
video slide
... o Can be caused by any hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, and Van der Waals interactions within the protein molecule. o Disulfide bonds between atoms of sulfur within the amino acids can also be formed. • This is what makes hair curly! ...
... o Can be caused by any hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, and Van der Waals interactions within the protein molecule. o Disulfide bonds between atoms of sulfur within the amino acids can also be formed. • This is what makes hair curly! ...
Proteins * Structure and Function
... The R group represents a side chain from the central ‘alpha’ carbon atom, and can be anything from a simple hydrogen atom to a more complex ring structure. 3 of 29 ...
... The R group represents a side chain from the central ‘alpha’ carbon atom, and can be anything from a simple hydrogen atom to a more complex ring structure. 3 of 29 ...
DNA and Proteins
... from the mRNA by enzymes and the resulting exon pieces pasted back together before it the mRNA can move out of the nucleus and function to make a protein. ...
... from the mRNA by enzymes and the resulting exon pieces pasted back together before it the mRNA can move out of the nucleus and function to make a protein. ...
Chapter 3 Review Questions
... 10. ________________ are a source of long-term stored energy. 11. Organic molecules that have the same chemical formula but different structural arrangements are called ___________. 12. Carbohydrates are important because they _____________________. 13. Meat, eggs, soy, and beans contain ___________ ...
... 10. ________________ are a source of long-term stored energy. 11. Organic molecules that have the same chemical formula but different structural arrangements are called ___________. 12. Carbohydrates are important because they _____________________. 13. Meat, eggs, soy, and beans contain ___________ ...
Amino Acids - Sehr Gut Web
... the three-letter abbreviations (since they’re all self-explanatory), I did come up with some nonsense mnemonics on the one-letter abbreviations which helped me to be able to reconstruct the chart: (No, they make no sense. They’re not supposed to. If they made sense, they wouldn’t be mnemonics, eh?) ...
... the three-letter abbreviations (since they’re all self-explanatory), I did come up with some nonsense mnemonics on the one-letter abbreviations which helped me to be able to reconstruct the chart: (No, they make no sense. They’re not supposed to. If they made sense, they wouldn’t be mnemonics, eh?) ...
Mechanism of action of trypsin and chymotrypsin
... • Elastase preferes small hydrophobic residues like alanine. ...
... • Elastase preferes small hydrophobic residues like alanine. ...
Study Guide for Chapter 3
... Describe and draw the structure of a water molecule Explain how water’s polarity affects it’s ability to dissolve substances List 2 of water’s properties that result from hydrogen bonding Define organic compound and name 3 elements often found in organic compounds Explain why carbon forms ...
... Describe and draw the structure of a water molecule Explain how water’s polarity affects it’s ability to dissolve substances List 2 of water’s properties that result from hydrogen bonding Define organic compound and name 3 elements often found in organic compounds Explain why carbon forms ...
Organic Compounds: Carbohydrates
... Hydrogen bonds are critically important in maintaining structure, but are fragile & easily broken by heat and pH changes When the 3 dimensional structure is destroyed, called denatured proteins, no longer can perform their roles (function depends on structure) active sites – are structure on t ...
... Hydrogen bonds are critically important in maintaining structure, but are fragile & easily broken by heat and pH changes When the 3 dimensional structure is destroyed, called denatured proteins, no longer can perform their roles (function depends on structure) active sites – are structure on t ...
BIO520 Final Exam 5/07 Jim Lund You may use any books, notes
... 3b (1 pt). Examine the HSP shown below. What is the difference between ‘Identities’ and ‘Positives’? 3c (1 pt). Examine the HSP shown below. Does the E-value for this HSP indicate this is a excellent, borderline, or insignificant match? 3d (1 pt). Examine the HSP shown below. Would you expect a BLAS ...
... 3b (1 pt). Examine the HSP shown below. What is the difference between ‘Identities’ and ‘Positives’? 3c (1 pt). Examine the HSP shown below. Does the E-value for this HSP indicate this is a excellent, borderline, or insignificant match? 3d (1 pt). Examine the HSP shown below. Would you expect a BLAS ...
Slide 1
... acid molecule There is a central carbon atom (called the "alpha carbon"), with four different chemical groups attached to it: a hydrogen atom a basic amino group an acidic carboxyl group a variable "R" group (or side chain) ...
... acid molecule There is a central carbon atom (called the "alpha carbon"), with four different chemical groups attached to it: a hydrogen atom a basic amino group an acidic carboxyl group a variable "R" group (or side chain) ...
Mutations - Broken Arrow Public Schools
... one small area or one nucleotide in a gene. • Point mutations include substitution , in which one base is changed to another, as well as insertions and deletions, in which a base is inserted or removed from the DNA sequence. ...
... one small area or one nucleotide in a gene. • Point mutations include substitution , in which one base is changed to another, as well as insertions and deletions, in which a base is inserted or removed from the DNA sequence. ...
Protein Turnover and Amino Acid Catabolism
... Hemoglobin lasts as long as a red blood cell. Υ-Crystallin (eye lens protein) lasts as long as the organism does. ...
... Hemoglobin lasts as long as a red blood cell. Υ-Crystallin (eye lens protein) lasts as long as the organism does. ...
