Structure-Based Prediction of DNA Target Sites by Regulatory Proteins
... flexibility of DNA is sequence dependent,12 and it can affect the binding affinity with protein as well.13 Given the complexity of protein–DNA recognition, how can we explain the specific recognition of particular sequences by regulatory proteins, and how can we predict target sites recognized by pr ...
... flexibility of DNA is sequence dependent,12 and it can affect the binding affinity with protein as well.13 Given the complexity of protein–DNA recognition, how can we explain the specific recognition of particular sequences by regulatory proteins, and how can we predict target sites recognized by pr ...
Characterisation of new intracellular membranes in Escherichia coli
... (Fig. 4). Its N-terminal sequence is that of intact subunit b, and its molecular mass measured by e.s.i.-m.s. was 4113.3, corresponding to residues 1^36 of subunit b, and arising by tryptic cleavage after arginine-36. There was no evidence for cleavage after lysine-23, which is consistent with the r ...
... (Fig. 4). Its N-terminal sequence is that of intact subunit b, and its molecular mass measured by e.s.i.-m.s. was 4113.3, corresponding to residues 1^36 of subunit b, and arising by tryptic cleavage after arginine-36. There was no evidence for cleavage after lysine-23, which is consistent with the r ...
Purification, Characterization, and Amino Acid
... Platelet aggregation plays a vital role in hemostasis by maintaining the integrity of blood vessel walls (1–3), in facilitating the activation of coagulant factors (4 – 6), and in clot retraction (7, 8). Thus an aberration in platelet aggregation can cause havoc as seen in myocardial infarction and ...
... Platelet aggregation plays a vital role in hemostasis by maintaining the integrity of blood vessel walls (1–3), in facilitating the activation of coagulant factors (4 – 6), and in clot retraction (7, 8). Thus an aberration in platelet aggregation can cause havoc as seen in myocardial infarction and ...
(PDF, Unknown)
... immune system. Data show that BCAA supplementation before and after exercise has beneficial effects for decreasing exercise-induced muscle damage and promoting muscle-protein synthesis. Muscle damage develops delayed onset muscle soreness: a syndrome that occurs 24-48 h after intensive physical acti ...
... immune system. Data show that BCAA supplementation before and after exercise has beneficial effects for decreasing exercise-induced muscle damage and promoting muscle-protein synthesis. Muscle damage develops delayed onset muscle soreness: a syndrome that occurs 24-48 h after intensive physical acti ...
Postexercise nutrient intake timing in humans is critical to recovery
... Exercise induces a greater sensitivity and responsiveness to the events controlled by insulin (44). In vitro and in vivo studies have demonstrated increased insulin-mediated glucose uptake in response to muscle contraction (6, 9, 10, 28, 34, 35, 48). Furthermore, exercise has been shown to benefit p ...
... Exercise induces a greater sensitivity and responsiveness to the events controlled by insulin (44). In vitro and in vivo studies have demonstrated increased insulin-mediated glucose uptake in response to muscle contraction (6, 9, 10, 28, 34, 35, 48). Furthermore, exercise has been shown to benefit p ...
Corn Bt11 x MIR162 x TC1507 x GA21
... For Bt11, the Cry1Ab and PAT gene expression is both driven by the 35S promoter. No cellular localization sequences are present, so the cytoplasm is the location of accumulation. For MIR162, the Vip3Aa20 and pmi gene expression is both driven by the ZmUbi (Maize Ubiquitin promoter). No cellular loca ...
... For Bt11, the Cry1Ab and PAT gene expression is both driven by the 35S promoter. No cellular localization sequences are present, so the cytoplasm is the location of accumulation. For MIR162, the Vip3Aa20 and pmi gene expression is both driven by the ZmUbi (Maize Ubiquitin promoter). No cellular loca ...
Structure of HIV-1 gp120 with gp41-interactive
... Glycine to Arginine at Position Forty-three • Lysine to Arginine substitution is small uncharged to bulky positive charge • The residue is located on the surface of the protein structure ...
... Glycine to Arginine at Position Forty-three • Lysine to Arginine substitution is small uncharged to bulky positive charge • The residue is located on the surface of the protein structure ...
Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry
... of these amino acids because of the existence of tryptophan and tyrosine. Khan et al. (1980) observed that tyrosine has a lower extinction coefficient than tryptophan. The energy transfer also shows the dominance of the tryptophan fluorescence response. The presence of even one tryptophan residue in ...
