9 The AMP-activated protein kinase: more than an energy sensor
... AMP concentration are directly related to changes in ATP concentrations. At any time, intracellular ATP concentrations reflect the balance between energy supply-and-demand. In most cells, ATP supply relies on mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, whereas ATP demand depends on the energy required ...
... AMP concentration are directly related to changes in ATP concentrations. At any time, intracellular ATP concentrations reflect the balance between energy supply-and-demand. In most cells, ATP supply relies on mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, whereas ATP demand depends on the energy required ...
Gluconeogenesis
... Gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of glucose from precursors that are not sugars, like lactate, pyruvate, glycerol or glycogenic amino acids. The synthesis of glucose from other sugars simply is not gluconeogenesis. The neo means de novo from non-carbohydrate molecules. (By the way, what was a carbo ...
... Gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of glucose from precursors that are not sugars, like lactate, pyruvate, glycerol or glycogenic amino acids. The synthesis of glucose from other sugars simply is not gluconeogenesis. The neo means de novo from non-carbohydrate molecules. (By the way, what was a carbo ...
Evolution of the Aldose Reductase-Related Gecko Eye Lens Protein
... component (20%) in the eye lens of the gecko Lepidodactylus lugubris. Limited peptide sequence analysis earlier revealed that it belongs to the aldo-keto reductase superfamily, as does the frog lens -crystallin. We have now determined the complete cDNA sequence of Bcrystallin and established that ...
... component (20%) in the eye lens of the gecko Lepidodactylus lugubris. Limited peptide sequence analysis earlier revealed that it belongs to the aldo-keto reductase superfamily, as does the frog lens -crystallin. We have now determined the complete cDNA sequence of Bcrystallin and established that ...
©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies
... Both starch and glycogen are polysaccharides used for storage, but cellulose is used for structure. Cellulose is a major cell wall component of plants. Cellulose is not digestible by humans, but herbivores such as cows, deer, and horses have developed specialized digestive systems that can break dow ...
... Both starch and glycogen are polysaccharides used for storage, but cellulose is used for structure. Cellulose is a major cell wall component of plants. Cellulose is not digestible by humans, but herbivores such as cows, deer, and horses have developed specialized digestive systems that can break dow ...
Analysis of 25 underivatized amino acids in human plasma using
... identity of an analyte with a much higher degree of certainty than a standard, high-resolution single quadrupole mass spectrometer. With the exception of isobaric molecules such as leucine and isoleucine, the mass-to-charge (m/z) of amino acids can be verified to within 1–5 ppm, reducing misidentifi ...
... identity of an analyte with a much higher degree of certainty than a standard, high-resolution single quadrupole mass spectrometer. With the exception of isobaric molecules such as leucine and isoleucine, the mass-to-charge (m/z) of amino acids can be verified to within 1–5 ppm, reducing misidentifi ...
Recycling of vitamin B12 and NAD+ within the Pdu
... The cobalt atom in cobalamins can exist under three main formal oxidation states, Co+3, Co+2, and Co+1, which display quite different chemical properties. Roughly speaking, Co+3 appears as an electrophile, Co+2 as a radical, and Co+1 as a nucleophile. Oxidoreductive conversions between the three oxi ...
... The cobalt atom in cobalamins can exist under three main formal oxidation states, Co+3, Co+2, and Co+1, which display quite different chemical properties. Roughly speaking, Co+3 appears as an electrophile, Co+2 as a radical, and Co+1 as a nucleophile. Oxidoreductive conversions between the three oxi ...
The Chemical Composition of the Cell Wall in some Gram
... In most cases strains of known origin have been used, either from the NCTC or NCIB. These were checked for purity, but not investigated further. Strains of Corynebacterium diphtheriae had been isolated from cases, and had the typical morphology and fermentation reactions. Strains of C . hofmanni iso ...
... In most cases strains of known origin have been used, either from the NCTC or NCIB. These were checked for purity, but not investigated further. Strains of Corynebacterium diphtheriae had been isolated from cases, and had the typical morphology and fermentation reactions. Strains of C . hofmanni iso ...
By-product Utilization in Potato
... stock or processing. The utilization of by-products contributes to reduced amount of waste and thus to sustainable production. ...
... stock or processing. The utilization of by-products contributes to reduced amount of waste and thus to sustainable production. ...
