Lecture 11 Notes
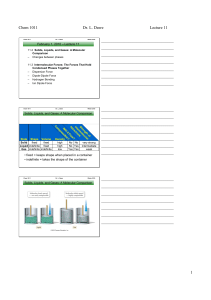
... Intermolecular forces explain many properties of liquids. (a) Molecules at the surface interact with other surface molecules and with molecules directly below the surface. (b) Molecules in the ...
... Intermolecular forces explain many properties of liquids. (a) Molecules at the surface interact with other surface molecules and with molecules directly below the surface. (b) Molecules in the ...
CH 13
... 2. The higher the concentration of molecules, the greater the # of collisions in unit time and a faster reaction 3. As the reactants are consumed the concentration decreases, collisions decrease, reaction rate decreases 4. Reaction rate decreases with time and eventually = 0, all reactants consumed ...
... 2. The higher the concentration of molecules, the greater the # of collisions in unit time and a faster reaction 3. As the reactants are consumed the concentration decreases, collisions decrease, reaction rate decreases 4. Reaction rate decreases with time and eventually = 0, all reactants consumed ...
KEY + + - UIC Department of Chemistry
... mass N2 possible = (0.0880778 mol NH3)(2 mol N2/4 mol NH3)(28.0134 g/1 mol N2) = 1.23 g N 2 (theoretical yield) Not possible to form 1.80 g N2. Can't make more N2 than the theoretical yield. ...
... mass N2 possible = (0.0880778 mol NH3)(2 mol N2/4 mol NH3)(28.0134 g/1 mol N2) = 1.23 g N 2 (theoretical yield) Not possible to form 1.80 g N2. Can't make more N2 than the theoretical yield. ...
Chemistry I
... Cl + e → Cl Negative ions = anions. anions. Cations derived from metal name (sodium (cat)ion (cat)ion,, silver (cat)ion (cat)ion)) or have the suffix –ium (NH4+ = ammonium ion) Anions from nonnon-metal atoms have the suffix –ide (chloride) in compounds with oxygen –ate (SO42-=sulfate) or –ite (SO32- ...
... Cl + e → Cl Negative ions = anions. anions. Cations derived from metal name (sodium (cat)ion (cat)ion,, silver (cat)ion (cat)ion)) or have the suffix –ium (NH4+ = ammonium ion) Anions from nonnon-metal atoms have the suffix –ide (chloride) in compounds with oxygen –ate (SO42-=sulfate) or –ite (SO32- ...
Chemistry - talcher autonomous college
... Kapustinskii expression for lattice energy. Madelung constant, Born-Haber cycle and its application, Solvation energy. (ii) Covalent bond: Lewis structure, Valence Bond theory (Heitler-London approach). Energetics of hybridization, equivalent and non-equivalent hybrid orbitals. Bent’s rule, Resonanc ...
... Kapustinskii expression for lattice energy. Madelung constant, Born-Haber cycle and its application, Solvation energy. (ii) Covalent bond: Lewis structure, Valence Bond theory (Heitler-London approach). Energetics of hybridization, equivalent and non-equivalent hybrid orbitals. Bent’s rule, Resonanc ...
chemistry - Rwanda Education Board
... In order to assist learners in having positive attitudes towards chemistry, confidence and thinking systematically, students have to be involved into the teaching and learning process. Good moral values can be cultivated through suitable contexts. Learning in groups should be emphasized to help lear ...
... In order to assist learners in having positive attitudes towards chemistry, confidence and thinking systematically, students have to be involved into the teaching and learning process. Good moral values can be cultivated through suitable contexts. Learning in groups should be emphasized to help lear ...
Catalytic decomposition of N2O over Rh/Zn–Al2O3 catalysts
... lead to more active catalysts due to the improved dispersion of Rh species.28 Parres-Esclapez et al. found that Sr can promote the activity of Rh/Al2O3 due to the improved dispersion and reducibility of Rh species.29 Zhao et al. reported that Rh/SiO2–Al2O3 shows high activity, because oxygen desorpt ...
... lead to more active catalysts due to the improved dispersion of Rh species.28 Parres-Esclapez et al. found that Sr can promote the activity of Rh/Al2O3 due to the improved dispersion and reducibility of Rh species.29 Zhao et al. reported that Rh/SiO2–Al2O3 shows high activity, because oxygen desorpt ...
3/23/2014 1 8 Chemical Equations Chapter Outline Chemical
... Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
... Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
Chapter 8
... Note: If polyatomic ions do not change, they can be balanced as a “unit”. © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
... Note: If polyatomic ions do not change, they can be balanced as a “unit”. © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
Chemistry FIFTH EDITION by Steven S. Zumdahl University of Illinois
... (1) Oxidation of SO2 (g) and SO3 (g) ...
... (1) Oxidation of SO2 (g) and SO3 (g) ...
Chemistry - Ysgol Bro Pedr
... Oxidation numbers can be used to show how many of each type of atom combine in compounds. It is the number of electrons that need to be added (or taken away from) an element to make it neutral. (You don’t need to learn this definition.) Eg, a calcium ion, Ca2+ needs two electrons added to it in orde ...
... Oxidation numbers can be used to show how many of each type of atom combine in compounds. It is the number of electrons that need to be added (or taken away from) an element to make it neutral. (You don’t need to learn this definition.) Eg, a calcium ion, Ca2+ needs two electrons added to it in orde ...
Chemistry (SPA)
... particle of matter. It translates to mean something that is indivisible. In the eighteenth century, chemist, John Dalton, revived the term when he suggested that each element was made up of unique atoms and the atoms of an element are all the same. At that time, there were about 35 known elements. T ...
... particle of matter. It translates to mean something that is indivisible. In the eighteenth century, chemist, John Dalton, revived the term when he suggested that each element was made up of unique atoms and the atoms of an element are all the same. At that time, there were about 35 known elements. T ...