Biochem ch 37a [2-9
... -enzymes are released as [inactive] zymogens (larger than their active forms) -cleaved in digestive tract -no single enzyme can digest a protein, must act as a group -broken into a.a’s and small peptides; cleaved by peptidases of intestinal epithelium A. Digestion of Proteins in the stomach -Chief c ...
... -enzymes are released as [inactive] zymogens (larger than their active forms) -cleaved in digestive tract -no single enzyme can digest a protein, must act as a group -broken into a.a’s and small peptides; cleaved by peptidases of intestinal epithelium A. Digestion of Proteins in the stomach -Chief c ...
Document
... – protomers no stable structures on their own (i.e. they need to interact in complexes) – (functionally obligate) ...
... – protomers no stable structures on their own (i.e. they need to interact in complexes) – (functionally obligate) ...
Document
... they are brought into the ribosome bound to tRNA molecules tRNA molecule consists of a single strand of RNA - about 80 RNA nucleotides ...
... they are brought into the ribosome bound to tRNA molecules tRNA molecule consists of a single strand of RNA - about 80 RNA nucleotides ...
Section 4 – Molecules
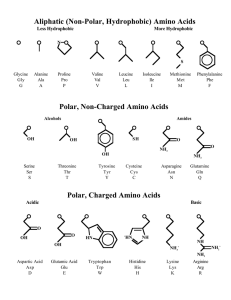
... affects the solubility of the amino acid. Hydrophobic features include long non-polar (uncharged) chains or complex aromatic rings. Hydrophilic features include additional carboxyl groups or amino groups not involved in peptide bonding which are ionised in solution. ...
... affects the solubility of the amino acid. Hydrophobic features include long non-polar (uncharged) chains or complex aromatic rings. Hydrophilic features include additional carboxyl groups or amino groups not involved in peptide bonding which are ionised in solution. ...
Self-Organizing Bio-structures
... Only folded peptides resist to thrombin cleavage 80 clones tested: 20% resistant ...
... Only folded peptides resist to thrombin cleavage 80 clones tested: 20% resistant ...
Download PDF
... diverse reactions, one must assimilate aspects of organic chemistry, inorganic chemistry, and physical chemistry and apply these chemical principles to the complex structural environment presented by natural proteins, nucleotides, and membranes. The goal of this course is to learn about general aspe ...
... diverse reactions, one must assimilate aspects of organic chemistry, inorganic chemistry, and physical chemistry and apply these chemical principles to the complex structural environment presented by natural proteins, nucleotides, and membranes. The goal of this course is to learn about general aspe ...
Protein Enriched Porridge High Protein Porridge
... Protein Enriched Porridge High Protein Porridge WPC 515 is a high quality, 80% whey protein ingredient that gives manufacturers the ability to double the protein content in porridge whilst keeping the taste and texture experience the same, unlike other WPC 80 ingredients. Ingredients (makes 50g): WP ...
... Protein Enriched Porridge High Protein Porridge WPC 515 is a high quality, 80% whey protein ingredient that gives manufacturers the ability to double the protein content in porridge whilst keeping the taste and texture experience the same, unlike other WPC 80 ingredients. Ingredients (makes 50g): WP ...
Amino Acids - Newcastle University
... Amino acids are often referred to as ‘the building blocks of life’. This is because they combine in different sequences to form proteins, which are fundamental to all living organisms. There are 21 amino acids, 9 of which are called ‘essential’ because they cannot be naturally found in the body. Thi ...
... Amino acids are often referred to as ‘the building blocks of life’. This is because they combine in different sequences to form proteins, which are fundamental to all living organisms. There are 21 amino acids, 9 of which are called ‘essential’ because they cannot be naturally found in the body. Thi ...
Protein Synthesis: Translation
... 1) The amino acid-charged tRNA that corresponds to the next mRNA codon binds to the A site on the ribosome. 2) A peptide bond forms between two adjacent amino acids. (condensation reaction) ...
... 1) The amino acid-charged tRNA that corresponds to the next mRNA codon binds to the A site on the ribosome. 2) A peptide bond forms between two adjacent amino acids. (condensation reaction) ...
Bio1A Unit 1-2 Biological Molecules Notes File
... Variations in sided chains determine how the protein will interact with other molecules or itself. • Cysteine (R = -SH) can form a disulfide bond (covalent, rare) • Other side chains will interact through hydrogen (primary) ionic bonding • Ultimate structure is typically most thermodynamically stabl ...
... Variations in sided chains determine how the protein will interact with other molecules or itself. • Cysteine (R = -SH) can form a disulfide bond (covalent, rare) • Other side chains will interact through hydrogen (primary) ionic bonding • Ultimate structure is typically most thermodynamically stabl ...
Protein structure prediction

Protein structure prediction is the prediction of the three-dimensional structure of a protein from its amino acid sequence — that is, the prediction of its folding and its secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure from its primary structure. Structure prediction is fundamentally different from the inverse problem of protein design. Protein structure prediction is one of the most important goals pursued by bioinformatics and theoretical chemistry; it is highly important in medicine (for example, in drug design) and biotechnology (for example, in the design of novel enzymes). Every two years, the performance of current methods is assessed in the CASP experiment (Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction). A continuous evaluation of protein structure prediction web servers is performed by the community project CAMEO3D.












![Biochemistry_and_Digestion_2010[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008289894_1-a2dae968af20e40d29d6bcd9c3fab727-300x300.png)









