Nucleotide Metabolism - Indiana University
... • Purine biosynthesis – Salvage is a major pathway – Base synthesized while attached to ribose – IMP is common intermediate for AMP and GMP, but itself is not a typical nucleotide ...
... • Purine biosynthesis – Salvage is a major pathway – Base synthesized while attached to ribose – IMP is common intermediate for AMP and GMP, but itself is not a typical nucleotide ...
MIAPE_Quant_v1.0_Template
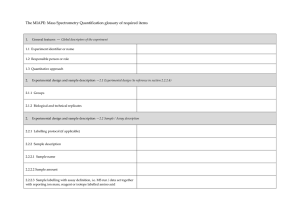
... Replicates: experiment to be reproduced or repeated in order to test the variability of observed values. Technical replicates: Replicates that share the same sample; i.e. the measurements are repeated. The technical variability is tested. Biological replicates: Replicate where different samples are ...
... Replicates: experiment to be reproduced or repeated in order to test the variability of observed values. Technical replicates: Replicates that share the same sample; i.e. the measurements are repeated. The technical variability is tested. Biological replicates: Replicate where different samples are ...
Chapter 10
... translated into amino acid sequences • The flow of information from gene to protein is based on a triplet code. • The genetic instructions for the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide chain are written in DNA and RNA as a series of nonoverlapping three-base “words” called ...
... translated into amino acid sequences • The flow of information from gene to protein is based on a triplet code. • The genetic instructions for the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide chain are written in DNA and RNA as a series of nonoverlapping three-base “words” called ...
Figure 5.15 The 20 amino acids of proteins
... • Water is more dense than ice. At 4°C water is at its most dense state, then as it cools to O°C, the molecules freeze. The H bonds keep the water molecules slightly apart (like a lattice) so air pockets form ...
... • Water is more dense than ice. At 4°C water is at its most dense state, then as it cools to O°C, the molecules freeze. The H bonds keep the water molecules slightly apart (like a lattice) so air pockets form ...
Chem*3560 Lecture 16: Reciprocal regulation of glycolysis and
... Glucose produced by the liver is quickly secreted, and this breaks the circuit that might give rise to a futile cycle. ...
... Glucose produced by the liver is quickly secreted, and this breaks the circuit that might give rise to a futile cycle. ...
www.iplantcollaborative.org
... D. Hedgecock et al. (2007) Transcriptomic analysis of growth heterosis in larval Pacific oysters (Crassostrea gigas) PNAS 104; p2313-2318 ...
... D. Hedgecock et al. (2007) Transcriptomic analysis of growth heterosis in larval Pacific oysters (Crassostrea gigas) PNAS 104; p2313-2318 ...
unit 3 – photosynthesis and cellular respiration
... enzymes to intermediates of glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. Before amino acids can enter these processes, deamination must take place – the amino groups must be removed. The nitrogen containing wastes are excreted in the form of ammonia, urea or uric acid. Fats are also digested and absorbed ...
... enzymes to intermediates of glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. Before amino acids can enter these processes, deamination must take place – the amino groups must be removed. The nitrogen containing wastes are excreted in the form of ammonia, urea or uric acid. Fats are also digested and absorbed ...
File
... alternating double bonds and single bonds between carbon atoms 3. Amino acids: are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side chain (specific) ...
... alternating double bonds and single bonds between carbon atoms 3. Amino acids: are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side chain (specific) ...
Classification and domain analysis of protein
... BCR, BRD, FAST, G11, PDHK, PIKK, RIO, TAF1 and TIF1, and have been analysed in this study. Figure 1 displays the kinase group representation of hominids, which includes both ePKs and aPKs. Table 2 shows the distribution of ePKs (serine/threonine (Ser/Thr) and tyrosine kinases (Tyk)) in various group ...
... BCR, BRD, FAST, G11, PDHK, PIKK, RIO, TAF1 and TIF1, and have been analysed in this study. Figure 1 displays the kinase group representation of hominids, which includes both ePKs and aPKs. Table 2 shows the distribution of ePKs (serine/threonine (Ser/Thr) and tyrosine kinases (Tyk)) in various group ...
Fibrous proteins and collagen
... 6. Formation of collagen fibrils: Individual tropocollagen molecules spontaneously associate to form collagen fibrils. They form an ordered, overlapping, parallel array, with adjacent collagen molecules arranged in a staggered pattern, each overlapping its neighbor by a length approximately three-q ...
... 6. Formation of collagen fibrils: Individual tropocollagen molecules spontaneously associate to form collagen fibrils. They form an ordered, overlapping, parallel array, with adjacent collagen molecules arranged in a staggered pattern, each overlapping its neighbor by a length approximately three-q ...
Abstract Here we describe our unprecedented approach in
... PAR down-regulated the gene expression levels of the following members of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family, which are involved in the breakdown of the extracellular matrix and tissue remodeling in normal physiological processes and disease progression: Mmp3, Mmp10, Mmp13, Mmp 19 and tissue ...
... PAR down-regulated the gene expression levels of the following members of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family, which are involved in the breakdown of the extracellular matrix and tissue remodeling in normal physiological processes and disease progression: Mmp3, Mmp10, Mmp13, Mmp 19 and tissue ...
The activity reaction core and plasticity of metabolic networks
... tetrahydrofolte biosynthesis. Both pathways are present in H. pylori and E. coli. ...
... tetrahydrofolte biosynthesis. Both pathways are present in H. pylori and E. coli. ...