2.3 ThermoChemistry - Chemistry Teaching Resources
... Calorimetry is the term used to describe the quantitative determination of the change in heat energy which occurs during a chemical reaction. ...
... Calorimetry is the term used to describe the quantitative determination of the change in heat energy which occurs during a chemical reaction. ...
chapter 4 - reactions in solution
... attractions of the ions for each other and the interactions of the ions for water molecules. If ion-dipole interactions are strong, compounds will not dissolve in water. Salt does not dissolve in nonpolar solvent, such as gasoline, because interactions between solvent molecules and ions are very w ...
... attractions of the ions for each other and the interactions of the ions for water molecules. If ion-dipole interactions are strong, compounds will not dissolve in water. Salt does not dissolve in nonpolar solvent, such as gasoline, because interactions between solvent molecules and ions are very w ...
Exam - Vcaa
... A student prepares 1.0 M aqueous solutions of AgNO3, Fe(NO3)2 and KNO3. Equal volumes of each solution are placed in separate beakers, identical platinum electrodes are placed in each beaker and each solution undergoes electrolysis with the same current applied for 5.0 minutes under SLC. Each cathod ...
... A student prepares 1.0 M aqueous solutions of AgNO3, Fe(NO3)2 and KNO3. Equal volumes of each solution are placed in separate beakers, identical platinum electrodes are placed in each beaker and each solution undergoes electrolysis with the same current applied for 5.0 minutes under SLC. Each cathod ...
Chemistry Entrance Material for Grade 11 to 12
... Variation of molar heat of vaporization 10. Which of the following liquids has the lowest molar heat of vaporization? Which one has the highest molar heat of vaporization? Which one has the highest vapour pressure at its boiling point? ...
... Variation of molar heat of vaporization 10. Which of the following liquids has the lowest molar heat of vaporization? Which one has the highest molar heat of vaporization? Which one has the highest vapour pressure at its boiling point? ...
Chemistry - Swami Ramanand Teerth Marathwada University
... Fusion of a solid. (ii) Vaporization of a liquid. (iii) Transition from one crystalline form to another. Entropy changes for an ideal gas as a function of V and T and as a function of P and T. Entropy changes of an ideal gas in different processes. Physical significance of entropy. ...
... Fusion of a solid. (ii) Vaporization of a liquid. (iii) Transition from one crystalline form to another. Entropy changes for an ideal gas as a function of V and T and as a function of P and T. Entropy changes of an ideal gas in different processes. Physical significance of entropy. ...
2.0 Chem 20 Final Review
... 2) From this chemical equation you can see that 13 mol of oxygen is required for every 2 mol of butane. Therefore, the volume of oxygen has to be greater than 120mL by a factor of 13/2. VO2: 120 ml C4H10 x ( 13 mL O2) 2 mL C4H10 ...
... 2) From this chemical equation you can see that 13 mol of oxygen is required for every 2 mol of butane. Therefore, the volume of oxygen has to be greater than 120mL by a factor of 13/2. VO2: 120 ml C4H10 x ( 13 mL O2) 2 mL C4H10 ...
Ch 4 Student
... consumed and limits amount of product • Reactant in excess – reactant present in greater quantity than limiting reactant • Theoretical Yield – amount of product made based on consumption of all the limiting reactant • Actual Yield – amount of product actually produced • Percent Yield – (actual/theor ...
... consumed and limits amount of product • Reactant in excess – reactant present in greater quantity than limiting reactant • Theoretical Yield – amount of product made based on consumption of all the limiting reactant • Actual Yield – amount of product actually produced • Percent Yield – (actual/theor ...
PPT
... OH + CH4 H2O + CH3 Basic requirements: A fast (ms to ms) method for detecting and quantifying [OH], as it decays via reaction with CH4. Generally, detection is via absorption or fluorescence-based methodologies. In this case, Laser-Induced Fluorescence (LIF) is used. ...
... OH + CH4 H2O + CH3 Basic requirements: A fast (ms to ms) method for detecting and quantifying [OH], as it decays via reaction with CH4. Generally, detection is via absorption or fluorescence-based methodologies. In this case, Laser-Induced Fluorescence (LIF) is used. ...
Reaction Kinetics Basics
... collide with a third molecular entity (e.g. a molecule or radical). In a unimolecular reaction, only one reaction partner species is changed. Examples include photochemical reactions (e.g. NO2 + hν ! NO + O, where hν represents a photon) and unimolecular decomposition such as the decomposition of fu ...
... collide with a third molecular entity (e.g. a molecule or radical). In a unimolecular reaction, only one reaction partner species is changed. Examples include photochemical reactions (e.g. NO2 + hν ! NO + O, where hν represents a photon) and unimolecular decomposition such as the decomposition of fu ...
- Kendriya Vidyalaya NKJ Katni
... Calculate the reaction rate when total pressure is 0.56 atm. 13. Decomposition of NH3 (g) on surface of catalyst 2NH3 à N2 (g) + 3H2(g) ...
... Calculate the reaction rate when total pressure is 0.56 atm. 13. Decomposition of NH3 (g) on surface of catalyst 2NH3 à N2 (g) + 3H2(g) ...
Chemistry IGCSE
... so quickly that they form bubbles of gas in the liquid. This is the boiling point at which the pressure of the gas forming above the liquid is the same as atmospheric pressure. On the other hand, cooling a gas will make its particles lose their kinetic energy and move closer and slower. Eventually t ...
... so quickly that they form bubbles of gas in the liquid. This is the boiling point at which the pressure of the gas forming above the liquid is the same as atmospheric pressure. On the other hand, cooling a gas will make its particles lose their kinetic energy and move closer and slower. Eventually t ...