THE CEREBRAL CORTEX
... bound up with the prodigious abundance and unusual wealth of forms of the so-called neurons with the short axons. ...
... bound up with the prodigious abundance and unusual wealth of forms of the so-called neurons with the short axons. ...
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY STUDY GUIDE
... What does the somatic sensory area allow you to do? Which side of the sensory cortex receives impulses from the right side of the body? Tell what is interpreted in each of these areas: parietal lobe, occipital lobe, temporal lobe. What part of the brain allows us to consciously move our skeletal mus ...
... What does the somatic sensory area allow you to do? Which side of the sensory cortex receives impulses from the right side of the body? Tell what is interpreted in each of these areas: parietal lobe, occipital lobe, temporal lobe. What part of the brain allows us to consciously move our skeletal mus ...
Cognitive Neuroscience
... Which mechanisms? Analogies with computers? RAM, CPU? Logic? Those are poor analogies. ...
... Which mechanisms? Analogies with computers? RAM, CPU? Logic? Those are poor analogies. ...
Lec 18 - Forgetting
... Forgetting (retention loss) refers to apparent loss of information already encoded and stored in an individual's long term memory. It is a spontaneous or gradual process in which oldmemories are unable to be recalled from memory storage. It is subject to delicately balanced optimization that ensures ...
... Forgetting (retention loss) refers to apparent loss of information already encoded and stored in an individual's long term memory. It is a spontaneous or gradual process in which oldmemories are unable to be recalled from memory storage. It is subject to delicately balanced optimization that ensures ...
MIND: The Cognitive Side of Mind and Brain
... assess aspects of perception, attention, and memory. Models of mental structures and processes of human perception, attention, memory, etc. based on data obtained from solid experimental procedures ...
... assess aspects of perception, attention, and memory. Models of mental structures and processes of human perception, attention, memory, etc. based on data obtained from solid experimental procedures ...
Neuroscience - HuskiesScience
... – Almost all sensory information passes through before going elsewhere ...
... – Almost all sensory information passes through before going elsewhere ...
Mind, Brain & Behavior
... Posterior when sensory input shifts attention. Frontal when a motor response is made. ...
... Posterior when sensory input shifts attention. Frontal when a motor response is made. ...
ap psychology
... AIM: Explain how neurons are at the center of our existence. How does neural communication relate to behavior? ...
... AIM: Explain how neurons are at the center of our existence. How does neural communication relate to behavior? ...
The Cerebral Cortex
... 12.2, a somatosensory and motor homunculus is drawn to explain which functions of the body take up more or less space on the cortex. Using that diagram, answer the following questions Which area(s) of the body is/are depicted as overly Why would these structures need greater space in large in the mo ...
... 12.2, a somatosensory and motor homunculus is drawn to explain which functions of the body take up more or less space on the cortex. Using that diagram, answer the following questions Which area(s) of the body is/are depicted as overly Why would these structures need greater space in large in the mo ...
BN21 subcortical motor control
... Subcortical Motor Systems: Cerebellum & Basal Ganglia Lecture 21 ...
... Subcortical Motor Systems: Cerebellum & Basal Ganglia Lecture 21 ...
I. Nerve Organization
... C. Forebrain: Most recent evolutionary component of brain. 1. Divided into two hemispheres 2. Cerebrum in mammals. 3. Thalamus: Relay or bridge to Cerebrum 4. Hypothalamus: Links brain with endocrine system; controls homeostatis. ...
... C. Forebrain: Most recent evolutionary component of brain. 1. Divided into two hemispheres 2. Cerebrum in mammals. 3. Thalamus: Relay or bridge to Cerebrum 4. Hypothalamus: Links brain with endocrine system; controls homeostatis. ...
text - Systems Neuroscience Course, MEDS 371, Univ. Conn. Health
... CNS before reaching cerebral cortex stop in the thalamus. Thalamus is an integration center- it receives reciprocal connections from the cortex, cerebellum and basal ganglia. It contains several groups of nuclei that are designated for various functions (see Table at the end of the syllabus). Nuclei ...
... CNS before reaching cerebral cortex stop in the thalamus. Thalamus is an integration center- it receives reciprocal connections from the cortex, cerebellum and basal ganglia. It contains several groups of nuclei that are designated for various functions (see Table at the end of the syllabus). Nuclei ...
