Chemical Assay of Serum, Plasma, or Whole Blood
... • Enzymes are proteins produced in cells. • Catalysts for chemical reactions. • Most enzymes are formed and function intracellularly. • Blood levels should be low in a healthy animal. • The blood level can increase if the enzyme has leaked out of damaged cells. • Substrates are substances enzymes he ...
... • Enzymes are proteins produced in cells. • Catalysts for chemical reactions. • Most enzymes are formed and function intracellularly. • Blood levels should be low in a healthy animal. • The blood level can increase if the enzyme has leaked out of damaged cells. • Substrates are substances enzymes he ...
ANTIDIABETICS AND HYPOGLYCEMICS
... after lente insulin (Intermediate-acting overdose), may persist for up to 53 hours after insulin glargine (Long-acting) overdose, and may persist up to 6 days after ultralente insulin overdose. • Death after insulin overdose cannot be correlated directly with either the dose or ...
... after lente insulin (Intermediate-acting overdose), may persist for up to 53 hours after insulin glargine (Long-acting) overdose, and may persist up to 6 days after ultralente insulin overdose. • Death after insulin overdose cannot be correlated directly with either the dose or ...
File
... 4. The ___pineal gland_______ helps to regulate the sleep-wake cycle. 5. ___Hormones________ (from the Greek word meaning “to excite”) flow into the bloodstream in order to excite the functioning of target organs. 6. The _______adrenal glands_________, located at the top of each kidney, stimulate th ...
... 4. The ___pineal gland_______ helps to regulate the sleep-wake cycle. 5. ___Hormones________ (from the Greek word meaning “to excite”) flow into the bloodstream in order to excite the functioning of target organs. 6. The _______adrenal glands_________, located at the top of each kidney, stimulate th ...
Endocrinology and Metabolism in Intensive care
... • Elevated glucose levels also predicted increased mortality and length of ICU and hospital stay of trauma patients and were associated with infectious morbidity Conclusions J Trauma 2003; 55:33—38. 2004; 56:1058—1062. ...
... • Elevated glucose levels also predicted increased mortality and length of ICU and hospital stay of trauma patients and were associated with infectious morbidity Conclusions J Trauma 2003; 55:33—38. 2004; 56:1058—1062. ...
Case Answers
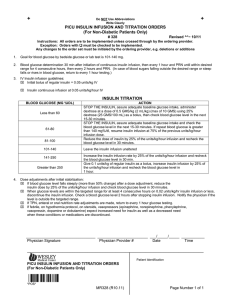
... DKA resolution. Once DKA is resolved (blood glucose less than 200 mg/dL and at least two of the following: serum bicarbonate of 15 mEq/L or greater, pH greater than 7.3, and normal anion gap) and the patient is able to eat, several dose insulins can be initiated with a long-acting subcutaneous insul ...
... DKA resolution. Once DKA is resolved (blood glucose less than 200 mg/dL and at least two of the following: serum bicarbonate of 15 mEq/L or greater, pH greater than 7.3, and normal anion gap) and the patient is able to eat, several dose insulins can be initiated with a long-acting subcutaneous insul ...
04 Endocrine and Cell Communication
... 1. Endocrine signals are produced by endocrine cells that release signaling molecules, which are specific and can travel long distances through the blood to reach all parts of the body. illustrative example-insulin ...
... 1. Endocrine signals are produced by endocrine cells that release signaling molecules, which are specific and can travel long distances through the blood to reach all parts of the body. illustrative example-insulin ...
Blood Glucose
... The peripheral tissues also contribute to the maintenance of normal blood level by using glucose for their energy requirement after ingestion and absorption of carbohydrates 60 % of absorbed glucose is transported to the liver. ...
... The peripheral tissues also contribute to the maintenance of normal blood level by using glucose for their energy requirement after ingestion and absorption of carbohydrates 60 % of absorbed glucose is transported to the liver. ...
Endocrine System
... are "Chemical Messengers." They are released from organs or glands in the body and travel through the blood stream. ...
... are "Chemical Messengers." They are released from organs or glands in the body and travel through the blood stream. ...
Control of blood glucose
... hypothalamus promote satiety: the appetite centre has an insulindriven ‘off’ button ...
... hypothalamus promote satiety: the appetite centre has an insulindriven ‘off’ button ...
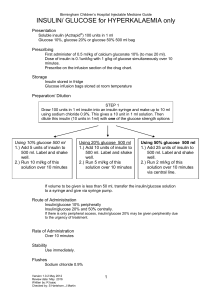
INSULIN/ GLUCOSE for HYPERKALAEMIA only
... First administer of 0.5 ml/kg of calcium gluconate 10% (to max 20 ml). Dose of insulin is 0.1unit/kg with 1 g/kg of glucose simultaneously over 10 minutes. Prescribe on the infusion section of the drug chart. ...
... First administer of 0.5 ml/kg of calcium gluconate 10% (to max 20 ml). Dose of insulin is 0.1unit/kg with 1 g/kg of glucose simultaneously over 10 minutes. Prescribe on the infusion section of the drug chart. ...
Diabetic Emergencies
... By converting Glycogen stored in the liver to glucose How? The pancreas produces “Glucagon” which releases Glycogen stored in the liver as glucose How do diabetic patients benefit from this? ...