... of these amino acids because of the existence of tryptophan and tyrosine. Khan et al. (1980) observed that tyrosine has a lower extinction coefficient than tryptophan. The energy transfer also shows the dominance of the tryptophan fluorescence response. The presence of even one tryptophan residue in ...
Effect of HDGF on Hepatic Stellate Cells
... Release of free radicals and signaling cytokines HSC activation ...
... Release of free radicals and signaling cytokines HSC activation ...
Regents Biology
... Other Functions of Lipids in your Body • Sex Hormones (Look WAY different than the other lipids… they are in rings). – Signals from one body system to another. ...
... Other Functions of Lipids in your Body • Sex Hormones (Look WAY different than the other lipids… they are in rings). – Signals from one body system to another. ...
PostScript - Theoretical Biochemistry Group
... Messenger RNA sequences often have to preserve functional secondary structure elements in addition to coding for proteins. We present a statistical analysis of retroviral mRNA which supports the hypothesis that the natural genetic code is adapted to such complementary coding. These sequences are sti ...
... Messenger RNA sequences often have to preserve functional secondary structure elements in addition to coding for proteins. We present a statistical analysis of retroviral mRNA which supports the hypothesis that the natural genetic code is adapted to such complementary coding. These sequences are sti ...
Oligomerization and activation of the FliI ATPase
... ATPase, and the lipid and protein interactions that locate and regulate it. A previous report has indicated that His-tagged FliI can exist in monomeric form (Minamino and Macnab, 2000a), and our gel filtration and multiangle light scattering analysis of the native soluble enzyme confirmed this earli ...
... ATPase, and the lipid and protein interactions that locate and regulate it. A previous report has indicated that His-tagged FliI can exist in monomeric form (Minamino and Macnab, 2000a), and our gel filtration and multiangle light scattering analysis of the native soluble enzyme confirmed this earli ...
Telomerase Is a True Reverse Transcriptase
... How, then, is the chromosome end maintained? The molecular basis of telomere replication came to light in 1985 with the discovery by Greider and Blackburn of the enzyme telomere terminal transferase or telomerase in Tetrahymena thermophila [10]. They later showed that telomerase was a ribonucleoprot ...
... How, then, is the chromosome end maintained? The molecular basis of telomere replication came to light in 1985 with the discovery by Greider and Blackburn of the enzyme telomere terminal transferase or telomerase in Tetrahymena thermophila [10]. They later showed that telomerase was a ribonucleoprot ...
Stress puts TIA on TOP
... stress remains elusive. Other data suggest that specific 59TOP mRNAs are regulated in a tissue- and cell typespecific manner. For example, eEF2 mRNA confers growthdependent regulation in cells of hematopoietic, but not in cells of nonhematopoietic, origins, while translation of b1-tubulin mRNA, whic ...
... stress remains elusive. Other data suggest that specific 59TOP mRNAs are regulated in a tissue- and cell typespecific manner. For example, eEF2 mRNA confers growthdependent regulation in cells of hematopoietic, but not in cells of nonhematopoietic, origins, while translation of b1-tubulin mRNA, whic ...
Predicting the Secondary Structure of Globular Proteins Using
... network models are designed to mimic them. This study was inspired by a previous application of network .learning to the problem of text-to-speech. In the NETtalk system (Sejnowski & Rosenberg, 1987), the input to the network is strings of letters representing words and the output is strings of phon ...
... network models are designed to mimic them. This study was inspired by a previous application of network .learning to the problem of text-to-speech. In the NETtalk system (Sejnowski & Rosenberg, 1987), the input to the network is strings of letters representing words and the output is strings of phon ...
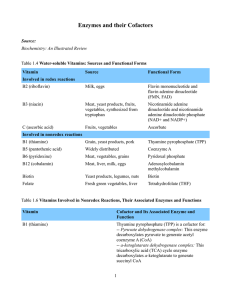
Enzymes and their Cofactors Source: Biochemistry: An Illustrated
... -- Coenzyme A: This molecule forms high-energy thioester bonds with other molecules to "activate" them and is involved in reactions that transfer fatty acyl groups between molecules -- Fatty acid synthase (FAS) complex: This enzyme catalyzes the synthesis of fatty acids ...
