Final Exam Practice-2017
... 20. Examine the Lewis structure for propanal, C3H6O. Which of the following descriptions about its structure is correct? a) This is a correct Lewis structure b) There are too many electrons in this diagram. The lone pair on carbon should be removed. c) There are too many electrons in this diagram. T ...
... 20. Examine the Lewis structure for propanal, C3H6O. Which of the following descriptions about its structure is correct? a) This is a correct Lewis structure b) There are too many electrons in this diagram. The lone pair on carbon should be removed. c) There are too many electrons in this diagram. T ...
PPT - Unit 5
... DH = - 537kJ C (s) + 2 F2 (g) CF4 (g) DH = - 680 kJ 2 C (s) + 2 H2 (g) C2H4 (g) DH = + 52.3 kJ Calculate the DH for the reaction of ethylene with F2. C2H4 (g) + 6F2 (g) 2 CF4 (g) + 4 HF(g) ...
... DH = - 537kJ C (s) + 2 F2 (g) CF4 (g) DH = - 680 kJ 2 C (s) + 2 H2 (g) C2H4 (g) DH = + 52.3 kJ Calculate the DH for the reaction of ethylene with F2. C2H4 (g) + 6F2 (g) 2 CF4 (g) + 4 HF(g) ...
part 3 - instructor version
... Historical definition = gain of oxygen (sometimes with a simultaneous loss of hydrogen) e.g. C2H6 + O2 CO2 + H2O Modern definition = loss of electrons ...
... Historical definition = gain of oxygen (sometimes with a simultaneous loss of hydrogen) e.g. C2H6 + O2 CO2 + H2O Modern definition = loss of electrons ...
AQA C2 revision book
... There are 4 main structures which substances can have. These are known as: SIMPLE MOLECULAR., GIANT COVALENT, GIANT IONIC and GIANT METALLIC Simple Molecular. Simple molecular substances have small molecules, such as H2O or CO2. The atoms in these molecules are held together by strong forces called ...
... There are 4 main structures which substances can have. These are known as: SIMPLE MOLECULAR., GIANT COVALENT, GIANT IONIC and GIANT METALLIC Simple Molecular. Simple molecular substances have small molecules, such as H2O or CO2. The atoms in these molecules are held together by strong forces called ...
Student Worksheet The Chemistry of Water Quality Tests
... relative strength of interactions among and between the components. b. The translation of an observed chemical change into a balanced chemical equation and justification of the choice of equation type (molecular, ionic, or net ionic) in terms of utility for the given circumstances. c. Production of ...
... relative strength of interactions among and between the components. b. The translation of an observed chemical change into a balanced chemical equation and justification of the choice of equation type (molecular, ionic, or net ionic) in terms of utility for the given circumstances. c. Production of ...
South Pasadena · AP Chemistry
... 115 grams/mol. Determine the empirical formula and the molecular formula of the compound. 13. Sodium metal reacts vigorously with water to produce a solution of sodium hydroxide and hydrogen gas: 2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g) What mass of hydrogen gas can be produced when 10 grams of sodium i ...
... 115 grams/mol. Determine the empirical formula and the molecular formula of the compound. 13. Sodium metal reacts vigorously with water to produce a solution of sodium hydroxide and hydrogen gas: 2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g) What mass of hydrogen gas can be produced when 10 grams of sodium i ...
Question Paper
... 21. i) Define “Standard Enthalpy of Vapourisation’. ii) Write thermo chemical equation for vaporisation of Ethanol (C2H5OH). iii) Calculate the enthalpy of vapourisation of Ethanol, given enthalpies of formation of liquid Ethanol and gaseous Ethanol as – 277.6 kJ and -235.4 kJ respectively. 22. a) ...
... 21. i) Define “Standard Enthalpy of Vapourisation’. ii) Write thermo chemical equation for vaporisation of Ethanol (C2H5OH). iii) Calculate the enthalpy of vapourisation of Ethanol, given enthalpies of formation of liquid Ethanol and gaseous Ethanol as – 277.6 kJ and -235.4 kJ respectively. 22. a) ...
