Quantum Number Describes
... FrequencyThe number of waves that pass a point each second (the unit is the Hertz, Hz). One complete wave or cycle per. second = 1 Hz. VelocityDistance a peak moves in a unit of time. ...
... FrequencyThe number of waves that pass a point each second (the unit is the Hertz, Hz). One complete wave or cycle per. second = 1 Hz. VelocityDistance a peak moves in a unit of time. ...
The Periodic table
... A quantized property is a property that can have only certain values. The energy of an electron is quantized, only certain behavior patterns are allowed. ...
... A quantized property is a property that can have only certain values. The energy of an electron is quantized, only certain behavior patterns are allowed. ...
Quantum Numbe
... 1. Electrons have a dual nature – they can be both particles and waves - Bohr: an electron should be treated as a particle - Schroedinger: an electron should be treated as a wave ...
... 1. Electrons have a dual nature – they can be both particles and waves - Bohr: an electron should be treated as a particle - Schroedinger: an electron should be treated as a wave ...
ATOMIC STRUCTURE NOTES n hcZ E ℜ
... General Periodic Trends – descending a group atomic radii increase, and with s & p blocks they decrease from left to right across period. Period 6 is different, due to lanthanide contraction. The 4f orbitals are being occupied by the lanthanides, and these have poor shielding properties. The repulsi ...
... General Periodic Trends – descending a group atomic radii increase, and with s & p blocks they decrease from left to right across period. Period 6 is different, due to lanthanide contraction. The 4f orbitals are being occupied by the lanthanides, and these have poor shielding properties. The repulsi ...
unit 7 hw packet File
... nature of light. H. Identify and compare electron orbitals (s, p, d, f). I. Write electron configurations for both neutral atoms and ions using the Aufbau principle, Pauli exclusion principal, and Hund’s rule. J. Use electron configurations to predict chemical trends and behaviors of elements. K. De ...
... nature of light. H. Identify and compare electron orbitals (s, p, d, f). I. Write electron configurations for both neutral atoms and ions using the Aufbau principle, Pauli exclusion principal, and Hund’s rule. J. Use electron configurations to predict chemical trends and behaviors of elements. K. De ...
Lecture 5
... In general, terms can be determined by applying three Hund's rules. Hund's second rule: for a given spin, the term with the largest value of the total orbital angular momentum quantum number L, consistent with overall antisymmetrization, has the lowest energy. ...
... In general, terms can be determined by applying three Hund's rules. Hund's second rule: for a given spin, the term with the largest value of the total orbital angular momentum quantum number L, consistent with overall antisymmetrization, has the lowest energy. ...
3. Analysis of distribution functions
... examine principles of statistical physics, distribution functions and properties of electrons in metals and semiconductors. Prepare to answer the questions: What statistics can by applied to electrons in a metal? What statistics is applied to a non-degenerate system of microparticles? What statistic ...
... examine principles of statistical physics, distribution functions and properties of electrons in metals and semiconductors. Prepare to answer the questions: What statistics can by applied to electrons in a metal? What statistics is applied to a non-degenerate system of microparticles? What statistic ...
Electron Configuration Class Notes
... Energy moves in waves, but it can act as particles (photons). Louie de Broglie – “matter waves” Postulated that since light shows a “dual nature” – has wave properties as well as particulate properties, then matter should also be able to move - not only as particles - but also as waves! - this prope ...
... Energy moves in waves, but it can act as particles (photons). Louie de Broglie – “matter waves” Postulated that since light shows a “dual nature” – has wave properties as well as particulate properties, then matter should also be able to move - not only as particles - but also as waves! - this prope ...
Name
... (b)Given the photoelectron spectra below for phosphorus, P, and sulfur, S, which of the following best explains why the 2p peak for S is further to the left than the 2p peak for P, but the 3p peak for S is further to the right than the 3p peak for P? Circle your answer. I. S has a greater effective ...
... (b)Given the photoelectron spectra below for phosphorus, P, and sulfur, S, which of the following best explains why the 2p peak for S is further to the left than the 2p peak for P, but the 3p peak for S is further to the right than the 3p peak for P? Circle your answer. I. S has a greater effective ...
Chapter Summary
... point corresponding to the probability of finding the electron at that point. Atomic spectra Exciting a gas causes light to be emitted. The resulting emission spectrum is the fingerprint of the gas – lines are seen at specific wavelengths. A photon produced by an atom comes from an electron that mak ...
... point corresponding to the probability of finding the electron at that point. Atomic spectra Exciting a gas causes light to be emitted. The resulting emission spectrum is the fingerprint of the gas – lines are seen at specific wavelengths. A photon produced by an atom comes from an electron that mak ...
