Energy level
... Explanation of atomic spectra • When we write electron configurations, we are writing the lowest energy. • The energy level, and where the electron starts from, is called it’s ground state the lowest energy level. ...
... Explanation of atomic spectra • When we write electron configurations, we are writing the lowest energy. • The energy level, and where the electron starts from, is called it’s ground state the lowest energy level. ...
Topic 12.1 Electron Configuration
... The principle quantum number (shell): electrons occupy the specific energy levels. The angular momentum quantum number (orbital shape): specifies the shape of the orbital. The magnetic quantum number (orbital orientation): specifies how this shape is arranged in three dimensions around the nucleus. ...
... The principle quantum number (shell): electrons occupy the specific energy levels. The angular momentum quantum number (orbital shape): specifies the shape of the orbital. The magnetic quantum number (orbital orientation): specifies how this shape is arranged in three dimensions around the nucleus. ...
amu (atomic mass unit): a unit used to express very small masses
... Niels Bohr's ideas of electron distribution within the atom are useful concepts and laid the foundation for much of the later progress in understanding atomic structure. But, as is the case with many theories, Bohr's assumptions have had to be modified. Difficulty arose in applying the theory to at ...
... Niels Bohr's ideas of electron distribution within the atom are useful concepts and laid the foundation for much of the later progress in understanding atomic structure. But, as is the case with many theories, Bohr's assumptions have had to be modified. Difficulty arose in applying the theory to at ...
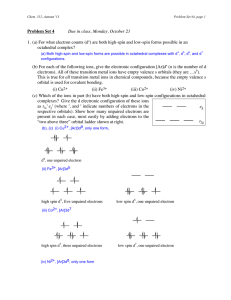
Chem312 Au03 Problem Set 4
... because a photon can be absorbed by promotion of one electron from the t2g set of orbitals to the t2g eg set. In a diagram like the one at right, add ground state excited state electrons to represent the ground state and the lowest energy excited state. When you put the electrons in, you should foll ...
... because a photon can be absorbed by promotion of one electron from the t2g set of orbitals to the t2g eg set. In a diagram like the one at right, add ground state excited state electrons to represent the ground state and the lowest energy excited state. When you put the electrons in, you should foll ...
Chem 115 POGIL Worksheet - Week 10 Periodic Trends Why? The
... Across the periodic table, sizes of atoms show the following trends, with many irregularities: Size increases down a group. The outermost electrons are in successively more extensive orbitals as n increases. Size decreases across a period. Electrons are added to the same shell and do not shield one ...
... Across the periodic table, sizes of atoms show the following trends, with many irregularities: Size increases down a group. The outermost electrons are in successively more extensive orbitals as n increases. Size decreases across a period. Electrons are added to the same shell and do not shield one ...
Electron Configuration
... This makes sense because we know that the third energy level would have 3 sublevels; an s sublevel with one orbital, a p sublevel with 3 orbitals and a d sublevel with 5 orbitals. 1 + 3 + 5 = 9, so the formula n2 works! ...
... This makes sense because we know that the third energy level would have 3 sublevels; an s sublevel with one orbital, a p sublevel with 3 orbitals and a d sublevel with 5 orbitals. 1 + 3 + 5 = 9, so the formula n2 works! ...
Electrical Conductivity: Classical Electron and Quantum Mechanical
... Electrical conductivity is one of the physical plastics, rubber etc, with no free electron, are bad properties of a material which depends on structure conductors/insulators of electricity. Conduction of of that material and hence on bonds that held the electricity through a material depends on numb ...
... Electrical conductivity is one of the physical plastics, rubber etc, with no free electron, are bad properties of a material which depends on structure conductors/insulators of electricity. Conduction of of that material and hence on bonds that held the electricity through a material depends on numb ...
Atomic Theory Notes Packet
... 4. The energy transitions you have seen occurred when the electrons fell back to the second energy level. Transitions back to the first level were not seen since they are in the ultraviolet region. 5. Use these values to construct the energy level diagram for hydrogen on the back of this page. For t ...
... 4. The energy transitions you have seen occurred when the electrons fell back to the second energy level. Transitions back to the first level were not seen since they are in the ultraviolet region. 5. Use these values to construct the energy level diagram for hydrogen on the back of this page. For t ...
Chap12_Multielectron Atoms_Notes_s10
... the states having the lowest energy being filled first. Hydrogen has only one electron, so the electron goes into a 1s state. The spin can be either up or down, since the energy is independent of spin (in the absence of a magnetic field). In helium (He), Z = 2. The second electron also goes into a 1 ...
... the states having the lowest energy being filled first. Hydrogen has only one electron, so the electron goes into a 1s state. The spin can be either up or down, since the energy is independent of spin (in the absence of a magnetic field). In helium (He), Z = 2. The second electron also goes into a 1 ...
PPT
... Just after the slit, the y-position has an uncertainty of about a/2. Therefore py must have an uncertainty Dpy 2/a. This corresponds to a change of direction by an angle, q = Dpy / p = 2/ap. Using p = h/l, we have q = l/(pa). This is almost the diffraction answer: q = l/a. The extra factor of ...
... Just after the slit, the y-position has an uncertainty of about a/2. Therefore py must have an uncertainty Dpy 2/a. This corresponds to a change of direction by an angle, q = Dpy / p = 2/ap. Using p = h/l, we have q = l/(pa). This is almost the diffraction answer: q = l/a. The extra factor of ...
Period #2 Notes: Electronic Structure of Atoms
... positive side with relatively few electrons, and a negative side with relatively many electrons. The inter-attraction between the opposite poles of different molecules is called van der Waals bonding. Usually, the strength of such bonds is very small relative to the strengths of the primary bonds. A ...
... positive side with relatively few electrons, and a negative side with relatively many electrons. The inter-attraction between the opposite poles of different molecules is called van der Waals bonding. Usually, the strength of such bonds is very small relative to the strengths of the primary bonds. A ...
SAMPLE midterm with solutions
... The quantum Hall effect is robust because it exists so long as there are edge states at opposite sides of the sample, which carry current in one direction only and are in separate equilibrium. The states on a single edge are chiral, that is, they propagate only in one direction. Therefore even if an ...
... The quantum Hall effect is robust because it exists so long as there are edge states at opposite sides of the sample, which carry current in one direction only and are in separate equilibrium. The states on a single edge are chiral, that is, they propagate only in one direction. Therefore even if an ...
Electron-beam lithography

Electron-beam lithography (often abbreviated as e-beam lithography) is the practice of scanning a focused beam of electrons to draw custom shapes on a surface covered with an electron-sensitive film called a resist (""exposing""). The electron beam changes the solubility of the resist, enabling selective removal of either the exposed or non-exposed regions of the resist by immersing it in a solvent (""developing""). The purpose, as with photolithography, is to create very small structures in the resist that can subsequently be transferred to the substrate material, often by etching.The primary advantage of electron-beam lithography is that it can draw custom patterns (direct-write) with sub-10 nm resolution. This form of maskless lithography has high resolution and low throughput, limiting its usage to photomask fabrication, low-volume production of semiconductor devices, and research & development.