Chemistry Name______________________________________
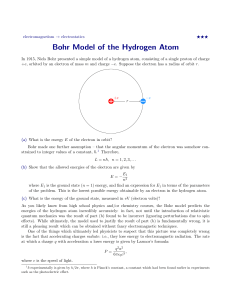
... While there are many different orbits they can only occupy one at a time. They will gain energy to jump to higher orbit and lose energy to fall to lower lowest energy for atom (all electrons in orbits closest to nucleus) couldnot explain other atom’s spectra couldnot account for chemical behavior of ...
... While there are many different orbits they can only occupy one at a time. They will gain energy to jump to higher orbit and lose energy to fall to lower lowest energy for atom (all electrons in orbits closest to nucleus) couldnot explain other atom’s spectra couldnot account for chemical behavior of ...
Scanning Electron Microscopy / Electron Probe X
... kinetic energy. Due to this low energy, only SE’s that are created near the surface can exit the sample and can be detected. Any variation in topography of the surface will change the yield of SE’s. This yield depends on the tilt angle of a surface, the enhanced emission at edges and small particles ...
... kinetic energy. Due to this low energy, only SE’s that are created near the surface can exit the sample and can be detected. Any variation in topography of the surface will change the yield of SE’s. This yield depends on the tilt angle of a surface, the enhanced emission at edges and small particles ...
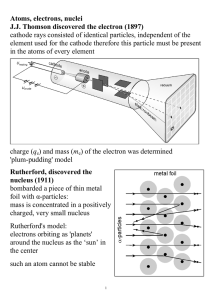
Atoms, electrons, nuclei J.J. Thomson discovered the electron (1897
... electron, and h is the Planck constant. Davisson and Germer (1927) used electron beams to induce diffraction through a thin metal foil: interference interference phenomena have been shown with various other particles: duality is a general characteristic of matter Propagation law of free electrons st ...
... electron, and h is the Planck constant. Davisson and Germer (1927) used electron beams to induce diffraction through a thin metal foil: interference interference phenomena have been shown with various other particles: duality is a general characteristic of matter Propagation law of free electrons st ...
Electron Configurations
... Principle we can not know the exact position and motion of electrons with complete certainty. • We can only describe the probable locations of electrons. • We will describe the location of electrons when the atom is at its lowest energy . ...
... Principle we can not know the exact position and motion of electrons with complete certainty. • We can only describe the probable locations of electrons. • We will describe the location of electrons when the atom is at its lowest energy . ...
AP Chem II Instructor: Mr. Malasky Name Period ______ Due Date
... ____ 1. The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that a. electrons have no momentum b. the position of an electron is impossible to determine c. the faster an electron moves, the more unreliable is its energy d. the momentum and the position of an electron cannot be precisely defined simultaneous ...
... ____ 1. The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that a. electrons have no momentum b. the position of an electron is impossible to determine c. the faster an electron moves, the more unreliable is its energy d. the momentum and the position of an electron cannot be precisely defined simultaneous ...
Atomic Radius and Ionization Energy
... • The pattern of properties within a period repeats as you move across a period from left to right… When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their physical and chemical properties ...
... • The pattern of properties within a period repeats as you move across a period from left to right… When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their physical and chemical properties ...
Chapter 5 Worksheet 1
... Chapter 5 Worksheet 1 – Key 1. State Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle as it pertains to atomic theory. It is impossible to determine the exact location and momentum of a moving object at the same time. 2. Why does the observation of a very small object such as an electron cause the electron to hav ...
... Chapter 5 Worksheet 1 – Key 1. State Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle as it pertains to atomic theory. It is impossible to determine the exact location and momentum of a moving object at the same time. 2. Why does the observation of a very small object such as an electron cause the electron to hav ...
Modern Model of the Atom
... atom can have the same four quantum numbers Hund’s rule: every orbital in a subshell is singly occupied with one electron before any one orbital is doubly occupied, and all electrons in singly occupied orbitals have the same spin. ...
... atom can have the same four quantum numbers Hund’s rule: every orbital in a subshell is singly occupied with one electron before any one orbital is doubly occupied, and all electrons in singly occupied orbitals have the same spin. ...
Periodic Properties of the Elements
... build ground state electron configuration for other elements. ...
... build ground state electron configuration for other elements. ...
Pauli Exclusion Principle
... The aufbau principle is really a thought process in which we think about building up an atom from the one that preceeds it in atomic number, by adding a proton and neutrons to the nucleus and one electron to the appropriate atomic orbital. There are some exceptions to the to the aufbau principle. T ...
... The aufbau principle is really a thought process in which we think about building up an atom from the one that preceeds it in atomic number, by adding a proton and neutrons to the nucleus and one electron to the appropriate atomic orbital. There are some exceptions to the to the aufbau principle. T ...
Atoms, electrons, nuclei J.J. Thomson discovered the electron (1897
... through a thin metal foil: interference interference phenomena have been shown with various other particles: duality is a general characteristic of matter Bohr's model (incorrect, but useful) electrons in an atom can only occupy certain distinct orbits around the nucleus: no radiation atoms radiate ...
... through a thin metal foil: interference interference phenomena have been shown with various other particles: duality is a general characteristic of matter Bohr's model (incorrect, but useful) electrons in an atom can only occupy certain distinct orbits around the nucleus: no radiation atoms radiate ...
Louie de Broglie
... describe the properties, such as the energy level and shape (s, p, d or f), and Orientation of the atomic orbitals. ...
... describe the properties, such as the energy level and shape (s, p, d or f), and Orientation of the atomic orbitals. ...
Constructive Interference
... Explanation: quantum superposition electrons can be in two places at once! Electron at a definite location Single electron at a superposition of two locations ...
... Explanation: quantum superposition electrons can be in two places at once! Electron at a definite location Single electron at a superposition of two locations ...
Electron-beam lithography

Electron-beam lithography (often abbreviated as e-beam lithography) is the practice of scanning a focused beam of electrons to draw custom shapes on a surface covered with an electron-sensitive film called a resist (""exposing""). The electron beam changes the solubility of the resist, enabling selective removal of either the exposed or non-exposed regions of the resist by immersing it in a solvent (""developing""). The purpose, as with photolithography, is to create very small structures in the resist that can subsequently be transferred to the substrate material, often by etching.The primary advantage of electron-beam lithography is that it can draw custom patterns (direct-write) with sub-10 nm resolution. This form of maskless lithography has high resolution and low throughput, limiting its usage to photomask fabrication, low-volume production of semiconductor devices, and research & development.