Document
... - the normal fuel is fatty acids which are converted to acetylCoA and oxidized in the citric acid cycle and ATP is produced by oxidative phosphorylation. - about half the volume of the cytoplasm of heart muscle cells made up of mitochondria. - the heart has low levels of glycogen and little phosphoc ...
... - the normal fuel is fatty acids which are converted to acetylCoA and oxidized in the citric acid cycle and ATP is produced by oxidative phosphorylation. - about half the volume of the cytoplasm of heart muscle cells made up of mitochondria. - the heart has low levels of glycogen and little phosphoc ...
Interpreting the Genetic Code
... meanings were “frozen” in other organisms, alternatively organisms that exhibit them must have evolved from organisms that never shared the universal genetic code All changes in stop codons must include three changes: 1 Replacement of former stop codons in genes vital for life, and whose activity wi ...
... meanings were “frozen” in other organisms, alternatively organisms that exhibit them must have evolved from organisms that never shared the universal genetic code All changes in stop codons must include three changes: 1 Replacement of former stop codons in genes vital for life, and whose activity wi ...
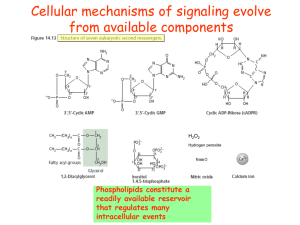
Phospholipid signaling
... Proposed functions of PX-domain proteins. a, Recruitment of the NADPH oxidase complex. Upon neutrophil activation, PI3K-I converts PI(4,5)P2 into PI(3,4,5)P3. The cytosolic subunits of the NADPH oxidase complex (p40, p47, p67) are recruited to developing phagosome at the plasma membrane by binding ...
... Proposed functions of PX-domain proteins. a, Recruitment of the NADPH oxidase complex. Upon neutrophil activation, PI3K-I converts PI(4,5)P2 into PI(3,4,5)P3. The cytosolic subunits of the NADPH oxidase complex (p40, p47, p67) are recruited to developing phagosome at the plasma membrane by binding ...
IR L Pre» Limited, Oxford, England. 3021
... sequence. Similarly, it is possible to convert an amino acid sequence to a linear order of base uncertainties, but this raises problems with the codons for leucine, arginine, serine and termination. With leucine, for example, the coding triplets are precisely specified by CTN and TTR, but combining ...
... sequence. Similarly, it is possible to convert an amino acid sequence to a linear order of base uncertainties, but this raises problems with the codons for leucine, arginine, serine and termination. With leucine, for example, the coding triplets are precisely specified by CTN and TTR, but combining ...
VITAMINS-6
... • Pyruvate carboxylase is a critical enzyme in gluconeogenesis—the formation of glucose from sources other than carbohydrates, for example, amino acids • Methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase catalyzes an essential step in the catabolism of leucine, an essential amino acid • Propionyl-CoA carboxylase catal ...
... • Pyruvate carboxylase is a critical enzyme in gluconeogenesis—the formation of glucose from sources other than carbohydrates, for example, amino acids • Methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase catalyzes an essential step in the catabolism of leucine, an essential amino acid • Propionyl-CoA carboxylase catal ...
103 Lecture Ch21b
... dinucleotide (NAD+) and NADP+ (P = phosphate) • NAD+ and NADP+ are used in redox reactions involving carbohydrates, proteins and fats • A deficiency of niacin can result in dermatitis, muscle fatigue and loss of appetite • Dietary sources include meats, rice, and whole grains ...
... dinucleotide (NAD+) and NADP+ (P = phosphate) • NAD+ and NADP+ are used in redox reactions involving carbohydrates, proteins and fats • A deficiency of niacin can result in dermatitis, muscle fatigue and loss of appetite • Dietary sources include meats, rice, and whole grains ...
Calcium binding to chromaffin vesicle matrix proteins
... and condensed by centrifugation (146000g,, 30 min). Afterward they were lysed in 20 mM MOPS/KOH, pH 7.0 (1 volume of vesicle fraction diluted with 40 volumes of buffer). The secretory vesicle membranes were spun down by centrifugation (146000g, for 30 min), and the supernatant was lyophilized. The m ...
... and condensed by centrifugation (146000g,, 30 min). Afterward they were lysed in 20 mM MOPS/KOH, pH 7.0 (1 volume of vesicle fraction diluted with 40 volumes of buffer). The secretory vesicle membranes were spun down by centrifugation (146000g, for 30 min), and the supernatant was lyophilized. The m ...
28 - Weebly
... Metabolism (pp. 920-930; Figs. 24.6-24.13; Table 24.4) • Glucose enters the cell by facilitated diffusion, and is phosphorylated to glucose-6-phosphate, essentially trapping glucose within the cell. • Glucose enters glycolysis: an anaerobic process that occurs in the cytosol. • Phase 1 (Sugar Activa ...
... Metabolism (pp. 920-930; Figs. 24.6-24.13; Table 24.4) • Glucose enters the cell by facilitated diffusion, and is phosphorylated to glucose-6-phosphate, essentially trapping glucose within the cell. • Glucose enters glycolysis: an anaerobic process that occurs in the cytosol. • Phase 1 (Sugar Activa ...
