第六章 脂类代谢
... Essential Fatty Acids (EFA) • Linoleic, linolenic and arachidonic acids are called essential fatty acids, because they cannot be synthesized by the body and must be obtained ...
... Essential Fatty Acids (EFA) • Linoleic, linolenic and arachidonic acids are called essential fatty acids, because they cannot be synthesized by the body and must be obtained ...
Chemical Modifications and Kinetic Study of Ribonuclease Sa Active
... binds the anionic phosphate group of the substrate (Takahashi 1970). In contrary to RNase Ti, the activity of ribonuclease Sa is not affected by this reagent. Similarly diketene, a specific reagent for the second basic amino acid, lysine, does not inactivate ribonuclease Sa, either. Since we have el ...
... binds the anionic phosphate group of the substrate (Takahashi 1970). In contrary to RNase Ti, the activity of ribonuclease Sa is not affected by this reagent. Similarly diketene, a specific reagent for the second basic amino acid, lysine, does not inactivate ribonuclease Sa, either. Since we have el ...
Vitamins
... vitamin naturally by itself. This is vitamin D. All other vitamins that the body requires to function properly have to be derived from the diet. Lack of vitamins can have a serious affect on your health and may end in metabolic and other dysfunctions. ...
... vitamin naturally by itself. This is vitamin D. All other vitamins that the body requires to function properly have to be derived from the diet. Lack of vitamins can have a serious affect on your health and may end in metabolic and other dysfunctions. ...
University of Groningen Molecular basis of two novel
... Halogenated compounds are, however, not only of anthropogenic origin. Over 1500 organohalogens are known that are produced naturally (Odberg, 2002; Balschmitter, 2003). They range from volatile compounds such as methylchloride to antibiotics like vancomycin and chloramphenicol. Insight into the enzy ...
... Halogenated compounds are, however, not only of anthropogenic origin. Over 1500 organohalogens are known that are produced naturally (Odberg, 2002; Balschmitter, 2003). They range from volatile compounds such as methylchloride to antibiotics like vancomycin and chloramphenicol. Insight into the enzy ...
Standard for the presentation of nucleotide and amino acid
... signal sequences, when present, may have negative numbers, counting backwards starting with the amino acid next to number 1. Zero (0) is not used when the numbering of amino acids uses negative numbers to distinguish the mature protein. It shall be marked under the sequence every five amino acids. T ...
... signal sequences, when present, may have negative numbers, counting backwards starting with the amino acid next to number 1. Zero (0) is not used when the numbering of amino acids uses negative numbers to distinguish the mature protein. It shall be marked under the sequence every five amino acids. T ...
Mechanism of Succinyl
... nucleophilic than alcohols or amines • Thiols are also better leaving groups (pKa 89), which explains why the hydrolysis of thioesters under basic conditions is more rapid than ester hydrolysis ...
... nucleophilic than alcohols or amines • Thiols are also better leaving groups (pKa 89), which explains why the hydrolysis of thioesters under basic conditions is more rapid than ester hydrolysis ...
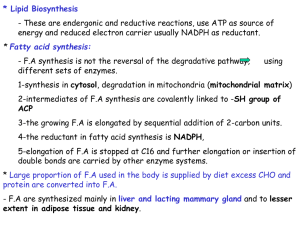
13synthesis
... * Polar lipids are targeted to specific cell membrane. After the synthesis in the S.E.R. the polar lipids (phospho, sphingo, glyco lipids) they transferred to different cell membranes by Golgi apparatus in form of vesicles. ...
... * Polar lipids are targeted to specific cell membrane. After the synthesis in the S.E.R. the polar lipids (phospho, sphingo, glyco lipids) they transferred to different cell membranes by Golgi apparatus in form of vesicles. ...
Science Course Outline Template
... have tidied and cleaned your equipment and workspace as instructed by the demonstrators and technical staff. ...
... have tidied and cleaned your equipment and workspace as instructed by the demonstrators and technical staff. ...
Amendment Determination 2007
... Treatment of type 2 diabetes, in combination with insulin, in a patient: (a) whose glycosylated haemoglobin (HbA1c) prior to initiation of a thiazolidinedione (glitazone) is greater than 7%, despite treatment with insulin and oral anti-diabetic agents, or with insulin alone where metformin hydrochlo ...
... Treatment of type 2 diabetes, in combination with insulin, in a patient: (a) whose glycosylated haemoglobin (HbA1c) prior to initiation of a thiazolidinedione (glitazone) is greater than 7%, despite treatment with insulin and oral anti-diabetic agents, or with insulin alone where metformin hydrochlo ...
MICROBIAL PHYSIOLOGY AND BIOCHEMISTRY
... In addition to the above, there is a special “form” of proteins which are inactive precursors and need to be themselves chemically modified (usually by cleavage of one or more peptide bonds), before they are able to work as enzymes. This form of proteins is called the Zymogen form of proteins. Thus ...
... In addition to the above, there is a special “form” of proteins which are inactive precursors and need to be themselves chemically modified (usually by cleavage of one or more peptide bonds), before they are able to work as enzymes. This form of proteins is called the Zymogen form of proteins. Thus ...
18. Metabolism of lipids 1
... • contain 85 % of TGs (it is the main transport form of dietary TGs). • apoprotein B-48 (apo B-48) is the main protein component • deliver TGs from the intestine (via lymph and blood) to tissues (muscle for energy, adipose for storage). • bind to membrane-bound lipoprotein lipase (at adipose tissue ...