... -- Coenzyme A: This molecule forms high-energy thioester bonds with other molecules to "activate" them and is involved in reactions that transfer fatty acyl groups between molecules -- Fatty acid synthase (FAS) complex: This enzyme catalyzes the synthesis of fatty acids ...
ICE 6 Review
... concentration of CD4 once synthesis of gp120 begins? Why is it less necessary for the cell to also decrease its cellular concentration of CCR5 or CXCR4? Newly synthesized cellular CD4 would bind newly synthesized gp120 in the endomembrane system and render it nonfunctional (it actually stalls it in ...
... concentration of CD4 once synthesis of gp120 begins? Why is it less necessary for the cell to also decrease its cellular concentration of CCR5 or CXCR4? Newly synthesized cellular CD4 would bind newly synthesized gp120 in the endomembrane system and render it nonfunctional (it actually stalls it in ...
Chapter 23 - Evangel University
... • Reduction of folic acid gives tetrahydrofolic acid (THF), the ________________ form of the coenzyme • Tetrahydrofolate is a carrier of the one-carbon ...
... • Reduction of folic acid gives tetrahydrofolic acid (THF), the ________________ form of the coenzyme • Tetrahydrofolate is a carrier of the one-carbon ...
Full-Text PDF
... on the metabolism, yet its components derive from this very metabolism. The cell structure derives from the genetically controlled metabolism, yet it is required to hold genetics and metabolism together. How did this interdependence come about? Did a primordial metabolism invent its own genetic cont ...
... on the metabolism, yet its components derive from this very metabolism. The cell structure derives from the genetically controlled metabolism, yet it is required to hold genetics and metabolism together. How did this interdependence come about? Did a primordial metabolism invent its own genetic cont ...
Six Major Classes of Enzymes and Examples of Their Subclasses
... substrate or exhibit a broad specificity, using more than one substrate. d. Enzymes usually function within a moderate pH and temperature range. ...
... substrate or exhibit a broad specificity, using more than one substrate. d. Enzymes usually function within a moderate pH and temperature range. ...
life - MDPI
... on the metabolism, yet its components derive from this very metabolism. The cell structure derives from the genetically controlled metabolism, yet it is required to hold genetics and metabolism together. How did this interdependence come about? Did a primordial metabolism invent its own genetic cont ...
... on the metabolism, yet its components derive from this very metabolism. The cell structure derives from the genetically controlled metabolism, yet it is required to hold genetics and metabolism together. How did this interdependence come about? Did a primordial metabolism invent its own genetic cont ...
Research Vita (314 Kb OTHER)
... Study the yeast model for cellular iron metabolism Conduct experiments contributing to the understanding of mitochondria in iron related diseases Cloned SSC2 (SSQ1), a mitochondrial heat shock protein, using classical S. cerevisiae molecular genetic techniques Show involvement of Ssc2p in Yfh1p (fra ...
... Study the yeast model for cellular iron metabolism Conduct experiments contributing to the understanding of mitochondria in iron related diseases Cloned SSC2 (SSQ1), a mitochondrial heat shock protein, using classical S. cerevisiae molecular genetic techniques Show involvement of Ssc2p in Yfh1p (fra ...
Practice Final Exam - mvhs
... 6a) For the above sequence, underline the promoter sites and label them. 6b) Circle the approximate +1 position in the above gene. 6c) How (molecularly) does the RNA polymerase recognize where to begin transcription? _______________ ___________________________________________________________________ ...
... 6a) For the above sequence, underline the promoter sites and label them. 6b) Circle the approximate +1 position in the above gene. 6c) How (molecularly) does the RNA polymerase recognize where to begin transcription? _______________ ___________________________________________________________________ ...
answer key
... reaction ADP + Pi ATP. Bogus! A chemical reaction that has a ΔG > 0 can proceed if it is coupled to the reverse reaction (ATP ADP + Pi). ATP synthesis does not proceed spontaneously, but ATP hydrolysis does. [This question is based on review sheet questions #32-33.] ...
... reaction ADP + Pi ATP. Bogus! A chemical reaction that has a ΔG > 0 can proceed if it is coupled to the reverse reaction (ATP ADP + Pi). ATP synthesis does not proceed spontaneously, but ATP hydrolysis does. [This question is based on review sheet questions #32-33.] ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.