Structure Determination and Sequence Analysis - Rose
... conditions of pH and ionic strength, and to the fact that crystal-packing contacts may distort the protein structure. NMR NMR is frequently used to determine the structure of organic molecules. It is much more difficult to use NMR to solve the structure of proteins, but it has been done for a number ...
... conditions of pH and ionic strength, and to the fact that crystal-packing contacts may distort the protein structure. NMR NMR is frequently used to determine the structure of organic molecules. It is much more difficult to use NMR to solve the structure of proteins, but it has been done for a number ...
Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen
... functional group (-COOH) is found on the end of the fatty acid that does NOT attach to glycerol. CIRCLE AND LABEL the carboxyl groups in the 2 fatty acids on this worksheet. Color the fatty acid chains the same colors for carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen as you did before. A special type of lipid called ...
... functional group (-COOH) is found on the end of the fatty acid that does NOT attach to glycerol. CIRCLE AND LABEL the carboxyl groups in the 2 fatty acids on this worksheet. Color the fatty acid chains the same colors for carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen as you did before. A special type of lipid called ...
Proteins and Enzymes Assessment Statements 7.5.1 Explain the
... substance than it needs. Many metabolic reactions occur in an assembly line type of process so that a specific end product can be achieved. Each step is catalyzed by a specific enzyme. When the end product is made in a sufficient quantity, the assembly line is shut down. This is usually done by inhi ...
... substance than it needs. Many metabolic reactions occur in an assembly line type of process so that a specific end product can be achieved. Each step is catalyzed by a specific enzyme. When the end product is made in a sufficient quantity, the assembly line is shut down. This is usually done by inhi ...
BIOCHEMISTRY WEBQUEST
... temperature. Notice how these have only single covalent bonds between their carbon atoms. 7) ____________________ fats originate from plants and are _________________ at room temperature. Notice how these have some double covalent bonds between their carbon atoms. 8) _____________________________ ar ...
... temperature. Notice how these have only single covalent bonds between their carbon atoms. 7) ____________________ fats originate from plants and are _________________ at room temperature. Notice how these have some double covalent bonds between their carbon atoms. 8) _____________________________ ar ...
Protein 1 File
... (1) bond lengths and angles – should be similar to those found in individual amino acids and small peptides (2) peptide bond – should be planer (3) overlaps – not permitted, pairs of atoms no closer than sum of their covalent radii (4) stabilization – have sterics that permit hydrogen bonding ...
... (1) bond lengths and angles – should be similar to those found in individual amino acids and small peptides (2) peptide bond – should be planer (3) overlaps – not permitted, pairs of atoms no closer than sum of their covalent radii (4) stabilization – have sterics that permit hydrogen bonding ...
The nature of matter
... charged electrons which move extremely fast. It is impossible to know where any electron is at any given time… ...
... charged electrons which move extremely fast. It is impossible to know where any electron is at any given time… ...
file
... fragment connected to hydrophobic fragment. • Spontaneously form sheets (lipid bilayers, membranes) in which all the hydrophilic ends align on the outside, and hydrophobic ends align on the inside. • Creates a very stable separation, not easy to pass through except for water and a few other small at ...
... fragment connected to hydrophobic fragment. • Spontaneously form sheets (lipid bilayers, membranes) in which all the hydrophilic ends align on the outside, and hydrophobic ends align on the inside. • Creates a very stable separation, not easy to pass through except for water and a few other small at ...
Protein Synthesis Bead Activity
... Protein Synthesis Bead Activity Let’s make proteins! Fill in the paragraph below and then follow the instructions to make a beaded protein. ________ is copied down as a form of RNA called ___________. This process is called __________________________________ and it occurs in the ____________________ ...
... Protein Synthesis Bead Activity Let’s make proteins! Fill in the paragraph below and then follow the instructions to make a beaded protein. ________ is copied down as a form of RNA called ___________. This process is called __________________________________ and it occurs in the ____________________ ...
Unit 1 exam Review
... 7. RESPONDS TO STIMULI: Organisms must respond to stimuli appropriately in order to stay alive Stimulus = anything in an organism’s external or internal environment that causes a reaction or response Response = a reaction to a stimulus Ex) if a shark smells blood in the water, it will respond by mo ...
... 7. RESPONDS TO STIMULI: Organisms must respond to stimuli appropriately in order to stay alive Stimulus = anything in an organism’s external or internal environment that causes a reaction or response Response = a reaction to a stimulus Ex) if a shark smells blood in the water, it will respond by mo ...
AP Biology - Membrane Structure
... Proteins embedded in membrane – specific receptor sites (area where they are – coated pits) ...
... Proteins embedded in membrane – specific receptor sites (area where they are – coated pits) ...
Review Problems #2 (Enzyme Review, Phosphatases
... 10) Name the cofactor required for hydroxylation of phenylalanine. Draw the structures of the three commonly observed forms of this cofactor. How are they related? ...
... 10) Name the cofactor required for hydroxylation of phenylalanine. Draw the structures of the three commonly observed forms of this cofactor. How are they related? ...