... • contain 85 % of TGs (it is the main transport form of dietary TGs). • apoprotein B-48 (apo B-48) is the main protein component • deliver TGs from the intestine (via lymph and blood) to tissues (muscle for energy, adipose for storage). • bind to membrane-bound lipoprotein lipase (at adipose tissue ...
linolenic acid prevent insulin resistance but have divergent impacts
... Mitochondrial dysfunction is a central hypothesis in the progression of skeletal muscle IR and is characterized traditionally by reduced content or impairment of function affecting rates of FAO (26). However, given that increased mitochondrial content can parallel the development of IR (15, 19, 53) ...
... Mitochondrial dysfunction is a central hypothesis in the progression of skeletal muscle IR and is characterized traditionally by reduced content or impairment of function affecting rates of FAO (26). However, given that increased mitochondrial content can parallel the development of IR (15, 19, 53) ...
... expression and covalent modifications of proteins. Research findings that have been generated by using molecular techniques have guided us into new territory, going way beyond classical nutrition studies such as characterization of clinical signs of nutrient deficiencies. Those nutritionists who inv ...
genetic code: a new understanding of codon
... realization of first four words (0. UUU, 1. UUC, 2. UUA, 3. UUG) on the binarycode tree and/or in GCT (cf. Rumer’s and Shcherbak’s idea about the four-codon AAs in next Section). The sum of their ordinal numbers equals 6, which is the first perfect number. After the realization of first eight words ...
... realization of first four words (0. UUU, 1. UUC, 2. UUA, 3. UUG) on the binarycode tree and/or in GCT (cf. Rumer’s and Shcherbak’s idea about the four-codon AAs in next Section). The sum of their ordinal numbers equals 6, which is the first perfect number. After the realization of first eight words ...
THE PLANT LECTINS
... the amino terminus, and an a-chain, corresponding to the carboxyl terminus. For example, jacalin lectin, from the jackfruit Artocarpus heterophyllus, is a tetrameric two-chain lectin (65 kD) (molecular mass 65 kD) with an a-chain of 133 amino acid residues and a bchain of 20-21 amino acid residues ...
... the amino terminus, and an a-chain, corresponding to the carboxyl terminus. For example, jacalin lectin, from the jackfruit Artocarpus heterophyllus, is a tetrameric two-chain lectin (65 kD) (molecular mass 65 kD) with an a-chain of 133 amino acid residues and a bchain of 20-21 amino acid residues ...
Research Associate, Dept
... oxidative phosphorylation (Krebs cycle and respiratory chain enzymes are not present) evidence is accumulating that it may serve for iron-sulfur cluster biosynthesis and assembly. C. parvum polyamine metabolism resembles that of certain bacteria and plants which use arginine decarboxylase (ADC) and ...
... oxidative phosphorylation (Krebs cycle and respiratory chain enzymes are not present) evidence is accumulating that it may serve for iron-sulfur cluster biosynthesis and assembly. C. parvum polyamine metabolism resembles that of certain bacteria and plants which use arginine decarboxylase (ADC) and ...
PDB format description
... within a chain represented by a set of SEQRES records, the component number assigned is that of the chain involved. (ii) If a HET group is composed of more than one distinct part, then the formulas for these parts will occur on separate FORMUL cards, each with the same component number and HET ident ...
... within a chain represented by a set of SEQRES records, the component number assigned is that of the chain involved. (ii) If a HET group is composed of more than one distinct part, then the formulas for these parts will occur on separate FORMUL cards, each with the same component number and HET ident ...
Planta
... aconitase isoforms, mitochondrial and cytosolic, are distinguishable by isozyme gel electrophoresis, and they display distinct sensitivities to iron availability: while the mitochondrial enzyme is resistant to iron limitation, the cytosolic enzyme loses its activity under iron depletion, resulting i ...
... aconitase isoforms, mitochondrial and cytosolic, are distinguishable by isozyme gel electrophoresis, and they display distinct sensitivities to iron availability: while the mitochondrial enzyme is resistant to iron limitation, the cytosolic enzyme loses its activity under iron depletion, resulting i ...
uncorrected proof
... Structural superposition of the a-actinin ABD with a single utrophin ABD domain can be performed only on a pair-wise CH domain basis, and not over the whole molecule, since the two CH domains adopt markedly different relative orientations (Figure 2(b)). Overlays of 101 superposable Ca atoms of the C ...
... Structural superposition of the a-actinin ABD with a single utrophin ABD domain can be performed only on a pair-wise CH domain basis, and not over the whole molecule, since the two CH domains adopt markedly different relative orientations (Figure 2(b)). Overlays of 101 superposable Ca atoms of the C ...
Role of Carnitine in Lipid Metabolism
... proteins needed for transport of long-chain fatty acids into the mitochondrial matrix has been reviewed (4) and will not be repeated at this time. The discovery that malonyl CoA is an inhibitor of carnitine palmitoyltransferase I has added to our understanding of the coordinated metabolic regulation ...
... proteins needed for transport of long-chain fatty acids into the mitochondrial matrix has been reviewed (4) and will not be repeated at this time. The discovery that malonyl CoA is an inhibitor of carnitine palmitoyltransferase I has added to our understanding of the coordinated metabolic regulation ...
IN VIVO ENOL CASTOR OIL SEEDS AT THREONINE-4 AND SERINE-451
... assimilated into glutamine or glutamate via glutamine synthetase and glutamateoxoglutarate amino transferase (GS/GOGAT) (Fig. 1.2A). In addition PEPC has been shown to contribute to fatty acid synthesis through generation of metabolic precursors and reducing power. Fatty acid synthesis within the l ...
... assimilated into glutamine or glutamate via glutamine synthetase and glutamateoxoglutarate amino transferase (GS/GOGAT) (Fig. 1.2A). In addition PEPC has been shown to contribute to fatty acid synthesis through generation of metabolic precursors and reducing power. Fatty acid synthesis within the l ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.