Introduction(s)
... 3. All metal chlorides, bromides, and iodides are soluble, except those of Ag1+, Hg22+, and Pb2+. 4. All sulfates are soluble except those of Ca2+, Ba2+, Sr2+, Ag1+, Hg22+, and Pb2+ 5. Except for those in Rule #1, everything else is ...
... 3. All metal chlorides, bromides, and iodides are soluble, except those of Ag1+, Hg22+, and Pb2+. 4. All sulfates are soluble except those of Ca2+, Ba2+, Sr2+, Ag1+, Hg22+, and Pb2+ 5. Except for those in Rule #1, everything else is ...
Memorization?
... 3. All metal chlorides, bromides, and iodides are soluble, except those of Ag1+, Hg22+, and Pb2+. 4. All sulfates are soluble except those of Ca2+, Ba2+, Sr2+, Ag1+, Hg22+, and Pb2+ 5. Except for those in Rule #1, everything else is ...
... 3. All metal chlorides, bromides, and iodides are soluble, except those of Ag1+, Hg22+, and Pb2+. 4. All sulfates are soluble except those of Ca2+, Ba2+, Sr2+, Ag1+, Hg22+, and Pb2+ 5. Except for those in Rule #1, everything else is ...
Final Review
... c. fructose d. maltose e. cellulose f. glucose Identify the storage form of glucose in animals and in plants. Identify the structural form of glucose in plants. Match the monomer to the polymer (monomers can be used more than once): POLYMER: 1. cellulose 3. DNA 5. starch 7. RNA 2. protein 4. lipid 6 ...
... c. fructose d. maltose e. cellulose f. glucose Identify the storage form of glucose in animals and in plants. Identify the structural form of glucose in plants. Match the monomer to the polymer (monomers can be used more than once): POLYMER: 1. cellulose 3. DNA 5. starch 7. RNA 2. protein 4. lipid 6 ...
Chemistry Lesson Plans #07 - Chemical Reactions
... millions of possible compounds o Just as we learned how to identify compounds (molecular and ionic) there are several ways to categorize chemical reactions Combination – two or more substances form a new compound Decomposition – a single compound is broken down into two or more products Single-Repla ...
... millions of possible compounds o Just as we learned how to identify compounds (molecular and ionic) there are several ways to categorize chemical reactions Combination – two or more substances form a new compound Decomposition – a single compound is broken down into two or more products Single-Repla ...
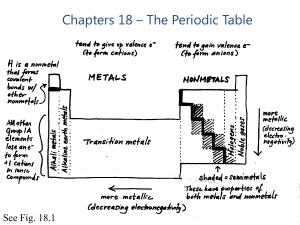
Chapters 18 – The Periodic Table
... trisulfide (P4S3), glass and binder. The phosphorus sulfide is easily ignited, the potassium chlorate decomposes to give oxygen, which in turn causes the phosphorus sulfide to burn more vigorously. The head of safety matches are made of an oxidizing agent such as potassium chlorate, mixed with sulfu ...
... trisulfide (P4S3), glass and binder. The phosphorus sulfide is easily ignited, the potassium chlorate decomposes to give oxygen, which in turn causes the phosphorus sulfide to burn more vigorously. The head of safety matches are made of an oxidizing agent such as potassium chlorate, mixed with sulfu ...
Cl Cl and
... Too much energy is needed to remove 4 electrons from an atom. Too much energy is needed to insert 4 electrons into an atom in order to overcome the repulsive forces between like charges. 28. Why do elements of groups 6 and 7 form ions of charge –2 and –1 respectively? By gaining electrons they achie ...
... Too much energy is needed to remove 4 electrons from an atom. Too much energy is needed to insert 4 electrons into an atom in order to overcome the repulsive forces between like charges. 28. Why do elements of groups 6 and 7 form ions of charge –2 and –1 respectively? By gaining electrons they achie ...
Chapter 8
... 1. Some oxy-acids, when heated, decompose to form water and the nonmetal oxide. Example: Sulfuric acid is heated Example: Nitric acid is heated 2. Some metallic hydroxides (bases), when heated, decompose to form the metal oxide and water. Example: Sodium hydroxide is heated Example: Calcium hydroxid ...