Evidence for the presence of photorespiration in desiccation
... ‘recycling’, photorespiration does not appear to be solely an energy-consuming process that plants use to cope with the oxygenase activity of Rubisco. Many authors have suggested different roles for the photorespiratory cycle other than carbon recovery. Tobacco plants grown for a long time in low O2 ...
... ‘recycling’, photorespiration does not appear to be solely an energy-consuming process that plants use to cope with the oxygenase activity of Rubisco. Many authors have suggested different roles for the photorespiratory cycle other than carbon recovery. Tobacco plants grown for a long time in low O2 ...
Structure, function and selective inhibition of bacterial acetyl
... De novo fatty acid biosynthesis is an important metabolic process ubiquitously performed throughout the biological world. The products produced from this pathway are required in numerous biological processes such as bacterial quorum sensing and protein modification. Crucially, fatty acids are also r ...
... De novo fatty acid biosynthesis is an important metabolic process ubiquitously performed throughout the biological world. The products produced from this pathway are required in numerous biological processes such as bacterial quorum sensing and protein modification. Crucially, fatty acids are also r ...
galanin - Personal Home Pages (at UEL)
... •Galanin is widely distributed in both the central and the peripheral nervous systems. •In the CNS: hypothalamus/hippocampus, brain stem, spinal cord. •In the peripheral organs: pancreas, adrenal gland, gastrointestinal tract, genital tract, urinary bladder ...
... •Galanin is widely distributed in both the central and the peripheral nervous systems. •In the CNS: hypothalamus/hippocampus, brain stem, spinal cord. •In the peripheral organs: pancreas, adrenal gland, gastrointestinal tract, genital tract, urinary bladder ...
Amino acid fluxes to and from seawater in axenic veliger larvae of a
... prior to use in 10 % HCl and given a final rinse in 50 '10 isopropyl alcohol in order to avoid problems with amino acid contamination. Filtered samples were frozen at -20 "C until analyzed. Changes in the concentrations of each amino acid with time were determined by reverse-phase HPLC analysis. The ...
... prior to use in 10 % HCl and given a final rinse in 50 '10 isopropyl alcohol in order to avoid problems with amino acid contamination. Filtered samples were frozen at -20 "C until analyzed. Changes in the concentrations of each amino acid with time were determined by reverse-phase HPLC analysis. The ...
Attachment 2 - Food Standards Australia New Zealand
... 35S gene promoter, derived from figwort mosaic virus (FMV). The 35S promoter is constitutively active in plants (Sheperd et al 1987; Richins et al 1987; Gowda et al 1989; Sanger et al 1990). The 3’ end of the pea rbcS E9 gene (E9 3’) terminates transcription and contains sequences that will direct t ...
... 35S gene promoter, derived from figwort mosaic virus (FMV). The 35S promoter is constitutively active in plants (Sheperd et al 1987; Richins et al 1987; Gowda et al 1989; Sanger et al 1990). The 3’ end of the pea rbcS E9 gene (E9 3’) terminates transcription and contains sequences that will direct t ...
Measurement of apolipoprotein E and amyloid β clearance rates in
... dementia[6]. Although the underlying cause of protein aggregation in these diseases remains unclear, it is likely due to abnormal proteostasis caused by alterations in protein production or clearance [7,8]. Therefore, the development of techniques that can assess protein dynamics in the brain are fu ...
... dementia[6]. Although the underlying cause of protein aggregation in these diseases remains unclear, it is likely due to abnormal proteostasis caused by alterations in protein production or clearance [7,8]. Therefore, the development of techniques that can assess protein dynamics in the brain are fu ...
Enzymatic
... 25. What region is the arrow pointing at in the enzyme? 26. What substance is the arrow pointing at which will enter the active site? 27. What protein is the arrow pointing at which catalyzes chemical reactions? 28. What is the result at the end of a chemical reaction? 29. We say that enzymes are sp ...
... 25. What region is the arrow pointing at in the enzyme? 26. What substance is the arrow pointing at which will enter the active site? 27. What protein is the arrow pointing at which catalyzes chemical reactions? 28. What is the result at the end of a chemical reaction? 29. We say that enzymes are sp ...