Mechanistic Role of an NS4A Peptide Cofactor with the Truncated
... the intermolecular consensus sequence site2 D/E-X-X-X-XC*-A/S differs from the intramolecular cleavage site by substitution of Thr for Cys at the P1 position (Grakoui et al., 1993a; Pizzi et al., 1994). A body of experimental evidence demonstrated that the 70 kDa NS3 protein is composed of two domai ...
... the intermolecular consensus sequence site2 D/E-X-X-X-XC*-A/S differs from the intramolecular cleavage site by substitution of Thr for Cys at the P1 position (Grakoui et al., 1993a; Pizzi et al., 1994). A body of experimental evidence demonstrated that the 70 kDa NS3 protein is composed of two domai ...
amino acid mixture
... acids when presented in the free form), or by glycylglycine, which has been shown to inhibit absorption of several di- and tri-peptides in vitro (Rubino et al., 1971; Addison et al., 1974; Das & Radhakrishnan, 1975), might be explained if these amino acid residues were absorbed by an alternative pep ...
... acids when presented in the free form), or by glycylglycine, which has been shown to inhibit absorption of several di- and tri-peptides in vitro (Rubino et al., 1971; Addison et al., 1974; Das & Radhakrishnan, 1975), might be explained if these amino acid residues were absorbed by an alternative pep ...
документ
... Phe biosynthesis in bacterial cell are quite uncommon, though today it is known a large number of RuMP cycle auxotrophic mutants of methylotrophs, covering numerious steps in aromatic amino acid biosynthesis (Dijkhuizen, 1996). The selection of new producers of Phe has a big importance for studies o ...
... Phe biosynthesis in bacterial cell are quite uncommon, though today it is known a large number of RuMP cycle auxotrophic mutants of methylotrophs, covering numerious steps in aromatic amino acid biosynthesis (Dijkhuizen, 1996). The selection of new producers of Phe has a big importance for studies o ...
Validation of an HPLC method for the determination of
... determination of amino acids.4–26 Mostly, the methods were based on the technology developed by Moore and Stein,4 which includes post-column derivatisation and detection in the visible region on an amino acid analyser. These analyses are reliable, but costly and time-consuming.9 The HPLC technique, ...
... determination of amino acids.4–26 Mostly, the methods were based on the technology developed by Moore and Stein,4 which includes post-column derivatisation and detection in the visible region on an amino acid analyser. These analyses are reliable, but costly and time-consuming.9 The HPLC technique, ...
CaoSpr10
... the presence of 10 M tRNA and 1 mM proline and C) the overall editing in the presence 10 M tRNA and 5 mM alaline by wild-type E. coli ProRS and two mutants (H302A and E303A), with the wild-type ProRS activity set at 100%. The enzyme concentrations used were 1 M (BioRad concentration). Values repo ...
... the presence of 10 M tRNA and 1 mM proline and C) the overall editing in the presence 10 M tRNA and 5 mM alaline by wild-type E. coli ProRS and two mutants (H302A and E303A), with the wild-type ProRS activity set at 100%. The enzyme concentrations used were 1 M (BioRad concentration). Values repo ...
Characterization and Cloning of the Chlorophyll
... Analyses of the N-terminal sequences were performed with the three peptides separated by SDSPAGE after heat treatment of the purified PPD type 2 (Fig. 4). The amino acid sequences of three peptides were determined: 16.8 kD, EEDIWEYIYGEGADKPPTGVLMKEEFFRRY; 15.9 kD, EDIWEYIYGEGADKPPTGVLMKEEFFRHYY; and ...
... Analyses of the N-terminal sequences were performed with the three peptides separated by SDSPAGE after heat treatment of the purified PPD type 2 (Fig. 4). The amino acid sequences of three peptides were determined: 16.8 kD, EEDIWEYIYGEGADKPPTGVLMKEEFFRRY; 15.9 kD, EDIWEYIYGEGADKPPTGVLMKEEFFRHYY; and ...
A Journey from the Pool of Chiral Synthetic Building Blocks to Cell
... C-terminal, fully active neurotensin segment NTS(8-13). The neurotensin GPC receptor family NT1-3 is present in the brain and in the digestive system, and NTS modulates numerous processes related to dopamine neurotransmission, analgesia, inhibition of food intake, growth of cancer cells etc.[26] For ...
... C-terminal, fully active neurotensin segment NTS(8-13). The neurotensin GPC receptor family NT1-3 is present in the brain and in the digestive system, and NTS modulates numerous processes related to dopamine neurotransmission, analgesia, inhibition of food intake, growth of cancer cells etc.[26] For ...
Document
... temperature, and time. Distinguish measured or exact numbers and determine the number of significant figures in a measured number. Adjust calculated answers to give the correct number of significant figures. Use the numerical values of metric prefixes. Write and use conversion factors. Calculate the ...
... temperature, and time. Distinguish measured or exact numbers and determine the number of significant figures in a measured number. Adjust calculated answers to give the correct number of significant figures. Use the numerical values of metric prefixes. Write and use conversion factors. Calculate the ...
pH stability of HLA-DR4 complexes with antigenic peptides .
... ABSTRACT: Complexes between antigenic peptides and class II proteins of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) trigger cellular immune responses. These complexes usually dissociate more rapidly at mildly acidic pH, where they are formed intracellularly, as compared to neutral pH, where they func ...
... ABSTRACT: Complexes between antigenic peptides and class II proteins of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) trigger cellular immune responses. These complexes usually dissociate more rapidly at mildly acidic pH, where they are formed intracellularly, as compared to neutral pH, where they func ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.