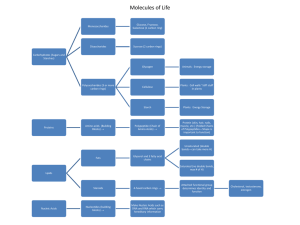
Macromolecules
... • 3 carbon backbone attached to three fatty acids – Saturated – all three fatty acids chains have maximum number of Hydrogen atoms • Butter – Unsaturated – contain less than the maximum number of hydrogen atoms in one or more of its fatty acid chains • fruits ...
... • 3 carbon backbone attached to three fatty acids – Saturated – all three fatty acids chains have maximum number of Hydrogen atoms • Butter – Unsaturated – contain less than the maximum number of hydrogen atoms in one or more of its fatty acid chains • fruits ...
Biochemistry LTF
... - four bases in DNA in different orders code for all characteristics of life! - adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine (fig. 15) ...
... - four bases in DNA in different orders code for all characteristics of life! - adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine (fig. 15) ...
Chapter 3: The Chemistry of Life: Organic Compounds
... VII. Amino acids are the subunits of proteins A. Amino acids are the subunits of proteins 1. Amino acids contain an amino group, a carboxyl group, an alpha carbon, and a unique R group 2. There are 20 commonly occurring amino acids 3. Essential amino acids are those that must be ingested in the diet ...
... VII. Amino acids are the subunits of proteins A. Amino acids are the subunits of proteins 1. Amino acids contain an amino group, a carboxyl group, an alpha carbon, and a unique R group 2. There are 20 commonly occurring amino acids 3. Essential amino acids are those that must be ingested in the diet ...
supersecondar, tertiary and quaternary structure
... others may consist of two or more polypeptide chains that may be structurally identical or totally unrelated. (Dimeric) ...
... others may consist of two or more polypeptide chains that may be structurally identical or totally unrelated. (Dimeric) ...
Prob_Set_2_2007
... - due Wednesday Feb 21 in class 1) Pick out a protein of known structure that is central to your research or is connected to your research interests. Download the coordinates from the Protein Data Bank (www.rcsb.org) and use a rendering program such as Chimera, Rasmol, Pymol, Molmol, iMol (Macs) etc ...
... - due Wednesday Feb 21 in class 1) Pick out a protein of known structure that is central to your research or is connected to your research interests. Download the coordinates from the Protein Data Bank (www.rcsb.org) and use a rendering program such as Chimera, Rasmol, Pymol, Molmol, iMol (Macs) etc ...
Chapter 4 - Organic Chemistry, Biochemistry
... protein to change. This can be caused by changes in temperature, pH, or salt concentration. For example, acid causes milk to curdle and heat (cooking) causes egg whites to coagulate because the proteins within them denature. If the protein is not severely denatured, it may regain its normal structur ...
... protein to change. This can be caused by changes in temperature, pH, or salt concentration. For example, acid causes milk to curdle and heat (cooking) causes egg whites to coagulate because the proteins within them denature. If the protein is not severely denatured, it may regain its normal structur ...
Brief overview of Bio backgound
... Still a good idea to pursue the Holy Grail 1.3m genes, but only 2,000 – 10,000 different conformations ...
... Still a good idea to pursue the Holy Grail 1.3m genes, but only 2,000 – 10,000 different conformations ...
3 - Food Nutrition
... • Primary Structure of proteins is the sequence of amino acids.Twenty-two amino acids are used in the chain structure of proteins. Amino acids can be linear or ring molecules but all contain an amino (-NH2) and a carboxyl (-COOH) group. • Secondary Structure is the folding of the long thin chains of ...
... • Primary Structure of proteins is the sequence of amino acids.Twenty-two amino acids are used in the chain structure of proteins. Amino acids can be linear or ring molecules but all contain an amino (-NH2) and a carboxyl (-COOH) group. • Secondary Structure is the folding of the long thin chains of ...
Capturing denaturing proteins * Small Heat Shock Protein substrate
... sHSP chaperone action and interaction with substrates, therefore, has wide-ranging implications for understanding cellular stress and disease processes. We are studying the mechanism of sHSP substrate recognition by identifying specific crosslinking sites between sHSPs and denaturing substrates. sHS ...
... sHSP chaperone action and interaction with substrates, therefore, has wide-ranging implications for understanding cellular stress and disease processes. We are studying the mechanism of sHSP substrate recognition by identifying specific crosslinking sites between sHSPs and denaturing substrates. sHS ...
Huang, David, Center for Structural Biochemistry
... from the protein crystals using x-ray crystallography. Structure Determination – The electron density data was used to determine the structure of the proteins in complex with the ligands using the COOT software. Analysis – The specific hydrogen bonds or hydrophobic interactions around the ligand ...