Optimizing cofactor availability for the production of recombinant
... production landscapes from microscale cultivations using 1 mM FeSO4-supplemented medium. Error bars are standard deviations from all measured clones of a landscape. Average activity from strains producing HRP alone was set to 100%. In addition to strong constitutive co-overexpression of either HEM1 ...
... production landscapes from microscale cultivations using 1 mM FeSO4-supplemented medium. Error bars are standard deviations from all measured clones of a landscape. Average activity from strains producing HRP alone was set to 100%. In addition to strong constitutive co-overexpression of either HEM1 ...
10.4 Factors That Affect Enzyme Activity, Continued
... There are two enzyme–substrate models: 1. In the Lock-and-key model, the active site is thought to be a rigid, inflexible shape that is an exact complement to the shape of the substrate. The substrate fits in the active site much like a key fits in a lock. 2. In the induced-fit model, the active sit ...
... There are two enzyme–substrate models: 1. In the Lock-and-key model, the active site is thought to be a rigid, inflexible shape that is an exact complement to the shape of the substrate. The substrate fits in the active site much like a key fits in a lock. 2. In the induced-fit model, the active sit ...
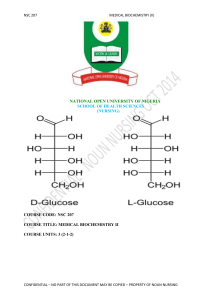
NSC 207 - National Open University of Nigeria
... The glycolytic pathway has a dual role (i) It degrades glucose to generate ATP and (ii) It provides building blocks for synthetic reactions. The rate of conversion of glucose into pyruvate is regulated to meet these 2 major cellular needs. Enzymes catalyzing essentially irreversible reactions are po ...
... The glycolytic pathway has a dual role (i) It degrades glucose to generate ATP and (ii) It provides building blocks for synthetic reactions. The rate of conversion of glucose into pyruvate is regulated to meet these 2 major cellular needs. Enzymes catalyzing essentially irreversible reactions are po ...
Glycoxidation of biological macromolecules: A critical
... cleared by scavenger receptors on macrophages and endothelial cells, to which its binding is not compromised by glycation, and subclasses of scavenger receptors specific for AGEs have been described (Schmidt et al. 1999). Furthermore, glycation and oxidation are by no means mutually exclusive natural ...
... cleared by scavenger receptors on macrophages and endothelial cells, to which its binding is not compromised by glycation, and subclasses of scavenger receptors specific for AGEs have been described (Schmidt et al. 1999). Furthermore, glycation and oxidation are by no means mutually exclusive natural ...
Cardosin A Molecular Determinants and Biosynthetic Pathways
... the Nicotiana tabacum one, this system was also validated for cardosin A expression and it allowed to conclude that the protein’s expression did not retrieved any phenotype to the cells or individuals. However, experiments conducted in BY-2 cells revealed to be inconclusive since cardosin A expressi ...
... the Nicotiana tabacum one, this system was also validated for cardosin A expression and it allowed to conclude that the protein’s expression did not retrieved any phenotype to the cells or individuals. However, experiments conducted in BY-2 cells revealed to be inconclusive since cardosin A expressi ...
Charakterisierung peroxisomaler und Lipid
... accumulation of nonpolar lipids and phospholipids upon growth on medium containing oleic acid as a sole carbon source. Ldh1p is thought to play a role in maintaining the lipid homeostasis in yeast by regulating both phospholipid and nonpolar lipid levels. It is known that the peroxisomal matrix prot ...
... accumulation of nonpolar lipids and phospholipids upon growth on medium containing oleic acid as a sole carbon source. Ldh1p is thought to play a role in maintaining the lipid homeostasis in yeast by regulating both phospholipid and nonpolar lipid levels. It is known that the peroxisomal matrix prot ...
The Chemical Composition of the Cell Wall in some
... In most cases strains of known origin have been used, either from the NCTC or NCIB. These were checked for purity, but not investigated further. Strains of Corynebacterium diphtheriae had been isolated from cases, and had the typical morphology and fermentation reactions. Strains of C . hofmanni iso ...
... In most cases strains of known origin have been used, either from the NCTC or NCIB. These were checked for purity, but not investigated further. Strains of Corynebacterium diphtheriae had been isolated from cases, and had the typical morphology and fermentation reactions. Strains of C . hofmanni iso ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.