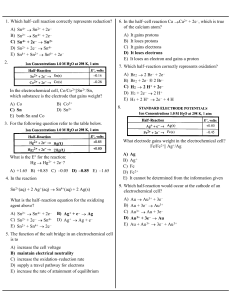
Bk2P06EE
... The temperature is maintained at 25 C. To determine the standard electrode potential of the I2(aq) / I(aq) system, a solution containing iodine and potassium iodide (each of concentration 1 mol dm3) is prepared. A platinum electrode is dipped into this solution. This is the I2(aq) / I(aq) half-c ...
... The temperature is maintained at 25 C. To determine the standard electrode potential of the I2(aq) / I(aq) system, a solution containing iodine and potassium iodide (each of concentration 1 mol dm3) is prepared. A platinum electrode is dipped into this solution. This is the I2(aq) / I(aq) half-c ...
College Grossmont 115
... or numbers obtained by definition. For example, we can count the fingers on our hand and get an exact number (most people have 5). There is no uncertainty in this result, but we cannot count large groups of objects without some degree of uncertainty. For example, the number of stars in our galaxy is ...
... or numbers obtained by definition. For example, we can count the fingers on our hand and get an exact number (most people have 5). There is no uncertainty in this result, but we cannot count large groups of objects without some degree of uncertainty. For example, the number of stars in our galaxy is ...
Web Appendix 6
... of potassium hydroxide, hydrochloric acid, and acetic acid are equal to their molar masses because each has but a single reactive hydrogen ion or hydroxide ion. Barium hydroxide, which contains two identical hydroxide ions, reacts with two hydrogen ions in any acid/base reaction, and so its equivale ...
... of potassium hydroxide, hydrochloric acid, and acetic acid are equal to their molar masses because each has but a single reactive hydrogen ion or hydroxide ion. Barium hydroxide, which contains two identical hydroxide ions, reacts with two hydrogen ions in any acid/base reaction, and so its equivale ...
revised Chemical Kinetics
... the mechanism by which chemical reactions proceed. It provides a rational approach to stabilization of drug products and prediction of shelf- life and optimum storage conditions. e.g. thiamine HCl is most stable at pH 2-3 and is unstable at pH above 6. If this is combined with a buffered vehicle of ...
... the mechanism by which chemical reactions proceed. It provides a rational approach to stabilization of drug products and prediction of shelf- life and optimum storage conditions. e.g. thiamine HCl is most stable at pH 2-3 and is unstable at pH above 6. If this is combined with a buffered vehicle of ...
3. d-Block elements. Biological role, application in medicine.
... Inside the cell the amount of Mg2+ is many times more, than in the extracellular space, whenСа2+ is predominantly extracellular cation. Mg2+ion is a stronger complex former than Са2+ ion. It serves as the center of some metalenzymes, for example, catalyzes animportant hydrolysis of ATP. Magnesium co ...
... Inside the cell the amount of Mg2+ is many times more, than in the extracellular space, whenСа2+ is predominantly extracellular cation. Mg2+ion is a stronger complex former than Са2+ ion. It serves as the center of some metalenzymes, for example, catalyzes animportant hydrolysis of ATP. Magnesium co ...
biogenic s, p, d-block elements, biological role, application in medicine
... Inside the cell the amount of Mg2+ is many times more, than in the extracellular space, whenСа2+ is predominantly extracellular cation. Mg2+ion is a stronger complex former than Са2+ ion. It serves as the center of some metalenzymes, for example, catalyzes animportant hydrolysis of ATP. Magnesium co ...
... Inside the cell the amount of Mg2+ is many times more, than in the extracellular space, whenСа2+ is predominantly extracellular cation. Mg2+ion is a stronger complex former than Са2+ ion. It serves as the center of some metalenzymes, for example, catalyzes animportant hydrolysis of ATP. Magnesium co ...