... from the protein crystals using x-ray crystallography. Structure Determination – The electron density data was used to determine the structure of the proteins in complex with the ligands using the COOT software. Analysis – The specific hydrogen bonds or hydrophobic interactions around the ligand ...
Practice Exam I
... a. amino acid + amino acid dipeptide + H20 b. dipeptide + H20 amino acid + amino acid c. denaturation of a polypeptide d. two single strands of DNA DNA double helix 14. The active site of an enzyme a. is similar to that of any other enzyme b. is the part of the enzyme where the substrate can f ...
... a. amino acid + amino acid dipeptide + H20 b. dipeptide + H20 amino acid + amino acid c. denaturation of a polypeptide d. two single strands of DNA DNA double helix 14. The active site of an enzyme a. is similar to that of any other enzyme b. is the part of the enzyme where the substrate can f ...
26.3 Synthesis of Amino Acids
... • Reaction of an -keto acid with NH3 and a reducing agent (see Section 24.6) produces an -amino acid ...
... • Reaction of an -keto acid with NH3 and a reducing agent (see Section 24.6) produces an -amino acid ...
protein pwrpt - Malibu High School
... • About half of them are considered “essential” (meaning you cannot make them in your body and you must get them from food). • About half are “nonessential” (meaning your body can manufacture them). ...
... • About half of them are considered “essential” (meaning you cannot make them in your body and you must get them from food). • About half are “nonessential” (meaning your body can manufacture them). ...
Carbon compounds - Sonoma Valley High School
... compounds that can be bonded together to form larger ones. • 3 important ones are: – sugars – amino acids ...
... compounds that can be bonded together to form larger ones. • 3 important ones are: – sugars – amino acids ...
PP-Protein Synthesis
... Identify the genetic code and explain how it is read. Summarize the process of translation. ...
... Identify the genetic code and explain how it is read. Summarize the process of translation. ...
document
... Nucleic acids are polymers of nucleotides. Each nucleotide monomer consists of a pentose (5-C sugar) covalently bonded to a phosphate group and to one of four nitrogenous bases (A,G,C, T or U). In making a chain, nucleotides join to form a sugar-phosphate backbone from which the ...
... Nucleic acids are polymers of nucleotides. Each nucleotide monomer consists of a pentose (5-C sugar) covalently bonded to a phosphate group and to one of four nitrogenous bases (A,G,C, T or U). In making a chain, nucleotides join to form a sugar-phosphate backbone from which the ...
Text 3
... […] An integral protein molecule with the appropriate size and structure […] may transverse the entire membrane; that is, they have regions in contact with the aqueous solvent on both sides of the membrane. […] The [...] protein molecules are postulated to be amphipathic2 as are the phospholipids. T ...
... […] An integral protein molecule with the appropriate size and structure […] may transverse the entire membrane; that is, they have regions in contact with the aqueous solvent on both sides of the membrane. […] The [...] protein molecules are postulated to be amphipathic2 as are the phospholipids. T ...
... surface would be used, but the speed of rotation would have to be high so as not to form a simple spiral. At high speeds the protein would be held on the wall by centrifugal force but liquids entering at the top would not just pass down and out the tip but would rise up again when they reached the b ...
33-6-ET-V1-S1__biomi.. - e-Acharya Integrated E
... Several Repositories and Databases • There are several protein data repositories and databases available online from where we can get necessary information about the protein. ...
... Several Repositories and Databases • There are several protein data repositories and databases available online from where we can get necessary information about the protein. ...
Overview
... Yuan Lecture 2, Class 24: Protein Folding and Molecular Chaperones April 20th, 2017 Overview The intracellular concentration of protein in bacterial cells can be estimated to be ~135 mg/ml. In this session, we will explore how bacteria employ a suite of molecular machines collectively known as chape ...
... Yuan Lecture 2, Class 24: Protein Folding and Molecular Chaperones April 20th, 2017 Overview The intracellular concentration of protein in bacterial cells can be estimated to be ~135 mg/ml. In this session, we will explore how bacteria employ a suite of molecular machines collectively known as chape ...
Protein structure prediction

Protein structure prediction is the prediction of the three-dimensional structure of a protein from its amino acid sequence — that is, the prediction of its folding and its secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure from its primary structure. Structure prediction is fundamentally different from the inverse problem of protein design. Protein structure prediction is one of the most important goals pursued by bioinformatics and theoretical chemistry; it is highly important in medicine (for example, in drug design) and biotechnology (for example, in the design of novel enzymes). Every two years, the performance of current methods is assessed in the CASP experiment (Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction). A continuous evaluation of protein structure prediction web servers is performed by the community project CAMEO3D.