Double-Slit Experiment
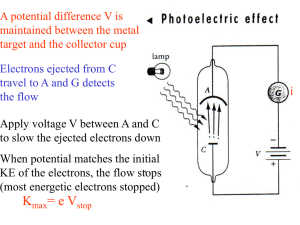
... electrons are emitted regardless of the intensity (amplitude) 3. For light with frequency greater than threshold frequency, the number of electrons emitted increases with intensity of light 4. For light with frequency greater than threshold frequency, the kinetic energy of the emitted electrons incr ...
... electrons are emitted regardless of the intensity (amplitude) 3. For light with frequency greater than threshold frequency, the number of electrons emitted increases with intensity of light 4. For light with frequency greater than threshold frequency, the kinetic energy of the emitted electrons incr ...
electron_theory
... Two types of experimental evidence which arose in the 1920s suggested an additional property of the electron. One was the closely spaced splitting of the hydrogen spectral lines, called fine structure. The other was the Stern-Gerlach experiment which showed in 1922 that a beam of silver atoms direct ...
... Two types of experimental evidence which arose in the 1920s suggested an additional property of the electron. One was the closely spaced splitting of the hydrogen spectral lines, called fine structure. The other was the Stern-Gerlach experiment which showed in 1922 that a beam of silver atoms direct ...
Document
... Electron configurations of the first transition element series are 4s23dn except for Cr and Cu, which are 4s13d5 and 4s13d10, respectively. These irregularities are a result of lower electronelectron repulsion energies. ...
... Electron configurations of the first transition element series are 4s23dn except for Cr and Cu, which are 4s13d5 and 4s13d10, respectively. These irregularities are a result of lower electronelectron repulsion energies. ...
The Quantum mechanical model of the atom
... atoms. n = principle quantum number = orbital’s energy level and relative size l = describe orbital’s shape (subshell) ml = describe orbital’s orientation in space (magnetic quantum number). ms= describes behaviour of a specific electron in an orbital (spin quantum number). ...
... atoms. n = principle quantum number = orbital’s energy level and relative size l = describe orbital’s shape (subshell) ml = describe orbital’s orientation in space (magnetic quantum number). ms= describes behaviour of a specific electron in an orbital (spin quantum number). ...
AP Exam Two Retake Qualifying Assignment
... If three electrons are available to fill three empty 2p atomic orbitals, how will the electrons be distributed in the three orbitals? a. one electron in each orbital b. two electrons in one orbital, one in another, none in the third c. three in one orbital, none in the other two d. Three electrons c ...
... If three electrons are available to fill three empty 2p atomic orbitals, how will the electrons be distributed in the three orbitals? a. one electron in each orbital b. two electrons in one orbital, one in another, none in the third c. three in one orbital, none in the other two d. Three electrons c ...
Draw atomic models showing the appropriate number of electrons
... 2. Type of bond that forms between two atoms of different electronegativities where electrons are unevenly shared 3. The electrical force of attraction that holds ions of opposite charge together 4. A chemical bond in which atoms are held together by their mutual attraction for two electrons they sh ...
... 2. Type of bond that forms between two atoms of different electronegativities where electrons are unevenly shared 3. The electrical force of attraction that holds ions of opposite charge together 4. A chemical bond in which atoms are held together by their mutual attraction for two electrons they sh ...
Modern Physics - Politechnika Wrocławska
... If the energy of a photon is less than the work function f, the photon cannot give enough energy to the electron to leave the surface Kmax does not depend on light intensity, because doubling the number of photons would only double the number of electrons and not double their energy Kmax increases w ...
... If the energy of a photon is less than the work function f, the photon cannot give enough energy to the electron to leave the surface Kmax does not depend on light intensity, because doubling the number of photons would only double the number of electrons and not double their energy Kmax increases w ...
Auger electron spectroscopy
.jpg?width=300)
Auger electron spectroscopy (AES; pronounced [oʒe] in French) is a common analytical technique used specifically in the study of surfaces and, more generally, in the area of materials science. Underlying the spectroscopic technique is the Auger effect, as it has come to be called, which is based on the analysis of energetic electrons emitted from an excited atom after a series of internal relaxation events. The Auger effect was discovered independently by both Lise Meitner and Pierre Auger in the 1920s. Though the discovery was made by Meitner and initially reported in the journal Zeitschrift für Physik in 1922, Auger is credited with the discovery in most of the scientific community. Until the early 1950s Auger transitions were considered nuisance effects by spectroscopists, not containing much relevant material information, but studied so as to explain anomalies in x-ray spectroscopy data. Since 1953 however, AES has become a practical and straightforward characterization technique for probing chemical and compositional surface environments and has found applications in metallurgy, gas-phase chemistry, and throughout the microelectronics industry.