QUESTION BANK CHEMISTRY-XII THE SOLID STATE CHAPTER
... 35. What is the useful of initial rate method ? 36. What is known as activation energy ? 37. What are photochemical reactions? 38. What will be the effect of temperature on the rate constant? 39. State the role of activated complex in the reaction and state its relation with activati ...
... 35. What is the useful of initial rate method ? 36. What is known as activation energy ? 37. What are photochemical reactions? 38. What will be the effect of temperature on the rate constant? 39. State the role of activated complex in the reaction and state its relation with activati ...
A) Sn4+ → Sn2+ + 2e
... A) Br 2 will oxidize the chloride ion, but not the iodide ion. B) Br2 will oxidize the iodide ion, but not the chloride ion. C) I 2 will oxidize the chloride ion, but not the bromide ion. D) I 2 will oxidize the chloride ion, but not the bromide ion. E) Cl 2 will oxidize the bromide ion, but not the ...
... A) Br 2 will oxidize the chloride ion, but not the iodide ion. B) Br2 will oxidize the iodide ion, but not the chloride ion. C) I 2 will oxidize the chloride ion, but not the bromide ion. D) I 2 will oxidize the chloride ion, but not the bromide ion. E) Cl 2 will oxidize the bromide ion, but not the ...
Campbell Biology, 10e (Reece) Chapter 2 The Chemical Context of
... A) the number of electrons in the element B) the number of protons in the element C) the number of protons plus neutrons in the element D) the number of protons plus electrons in the element Answer: C Bloom's Taxonomy: Application/Analysis Section: 2.2 6) In what way are elements in the same column ...
... A) the number of electrons in the element B) the number of protons in the element C) the number of protons plus neutrons in the element D) the number of protons plus electrons in the element Answer: C Bloom's Taxonomy: Application/Analysis Section: 2.2 6) In what way are elements in the same column ...
sec chemistry may 2011 marking scheme
... • Light is a form of energy and therefore it increases the rate of reaction / the energy of the reactants increases. • Reaction is photo-catalysed. The green colour of the chlorine gas disappears as the reaction proceeds. ...
... • Light is a form of energy and therefore it increases the rate of reaction / the energy of the reactants increases. • Reaction is photo-catalysed. The green colour of the chlorine gas disappears as the reaction proceeds. ...
Full Text PDF
... the second group μeffisbgerthanμSo,.p-biculngrsoyfthe ions of the second group. This trend can be easily justified if one supposes that kSE increases as the density of unpaired metal electrons increases at the collision site between complex and Ps atom (i.e. at the _complex boundaries and that the e ...
... the second group μeffisbgerthanμSo,.p-biculngrsoyfthe ions of the second group. This trend can be easily justified if one supposes that kSE increases as the density of unpaired metal electrons increases at the collision site between complex and Ps atom (i.e. at the _complex boundaries and that the e ...
Chem 150 Unit 2 - Hydrocarbons & Functional Groups
... Since all molecules have the London dispersion interaction, the boiling points of molecules is expected to increase with temperature. ...
... Since all molecules have the London dispersion interaction, the boiling points of molecules is expected to increase with temperature. ...
Adsorption studies of cyanide onto activated carbon
... does not appear to meet the strict regulatory requirements, and as for the fourth process, it is limited to certain climate conditions. The next best process used, is the oxidation with hydrogen peroxide where the cyanide concentration is reduced to low enough levels, but this process requires an ex ...
... does not appear to meet the strict regulatory requirements, and as for the fourth process, it is limited to certain climate conditions. The next best process used, is the oxidation with hydrogen peroxide where the cyanide concentration is reduced to low enough levels, but this process requires an ex ...
class xii – preparatory examination - 1
... [NiCl4]2- has tetrahedral geometry and paramagnetic.Explain these characteristics on the basis of hybridization of orbitals.[At no. of Ni=28] ii) Give an example of coordination compounds used in biological systems. 25. Complete the following reactions and balance them : i) NH3 + NaOCl ---- ii) P4O ...
