Crystal Structure of 4-Chlorobenzoate:CoA Ligase/Synthetase in the
... thioester formation from adenylated short or long chain fatty acids or adenylated benzoic acid derivatives. The nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs) are composed of numerous catalytic domains linked in a modular fashion, often within a single polypeptide that can be thousands of residues in leng ...
... thioester formation from adenylated short or long chain fatty acids or adenylated benzoic acid derivatives. The nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs) are composed of numerous catalytic domains linked in a modular fashion, often within a single polypeptide that can be thousands of residues in leng ...
amino acids - UniMAP Portal
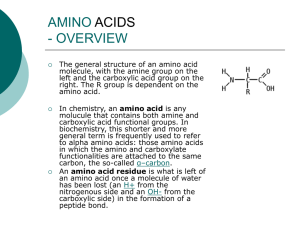
... functionalities are attached to the same carbon, the so-called α–carbon. An amino acid residue is what is left of an amino acid once a molecule of water has been lost (an H+ from the nitrogenous side and an OH- from the carboxylic side) in the formation of a peptide bond. ...
... functionalities are attached to the same carbon, the so-called α–carbon. An amino acid residue is what is left of an amino acid once a molecule of water has been lost (an H+ from the nitrogenous side and an OH- from the carboxylic side) in the formation of a peptide bond. ...
Studies on the Phosphorylation of the 58000 Dalton Early Region
... Phosphoamino acid determination. The area on SDS polyacrylamide gels containing the 58K band was excised, the gel piece was diced into small pieces and the protein was eluted for 24 h at 37 °C with constant shaking into a small volume of 0.05 M-ammonium bicarbonate containing 0.1% SDS. The gel fragm ...
... Phosphoamino acid determination. The area on SDS polyacrylamide gels containing the 58K band was excised, the gel piece was diced into small pieces and the protein was eluted for 24 h at 37 °C with constant shaking into a small volume of 0.05 M-ammonium bicarbonate containing 0.1% SDS. The gel fragm ...
Bioinformatics Tools Review ()
... the sequence above. Click on the link gi|1498054|gb|U64437.1|ZMU64437 (Zea mays novel protein mRNA, complete cds) to see the nucleotide sequence file. The sequence file is in Genbank format. Note that the accession number is U64437 and this sequence is an mRNA sequence. The nucleotide sequence U644 ...
... the sequence above. Click on the link gi|1498054|gb|U64437.1|ZMU64437 (Zea mays novel protein mRNA, complete cds) to see the nucleotide sequence file. The sequence file is in Genbank format. Note that the accession number is U64437 and this sequence is an mRNA sequence. The nucleotide sequence U644 ...
Problem Set 1 - Andrew.cmu.edu
... i) Sketch, on the same graph, the curves for the fraction protonated versus pH for all of the ionizable groups on the amino acid aspartic acid. ...
... i) Sketch, on the same graph, the curves for the fraction protonated versus pH for all of the ionizable groups on the amino acid aspartic acid. ...
Outline05 Enzymes - Napa Valley College
... energy captured from oxidation of substrates is used to make ATP (ADP + Pi → ATP) energy released from ATP hydrolysis powers energy-requiring processes ...
... energy captured from oxidation of substrates is used to make ATP (ADP + Pi → ATP) energy released from ATP hydrolysis powers energy-requiring processes ...
tRNA
... • Incorporated in only a few prokaryotic proteins – has its own tRNA, (codon UAG, normally “stop”), aaRS ...
... • Incorporated in only a few prokaryotic proteins – has its own tRNA, (codon UAG, normally “stop”), aaRS ...
Metabolism of erythrocytes
... non-enzymatic glycolysation (glycation)- sugar bonding to a protein normal level HbA1- 5%; a buildup of HbA1- increased glucose concentration the HbA1 level is proportional to average blood glucose concentration over previous weeks; in individuals with poorly controlled diabetes, increases in the qu ...
... non-enzymatic glycolysation (glycation)- sugar bonding to a protein normal level HbA1- 5%; a buildup of HbA1- increased glucose concentration the HbA1 level is proportional to average blood glucose concentration over previous weeks; in individuals with poorly controlled diabetes, increases in the qu ...