U3 Neurobiology Summary
... (e) Cerebral cortex is the centre of conscious thought; it also recalls memories and alters decision making behaviour in the light of experience. The cerebral cortex also receives sensory information and coordinates voluntary movement. (f) Different parts of the cerebrum control different aspects of ...
... (e) Cerebral cortex is the centre of conscious thought; it also recalls memories and alters decision making behaviour in the light of experience. The cerebral cortex also receives sensory information and coordinates voluntary movement. (f) Different parts of the cerebrum control different aspects of ...
The human brain
... After a neuron has fired, it takes it about one millisecond to return to its normal state. ...
... After a neuron has fired, it takes it about one millisecond to return to its normal state. ...
Bell Work - Boone County Schools
... »You have two minute to write down as many of the words as you can remember, GO! »How many did you get? _____ ...
... »You have two minute to write down as many of the words as you can remember, GO! »How many did you get? _____ ...
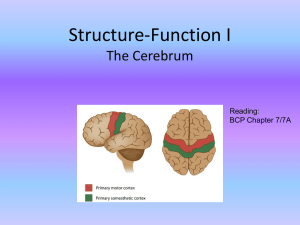
Structure-Function I
... reward learning, and in addiction. The nucleus basalis plays a role in the sleep-wake cycle and learning and memory (this nucleus undergoes damage in Alzheimer’s disease). ...
... reward learning, and in addiction. The nucleus basalis plays a role in the sleep-wake cycle and learning and memory (this nucleus undergoes damage in Alzheimer’s disease). ...
The human brain - "G. Galilei" – Pescara
... Brain : the part of the central nervous system enclosed in the cranium of humans and other vertebrates, consisting of a soft, convoluted mass of grey and white matter and serving to control and coordinate the mental and physical actions. Brainstem : is the posterior part of the brain which includes ...
... Brain : the part of the central nervous system enclosed in the cranium of humans and other vertebrates, consisting of a soft, convoluted mass of grey and white matter and serving to control and coordinate the mental and physical actions. Brainstem : is the posterior part of the brain which includes ...
Sensory Cells and Transduction of Stimuli
... Sensory Receptors • When receptors are triggered, they open up Na+ and K+ channels to trigger an action potential ...
... Sensory Receptors • When receptors are triggered, they open up Na+ and K+ channels to trigger an action potential ...
THE VISUAL SYSTEM PERIPHERAL MECHANISMS 1) Light enters
... b. Information goes to layer 4 of cx (monocular input), begins to mix as it projects to other layers (binocular input) c. Properties of receptive field change: from spot detector to bar/edge detector (then corner detector, finally complex celsl that rebuild image) d. Each column has preference for b ...
... b. Information goes to layer 4 of cx (monocular input), begins to mix as it projects to other layers (binocular input) c. Properties of receptive field change: from spot detector to bar/edge detector (then corner detector, finally complex celsl that rebuild image) d. Each column has preference for b ...
Myers AP - Unit 03B PowerPoint
... = a visual display of brain activity that detects where a radioactive form of glucose goes while the ...
... = a visual display of brain activity that detects where a radioactive form of glucose goes while the ...
Slide 1
... Broca’s Limbic Lobe – Cortex forming a ring around corpus callosum: Cingulate gyrus, medial surface temporal lobe, hippocampus ...
... Broca’s Limbic Lobe – Cortex forming a ring around corpus callosum: Cingulate gyrus, medial surface temporal lobe, hippocampus ...
Learning Activity 1
... 3 The cerebral cortex consists mainly of neurons. 4 Cortical areas may be classifi ed as: • sensory cortex areas, which receive and process information from our different senses • motor cortex area, which receives, processes and sends information about voluntary bodily movements • association cortex ...
... 3 The cerebral cortex consists mainly of neurons. 4 Cortical areas may be classifi ed as: • sensory cortex areas, which receive and process information from our different senses • motor cortex area, which receives, processes and sends information about voluntary bodily movements • association cortex ...
中原大學 95 學年度 碩士班入學考試
... c. serial searches take longer as the list of items to be searched gets longer. d. connectionist theories do not account for interference in long-term memory. 21. If you visited the old neighborhood where you grew up, you might recall events and other memories from many years earlier. The cues to me ...
... c. serial searches take longer as the list of items to be searched gets longer. d. connectionist theories do not account for interference in long-term memory. 21. If you visited the old neighborhood where you grew up, you might recall events and other memories from many years earlier. The cues to me ...
Neuroanatomy of memory

The neuroanatomy of memory encompasses a wide variety of anatomical structures in the brain.