... [NiCl4]2- has tetrahedral geometry and paramagnetic.Explain these characteristics on the basis of hybridization of orbitals.[At no. of Ni=28] ii) Give an example of coordination compounds used in biological systems. 25. Complete the following reactions and balance them : i) NH3 + NaOCl ---- ii) P4O ...
Chapter 12
... amine adduct with BF3 . Since the enthalpy of adduct formation is least favorable with BF3, however, it is concluded that the loss in BX double-bond character upon rehybridization to form an adduct is greater with BF3 than in the other tri halides. From this we can conclude that the double-bond cha ...
... amine adduct with BF3 . Since the enthalpy of adduct formation is least favorable with BF3, however, it is concluded that the loss in BX double-bond character upon rehybridization to form an adduct is greater with BF3 than in the other tri halides. From this we can conclude that the double-bond cha ...
3: Haloalkanes, Alcohols, Ethers, and Amines
... F attracts electrons more than C in C-F bonds because the electronegativity of F (3.9) is much greater than that of C (2.5). In contrast, C-H bonds are not very polar because the electronegativities of H (2.3) and C (2.5) are about the same. Positive (+) values for the electronegativity differences ...
... F attracts electrons more than C in C-F bonds because the electronegativity of F (3.9) is much greater than that of C (2.5). In contrast, C-H bonds are not very polar because the electronegativities of H (2.3) and C (2.5) are about the same. Positive (+) values for the electronegativity differences ...
Chemistry HSC - The Bored of Studies Community
... Polymerisation is the process of bonding monomers together to form long chains. Polymers are macromolecules consisting of small repeating units called monomers joined by covalent chemical bonds. Polymers can be divided into two categories: 1. Natural polymers – naturally occurring polymers used by h ...
... Polymerisation is the process of bonding monomers together to form long chains. Polymers are macromolecules consisting of small repeating units called monomers joined by covalent chemical bonds. Polymers can be divided into two categories: 1. Natural polymers – naturally occurring polymers used by h ...
Covalent Bonding and Nomenclature
... Compounds formed when atoms covalently bond are called molecular compounds. Binary molecular compounds are generally composed of two nonmetallic elements. When two nonmetallic elements combine, they often do so in more than one way. For example carbon can combine with oxygen to form carbon dioxide, ...
... Compounds formed when atoms covalently bond are called molecular compounds. Binary molecular compounds are generally composed of two nonmetallic elements. When two nonmetallic elements combine, they often do so in more than one way. For example carbon can combine with oxygen to form carbon dioxide, ...
answers to part a of the national high school
... These answers are designed to help students who are preparing to take the Canadian National High School Chemistry Examination in 2007 or subsequent years. Note that information given here will generally not include material from answers given for previous years exams, so that students should go thr ...
... These answers are designed to help students who are preparing to take the Canadian National High School Chemistry Examination in 2007 or subsequent years. Note that information given here will generally not include material from answers given for previous years exams, so that students should go thr ...
www.xtremepapers.net
... A study was carried out in which both [H2O2] and [H+] were kept constant at 0.05 mol dm–3, and [I–] was plotted against time. The following curve was obtained. ...
... A study was carried out in which both [H2O2] and [H+] were kept constant at 0.05 mol dm–3, and [I–] was plotted against time. The following curve was obtained. ...
Analyze
... Octane at –57˚C is a solid just about to melt. As energy is added the solid octane melts and its temperature does not change until all the solid is melted. Only when octane is entirely liquid does added energy increase the temperature of the liquid until the boiling point of octane is reached. Durin ...
... Octane at –57˚C is a solid just about to melt. As energy is added the solid octane melts and its temperature does not change until all the solid is melted. Only when octane is entirely liquid does added energy increase the temperature of the liquid until the boiling point of octane is reached. Durin ...