrons can have the same set of four quantum numbers Since electrons in the same orbital have the same value of the first three, this postulate says that they must have different values of spin. An orbital can only hold two electron ...
stage iii – learning plan - Woodland Hills School District
... What factors determine the types of chemical bonds that form between particles? In what ways has the theory of the atom changed over time due to technological improvements? ...
... What factors determine the types of chemical bonds that form between particles? In what ways has the theory of the atom changed over time due to technological improvements? ...
Periodic Table
... Hydrogen has 1 1s electron Helium adds another 1s Lithium must start 2s shell Boron starts 2p shell which holds 6 electrons ...
... Hydrogen has 1 1s electron Helium adds another 1s Lithium must start 2s shell Boron starts 2p shell which holds 6 electrons ...
Auger electron spectroscopy
.jpg?width=300)
Auger electron spectroscopy (AES; pronounced [oʒe] in French) is a common analytical technique used specifically in the study of surfaces and, more generally, in the area of materials science. Underlying the spectroscopic technique is the Auger effect, as it has come to be called, which is based on the analysis of energetic electrons emitted from an excited atom after a series of internal relaxation events. The Auger effect was discovered independently by both Lise Meitner and Pierre Auger in the 1920s. Though the discovery was made by Meitner and initially reported in the journal Zeitschrift für Physik in 1922, Auger is credited with the discovery in most of the scientific community. Until the early 1950s Auger transitions were considered nuisance effects by spectroscopists, not containing much relevant material information, but studied so as to explain anomalies in x-ray spectroscopy data. Since 1953 however, AES has become a practical and straightforward characterization technique for probing chemical and compositional surface environments and has found applications in metallurgy, gas-phase chemistry, and throughout the microelectronics industry.