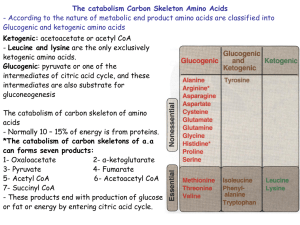
The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids
... The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids - According to the nature of metabolic end product amino acids are classified into Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids Ketogenic: acetoacetate or acetyl CoA - Leucine and lysine are the only exclusively ketogenic amino acids. Glucogenic: pyruvate or one of ...
... The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids - According to the nature of metabolic end product amino acids are classified into Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids Ketogenic: acetoacetate or acetyl CoA - Leucine and lysine are the only exclusively ketogenic amino acids. Glucogenic: pyruvate or one of ...
The Genetic Code
... The 4 different nucleotides in DNA (G, C, A, T) must code for 20 amino acids. So if: 1 nucleotide coded for 1 amino acid - we would only code for 4 amino acids 2 nucleotides coded for 1 amino acid - we would get 42 = 16 amino acids 3 nucleotides coded for 1 amino acid - we would get 43 = 64 combinat ...
... The 4 different nucleotides in DNA (G, C, A, T) must code for 20 amino acids. So if: 1 nucleotide coded for 1 amino acid - we would only code for 4 amino acids 2 nucleotides coded for 1 amino acid - we would get 42 = 16 amino acids 3 nucleotides coded for 1 amino acid - we would get 43 = 64 combinat ...
BI1
... R groups project from helix/side chains/part of active site (i.e. function of R groups) ...
... R groups project from helix/side chains/part of active site (i.e. function of R groups) ...
ATP
... living cell in a changing environment? 4. Buffers would aid the maintenance of homeostasis within a living cell in a changing environment by helping to keep the cell’s internal conditions stable. ...
... living cell in a changing environment? 4. Buffers would aid the maintenance of homeostasis within a living cell in a changing environment by helping to keep the cell’s internal conditions stable. ...
Identification of proteins co-purifying with scrapie infectivity
... Table shows PrP associated proteins which were identified in each spot after LC-MS/MS analysis. It also indicates the protein score, the number of matching peptides used for protein identification, the sequence, mass, m/z values and charge of each peptide. ...
... Table shows PrP associated proteins which were identified in each spot after LC-MS/MS analysis. It also indicates the protein score, the number of matching peptides used for protein identification, the sequence, mass, m/z values and charge of each peptide. ...
Study Guide Questions Midterm 2
... 1. What are proteins made up of? What are the differences among essential, non-‐essential, and conditionally essential amino acids? 2. Proteins are linked by what type of bond? 3. Name specific functio ...
... 1. What are proteins made up of? What are the differences among essential, non-‐essential, and conditionally essential amino acids? 2. Proteins are linked by what type of bond? 3. Name specific functio ...
Welcome to Biochemistry/Endocrinology
... 3. Receptor desensitization occurs. This process varies with the hormone. ...
... 3. Receptor desensitization occurs. This process varies with the hormone. ...
In vitro RNA-peptide co-evolution system for screening ATP
... Introduction: The advent of biological polymers was a key step for the emergence of life. Modern organisms use proteins to achieve energy harvest and transfer in various ways to sustain structural organization through reproduction of molecules. Whereas “evolvability” of the biological system is main ...
... Introduction: The advent of biological polymers was a key step for the emergence of life. Modern organisms use proteins to achieve energy harvest and transfer in various ways to sustain structural organization through reproduction of molecules. Whereas “evolvability” of the biological system is main ...
Regulation of Protein Synthesis (6.1)
... Heme Control of Globin Synthesis: Red blood cells are programmed to synthesize large amounts of globin. The globin chains, subsequent to translation, are assembled with heme into hemoglobin. If there is an insufficient supply of heme to insert into the newly synthesized globin chains, then translati ...
... Heme Control of Globin Synthesis: Red blood cells are programmed to synthesize large amounts of globin. The globin chains, subsequent to translation, are assembled with heme into hemoglobin. If there is an insufficient supply of heme to insert into the newly synthesized globin chains, then translati ...
Location and characterization of the three carbohydrate prosthetic
... The results obtained in this paper, which display the presence in protein HC of one O-glycosidic linkage and two N-glycosidic linkages, differ from those previously reported for the oq-microglobulin, which indicated the presence of three identical N-glycosidic linked carbohydrate chains without spec ...
... The results obtained in this paper, which display the presence in protein HC of one O-glycosidic linkage and two N-glycosidic linkages, differ from those previously reported for the oq-microglobulin, which indicated the presence of three identical N-glycosidic linked carbohydrate chains without spec ...
Trans-activation and DNA-binding properties of
... the basal vector GalO, by ~2- and 3-fold respectively (Fig. 2D). However, in the presence of the chimeric G-Soxl8 (160-255) plasmid, 8-Br-cAMP increased CAT expression -3.5-fold, whereas okadaic acid increased expression only 2-fold. These results, with respect to the effect of these phosphorylating ...
... the basal vector GalO, by ~2- and 3-fold respectively (Fig. 2D). However, in the presence of the chimeric G-Soxl8 (160-255) plasmid, 8-Br-cAMP increased CAT expression -3.5-fold, whereas okadaic acid increased expression only 2-fold. These results, with respect to the effect of these phosphorylating ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.