... By converting Glycogen stored in the liver to glucose How? The pancreas produces “Glucagon” which releases Glycogen stored in the liver as glucose How do diabetic patients benefit from this? ...
Diabetes
... – Food eaten and digested in stomach – broken down into glucose – blood sugar levels rise – Insulin made by the pancreas acts as a transporter. Moves the sugar from the blood into body cells for use now or at a later stage – which then lowers the blood sugar. ...
... – Food eaten and digested in stomach – broken down into glucose – blood sugar levels rise – Insulin made by the pancreas acts as a transporter. Moves the sugar from the blood into body cells for use now or at a later stage – which then lowers the blood sugar. ...
Diabetes Medication
... Because you are taking a drug that combines two medications it is possible you will have side effects from both types of drugs. These can include nausea, low blood sugar, weight gain, rash, diarrhea, excess gas, loss of appetite, liver damage, fluid retention/swelling. The purpose of this patient ed ...
... Because you are taking a drug that combines two medications it is possible you will have side effects from both types of drugs. These can include nausea, low blood sugar, weight gain, rash, diarrhea, excess gas, loss of appetite, liver damage, fluid retention/swelling. The purpose of this patient ed ...
Shawn Smith`s notes 12-06
... Causes cells to increase glucose uptake (move glucose across cell membrane into the cytosol). – Cells burn more glucose Causes liver to convert glucose to glycogen 2. Glucagon- released when [glucose] blood gets too low. Effects of Glucagon: Causes cells to burn fat as fuel instead of glucose ...
... Causes cells to increase glucose uptake (move glucose across cell membrane into the cytosol). – Cells burn more glucose Causes liver to convert glucose to glycogen 2. Glucagon- released when [glucose] blood gets too low. Effects of Glucagon: Causes cells to burn fat as fuel instead of glucose ...
Diabetes Questions
... c) vessel damage from beta cell fragments d) skin damage from repeated insulin injections ...
... c) vessel damage from beta cell fragments d) skin damage from repeated insulin injections ...
Aalborg Universitet
... Intravenous (IV) insulin-treatment protocols to manage blood glucose in critically ill patients in the ICU vary widely. They have different heuristics or use modeling techniques that are not based on reproducible methods. These protocols will generate different dosing recommendations which may lead ...
... Intravenous (IV) insulin-treatment protocols to manage blood glucose in critically ill patients in the ICU vary widely. They have different heuristics or use modeling techniques that are not based on reproducible methods. These protocols will generate different dosing recommendations which may lead ...
Admitted Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction with Diabetes Pre-printed Order Sheet
... Admitted Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction with Diabetes Pre-printed Order Sheet These orders are to be used as a guideline and do not replace sound clinical judgment and professional practice standards. Patient allergy and contraindications must be considered when completing these orders. S ...
... Admitted Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction with Diabetes Pre-printed Order Sheet These orders are to be used as a guideline and do not replace sound clinical judgment and professional practice standards. Patient allergy and contraindications must be considered when completing these orders. S ...
Maintaining homeostasis
... Positive feedback reinforces a stimulus to produce an even greater response. For example, in mammals oxytocin causes the release of milk, causing greater suckling by offspring, which stimulates the release of ...
... Positive feedback reinforces a stimulus to produce an even greater response. For example, in mammals oxytocin causes the release of milk, causing greater suckling by offspring, which stimulates the release of ...
View/Download PDF
... immune system. The company has perfected the immunology and technology to take a patient’s own dendritic cells (DC) from their blood, modify the cells through the use of small interfering oligonucleotides, and vaccinate the patient by injection of these modified cells under the skin with a small nee ...
... immune system. The company has perfected the immunology and technology to take a patient’s own dendritic cells (DC) from their blood, modify the cells through the use of small interfering oligonucleotides, and vaccinate the patient by injection of these modified cells under the skin with a small nee ...
Lab Blood Glucose & Diabetes
... break down glycogen into glucose and release glucose into blood – Signals liver cells to convert amino acids and glycerol into glucose and release glucose into blood ...
... break down glycogen into glucose and release glucose into blood – Signals liver cells to convert amino acids and glycerol into glucose and release glucose into blood ...
Artificial pancreas
The artificial pancreas is a technology in development to help people with diabetes automatically control their blood glucose level by providing the substitute endocrine functionality of a healthy pancreas.There are several important exocrine (digestive) and endocrine (hormonal) functions of the pancreas, but it is the lack of insulin production which is the motivation to develop a substitute. While the current state of insulin replacement therapy is appreciated for its life-saving capability, the task of manually managing the blood sugar level with insulin alone is arduous and inadequate.The goal of the artificial pancreas is two-fold:to improve insulin replacement therapy until glycemic control is practically normal as evident by the avoidance of the complications of hyperglycemia, and to ease the burden of therapy for the insulin-dependent.Different approaches under consideration include: the medical equipment approach—using an insulin pump under closed loop control using real-time data from a continuous blood glucose sensor. the bioengineering approach—the development of a bio-artificial pancreas consisting of a biocompatible sheet of encapsulated beta cells. When surgically implanted, the islet sheet will behave as the endocrine pancreas and will be viable for years. the gene therapy approach—the therapeutic infection of a diabetic person by a genetically engineered virus which causes a DNA change of intestinal cells to become insulin-producing cells.