... 1. Some oxy-acids, when heated, decompose to form water and the nonmetal oxide. Example: Sulfuric acid is heated Example: Nitric acid is heated 2. Some metallic hydroxides (bases), when heated, decompose to form the metal oxide and water. Example: Sodium hydroxide is heated Example: Calcium hydroxid ...
SAMPLE PAPER -2 Time Allowed: 3 Hrs
... When an chlorine atom, which is an electron withdrawing group is present in the chain attached to a carboxyl group, it exerts -I effect and withdraws electrons from the carbon of the carboxyl group as well as from the oxygen of the O-H bond. This decreases electron density at the oxygen atom of the ...
... When an chlorine atom, which is an electron withdrawing group is present in the chain attached to a carboxyl group, it exerts -I effect and withdraws electrons from the carbon of the carboxyl group as well as from the oxygen of the O-H bond. This decreases electron density at the oxygen atom of the ...
Enthalpy diagram relating the change for a reaction to enthalpies of
... 1. Physical state of the reactants: when reactants are in different phases for example when a solid reacts with a liquid the reaction is limited to the area of contact. Reactions involving solids will proceed faster if the surface area of the solid is increased. 2. Concentration of the reactants: as ...
... 1. Physical state of the reactants: when reactants are in different phases for example when a solid reacts with a liquid the reaction is limited to the area of contact. Reactions involving solids will proceed faster if the surface area of the solid is increased. 2. Concentration of the reactants: as ...
Section 16.1 A Model for Reaction Rates
... Collision Theory (cont.) • The minimum amount of energy that reacting particles must have to form the activated complex and lead to a reaction is called the activation energy ”Ea”. •A high Ea means that relatively few collisions have the required energy to produce the activated complex, and the rea ...
... Collision Theory (cont.) • The minimum amount of energy that reacting particles must have to form the activated complex and lead to a reaction is called the activation energy ”Ea”. •A high Ea means that relatively few collisions have the required energy to produce the activated complex, and the rea ...
Power point types of chemical rxn
... 1. Elements that form ionic compounds: Magnesium metal reacts with oxygen gas to form magnesium oxide. • 2Mg + O2 2MgO 2. Elements that form covalent compounds: Nitrogen gas and oxygen gas join to form dinitrogen monoxide. • 2N2 + O2 2N2O SYNTHESIS REACTION (iron + sulphur): http://www.youtube.c ...
... 1. Elements that form ionic compounds: Magnesium metal reacts with oxygen gas to form magnesium oxide. • 2Mg + O2 2MgO 2. Elements that form covalent compounds: Nitrogen gas and oxygen gas join to form dinitrogen monoxide. • 2N2 + O2 2N2O SYNTHESIS REACTION (iron + sulphur): http://www.youtube.c ...
Midterm 2 from Summer 2012
... 45.7 mL of 0.500 M H2SO4 is required to completely neutralize an NaOH solution. How many grams of NaOH were required to carry-out this neutralization? ...
... 45.7 mL of 0.500 M H2SO4 is required to completely neutralize an NaOH solution. How many grams of NaOH were required to carry-out this neutralization? ...
P. Mignon, J. Steyaert, R. Loris, P. Geerlings, and S. Loverix, J. Biol
... negatively charged Glu-58 carboxylate (the catalytic base) and/or the positively charged His-40 imidazolium lowers the Mulliken charge on the 2⬘-oxygen atom, thus affecting its nucleophilicity. In the wild type enzyme, the 2⬘-atomic charge and the polarity of the 2⬘-hydroxyl are maximal, illustratin ...
... negatively charged Glu-58 carboxylate (the catalytic base) and/or the positively charged His-40 imidazolium lowers the Mulliken charge on the 2⬘-oxygen atom, thus affecting its nucleophilicity. In the wild type enzyme, the 2⬘-atomic charge and the polarity of the 2⬘-hydroxyl are maximal, illustratin ...