A New Signal Sequence for Recombinant Protein Secretion in
... site at the end of the signal sequence. This is efficiently processed by Kex2 protease, resulting in the secretion of high levels of proteins to the medium. However, the proteins that are having the internal accessible dibasic amino acids such as KR and RR in the coding region cannot be expressed us ...
... site at the end of the signal sequence. This is efficiently processed by Kex2 protease, resulting in the secretion of high levels of proteins to the medium. However, the proteins that are having the internal accessible dibasic amino acids such as KR and RR in the coding region cannot be expressed us ...
Biochemistry with Elements of Chemistry
... essay, matching and formulas may be included. The grade obtained from the final exam may be increased for students who are very active during seminars, labs and have got high grades from intermediate tests by the head of the Department. Academic honesty: Cheating will not be tolerated! The minimum p ...
... essay, matching and formulas may be included. The grade obtained from the final exam may be increased for students who are very active during seminars, labs and have got high grades from intermediate tests by the head of the Department. Academic honesty: Cheating will not be tolerated! The minimum p ...
1. Name of a subject Chemistry (1st year, Faculty of Medicine
... Amino acids, peptides, proteins: Amino acids – structure, classification, chemical properties, ionic properties, isoelectric point. Biogenic amines. Structure and properties of peptide bond. Natural peptides (glutathione, insulin) and synthetic peptides (Kevlar, aspartam). Primary, secondary, tertia ...
... Amino acids, peptides, proteins: Amino acids – structure, classification, chemical properties, ionic properties, isoelectric point. Biogenic amines. Structure and properties of peptide bond. Natural peptides (glutathione, insulin) and synthetic peptides (Kevlar, aspartam). Primary, secondary, tertia ...
4.2.1 Liver MS - Mrs Miller`s Blog
... long loop of Henlé or/ deep / wide, medulla ; very low water potential in medulla / AW ; A higher concentration of salts collecting duct more permeable to water ; large number of, water permeable channels / aquaporins, in collecting duct ; more sensitive to ADH / more ADH produced ; AVP ; e.g. other ...
... long loop of Henlé or/ deep / wide, medulla ; very low water potential in medulla / AW ; A higher concentration of salts collecting duct more permeable to water ; large number of, water permeable channels / aquaporins, in collecting duct ; more sensitive to ADH / more ADH produced ; AVP ; e.g. other ...
sv-lncs - School of Mathematical and Computer Sciences
... point in time, but rather consist of proteins that participate in a particular cellular process while binding to each other at different times and places, such as in different conditions or phases of the cell cycle, in different cellular compartments, etc. [2] Examples of functional modules include ...
... point in time, but rather consist of proteins that participate in a particular cellular process while binding to each other at different times and places, such as in different conditions or phases of the cell cycle, in different cellular compartments, etc. [2] Examples of functional modules include ...
Chapter 3: Amino Acids and Peptides
... molecules are non-polar and uncharged. Amino acids with this property are usually buried within the hydrophobic core of the protein. Aliphatic: carbon atoms are joined together in straight or branched open chains rather than in rings. Aromatic: contains an aromatic ring system. q Hydrophilic: tendin ...
... molecules are non-polar and uncharged. Amino acids with this property are usually buried within the hydrophobic core of the protein. Aliphatic: carbon atoms are joined together in straight or branched open chains rather than in rings. Aromatic: contains an aromatic ring system. q Hydrophilic: tendin ...
Principles of Biology Exam
... C. cell plate formation occurs D. spindle fibers, made of microtubules, begin to form 5. Before beginning mitosis, new DNA is synthesized in: A. S phase B. G1 phase C. G2 phase 6. Product of cyclic photophosphorylation is ____________. A. NADPH B. ATP C. NADH 7. The four stages of mitosis in correct ...
... C. cell plate formation occurs D. spindle fibers, made of microtubules, begin to form 5. Before beginning mitosis, new DNA is synthesized in: A. S phase B. G1 phase C. G2 phase 6. Product of cyclic photophosphorylation is ____________. A. NADPH B. ATP C. NADH 7. The four stages of mitosis in correct ...
Gene expression: Translation
... Fig. 6.6 - Three nearby insertions (+) restore the reading frame, ...
... Fig. 6.6 - Three nearby insertions (+) restore the reading frame, ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.