Developmentally regulated, alternative splicing of the Rpn10 gene
... signal; and secondly, the proteolytic attack of multiubiquitylated proteins by the 26S proteasome. There are growing lines of evidence that the Ub±proteasome pathway plays a critical role in various biologically important processes, including cell cycle, apoptosis, signal transduction, development a ...
... signal; and secondly, the proteolytic attack of multiubiquitylated proteins by the 26S proteasome. There are growing lines of evidence that the Ub±proteasome pathway plays a critical role in various biologically important processes, including cell cycle, apoptosis, signal transduction, development a ...
GST SF in E. coli - Institute for Genomic Biology
... – YfcF metabolomics with cutting-edge labeling protocol allows measurement of small changes in metabolites ...
... – YfcF metabolomics with cutting-edge labeling protocol allows measurement of small changes in metabolites ...
Effects of rare codon clusters on high-level expression
... gene completely eliminated this prematurely terminated species, but did not affect the two minor molecular weight species. Interestingly, the culture medium also affected these values. In a rich medium, the full-length protein and frameshift fragment represented -5% and 2% o f total cell protein, re ...
... gene completely eliminated this prematurely terminated species, but did not affect the two minor molecular weight species. Interestingly, the culture medium also affected these values. In a rich medium, the full-length protein and frameshift fragment represented -5% and 2% o f total cell protein, re ...
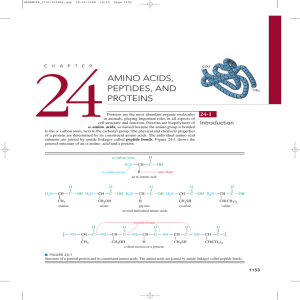
... Amino acid 2. Only the protonated form of histidine can participate acid in protein in electrostatic interactions, therefore any effects Energy HA A A HA on the deprotonated form can be ignored. 3. The negative charge on the aspartic acid residue will stabilize the + charge on the histidine side cha ...
Unit 10: Protein Catabolism - Central New Mexico Community College
... group from amino acids by breaking the bond between the central carbon and the carboxyl group. (See Figure 10-2 for examples of general enzyme cut sites.) The specific enzyme lysine decarboxylase, removes the carboxyl group from the amino acid lysine. Deaminases are enzymes that remove a molecule’s ...
... group from amino acids by breaking the bond between the central carbon and the carboxyl group. (See Figure 10-2 for examples of general enzyme cut sites.) The specific enzyme lysine decarboxylase, removes the carboxyl group from the amino acid lysine. Deaminases are enzymes that remove a molecule’s ...
NUTRITIONAL INTEREST OF CHEESE FAT A lot of new datas
... Ø Myristic acid and palmitic acid have not the same metabolic fate in the cell : Ø Myristic acid is rapidly b-oxidized, weakly secreted in the form of TGVLDL, but strongly elongated into palmitic acid. No accumulation ! Ø Palmitic acid is stored and secreted in the form of TG, weakly elongated into ...
... Ø Myristic acid and palmitic acid have not the same metabolic fate in the cell : Ø Myristic acid is rapidly b-oxidized, weakly secreted in the form of TGVLDL, but strongly elongated into palmitic acid. No accumulation ! Ø Palmitic acid is stored and secreted in the form of TG, weakly elongated into ...
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta
... studying RNA–protein interactions [21]. In this system, a first plasmid contains a modified lacZ reporter gene with an RNA-binding element located close to the translation initiation region. A second plasmid expresses the RNA-binding protein that recognizes this RNA element. When the protein is bound ...
... studying RNA–protein interactions [21]. In this system, a first plasmid contains a modified lacZ reporter gene with an RNA-binding element located close to the translation initiation region. A second plasmid expresses the RNA-binding protein that recognizes this RNA element. When the protein is bound ...
A New Subunit of Cytochrome b6f Complex Undergoes Reversible
... aligned with the sequence obtained from N terminus sequencing. These sequences are homologous to ones found within a library of recently released expressed sequence tags (cDNA sequences) of C. reinhardtii (20). The methionine codon, CACCAUGGCC, has features of an initiation codon with a consensus se ...
... aligned with the sequence obtained from N terminus sequencing. These sequences are homologous to ones found within a library of recently released expressed sequence tags (cDNA sequences) of C. reinhardtii (20). The methionine codon, CACCAUGGCC, has features of an initiation codon with a consensus se ...
- Sportscience
... have been used clinically for stimulating growth hormone release (Carlson et al., 1989; Iwasaki et al., 1987). In addition, preliminary clinical studies indicated that protein (20 to 60 g); arginine and lysine (1.2 g); and ornithine (70 mg/kg) increased growth hormone and somatomedin concentrations ...
... have been used clinically for stimulating growth hormone release (Carlson et al., 1989; Iwasaki et al., 1987). In addition, preliminary clinical studies indicated that protein (20 to 60 g); arginine and lysine (1.2 g); and ornithine (70 mg/kg) increased growth hormone and somatomedin concentrations ...
Enzymes - OpenStax CNX
... enzymes promote chemical reactions that involve more than one substrate by bringing the substrates together in an optimal orientation. The appropriate region (atoms and bonds) of one molecule is juxtaposed to the appropriate region of the other molecule with which it must react. Another way in which ...
... enzymes promote chemical reactions that involve more than one substrate by bringing the substrates together in an optimal orientation. The appropriate region (atoms and bonds) of one molecule is juxtaposed to the appropriate region of the other molecule with which it must react. Another way in which ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.