The relative advantages of sparse versus distributed encoding for
... extent to which this statement is valid in general is discussed here, by considering some simple formal models of associative memory which include different neurobiological constraints. In nets of linear neurons, trained with either a Hebbian (purely incremental) or a Stanton and Sejnowski learning ...
... extent to which this statement is valid in general is discussed here, by considering some simple formal models of associative memory which include different neurobiological constraints. In nets of linear neurons, trained with either a Hebbian (purely incremental) or a Stanton and Sejnowski learning ...
Long-term memory - Universitas Ciputra
... Memory types based on retention • Sensory memory memory bits from our sensory is automatically stored • Short term memory also coined as working memory, this is where information is received and processed • Long-term memory Keeps a lot of information over a long period of time. Visual Communication ...
... Memory types based on retention • Sensory memory memory bits from our sensory is automatically stored • Short term memory also coined as working memory, this is where information is received and processed • Long-term memory Keeps a lot of information over a long period of time. Visual Communication ...
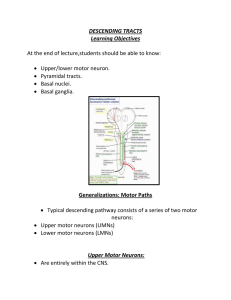
DESCENDING TRACTS Learning Objectives At the end of lecture
... Sequence movements. Regulate muscle tone and muscle force. May be involved in selecting and inhibiting specific motor synergies. ...
... Sequence movements. Regulate muscle tone and muscle force. May be involved in selecting and inhibiting specific motor synergies. ...
kainic acid oxidative stress J Appl Toxicol 2001
... seems that hypothalamus, striatum and cerebral cortex are resistant to KA-induced oxidative injury. The mechanisms underlying this highly region-specific pattern of oxidative damage are far from being well understood. In an attempt to explain, at least partially, this selective pattern of oxidative ...
... seems that hypothalamus, striatum and cerebral cortex are resistant to KA-induced oxidative injury. The mechanisms underlying this highly region-specific pattern of oxidative damage are far from being well understood. In an attempt to explain, at least partially, this selective pattern of oxidative ...
ppt file
... nucleus accumbens, globus pallidus, substantia nigra, subthalamic nucleus. • In principle the claustrum and the amygdala are part of this collection. ...
... nucleus accumbens, globus pallidus, substantia nigra, subthalamic nucleus. • In principle the claustrum and the amygdala are part of this collection. ...
Attention and Consciousness
... “Contrary to past beliefs, many aspects of consciousness are not untestable at all, as shown by productive research traditions on topics like attention, perception, psychophysics, problem solving, thought monitoring, imagery, dream research, and so on.“ ...
... “Contrary to past beliefs, many aspects of consciousness are not untestable at all, as shown by productive research traditions on topics like attention, perception, psychophysics, problem solving, thought monitoring, imagery, dream research, and so on.“ ...
Group 3, Week 10
... 1. Discuss the relationship of BG and hippocampus to place and response strategies. The authors suggest that the hippocampus does not compete with or function independently of the dorsal striatum. They can act together with other regions, such as the medial and ventral striatal regions form a funct ...
... 1. Discuss the relationship of BG and hippocampus to place and response strategies. The authors suggest that the hippocampus does not compete with or function independently of the dorsal striatum. They can act together with other regions, such as the medial and ventral striatal regions form a funct ...
Understanding Eye Movements Primary Motor Pathway
... Supranuclear: descending fibers from cerebral hemispheres to brain stem (frontal eye fields) ...
... Supranuclear: descending fibers from cerebral hemispheres to brain stem (frontal eye fields) ...
Cognition and miniature brain: What we can learn from a honeybee
... The incapacity of bees to solve positive & negative patterning in the absence of functional mushroom bodies was not due to side-effects of procaine as elemental differential conditioning was not impaired by mushroom body blockade. Mushroom bodies are required for solving non-elemental, ambiguous (co ...
... The incapacity of bees to solve positive & negative patterning in the absence of functional mushroom bodies was not due to side-effects of procaine as elemental differential conditioning was not impaired by mushroom body blockade. Mushroom bodies are required for solving non-elemental, ambiguous (co ...
Spikes not slots: noise in neural populations limits
... Figure 2. Evidence for normalisation in working memory (WM)-related neural activity. (A) Firing rate of an example prefrontal neuron with persistent WM activity. Firing rate declines with increasing memory load, whether the stimulus in the receptive field corresponds to a preferred (unbroken lines) ...
... Figure 2. Evidence for normalisation in working memory (WM)-related neural activity. (A) Firing rate of an example prefrontal neuron with persistent WM activity. Firing rate declines with increasing memory load, whether the stimulus in the receptive field corresponds to a preferred (unbroken lines) ...
Unit K: The Human Body
... Items referring to the male human reproductive system are limited to the seminal vesicle, prostate gland, vas deferens, urethra,epididymis, scrotum, penis, and testes. Items referring to the female human reproductive system are limited to the ovaries, oviduct (fallopian tube), uterus, cervix, and va ...
... Items referring to the male human reproductive system are limited to the seminal vesicle, prostate gland, vas deferens, urethra,epididymis, scrotum, penis, and testes. Items referring to the female human reproductive system are limited to the ovaries, oviduct (fallopian tube), uterus, cervix, and va ...
The Central Nervous System
... Now, let us move on to the neuron. As will be the general pattern of behavior for SPPA 205, we will begin discussion of the neuron with its basic structure, followed by its function. Although there is a great deal of diversity in the look of neurons, the vast majority of neurons have four structural ...
... Now, let us move on to the neuron. As will be the general pattern of behavior for SPPA 205, we will begin discussion of the neuron with its basic structure, followed by its function. Although there is a great deal of diversity in the look of neurons, the vast majority of neurons have four structural ...
DESCENDING TRACTS
... Sequence movements. Regulate muscle tone and muscle force. May be involved in selecting and inhibiting specific motor synergies. ...
... Sequence movements. Regulate muscle tone and muscle force. May be involved in selecting and inhibiting specific motor synergies. ...
Perception - Vision
... Perception is comparatively the easiest to understand although for many specific questions there are no clear answers. ...
... Perception is comparatively the easiest to understand although for many specific questions there are no clear answers. ...
Cognitive Informatics Models of the Brain
... long as the human history itself. The study of the brain was originally conducted in the domain of philosophy. Plato (428–347 B.C.) observed that the philosophy begins in human wonder, a powerful desire to understand the world, not merely to act in it as animals do. Aristotle (394–322 B.C.) perceive ...
... long as the human history itself. The study of the brain was originally conducted in the domain of philosophy. Plato (428–347 B.C.) observed that the philosophy begins in human wonder, a powerful desire to understand the world, not merely to act in it as animals do. Aristotle (394–322 B.C.) perceive ...
3.2 Our Brains Control Our Thoughts, Feelings, and Behavior
... difficulty walking, keeping their balance, and holding their hands steady. Consuming alcohol influences the cerebellum, which is why people who are drunk have more difficulty walking in a straight line. Also, the cerebellum contributes to emotional responses, helps us discriminate between different ...
... difficulty walking, keeping their balance, and holding their hands steady. Consuming alcohol influences the cerebellum, which is why people who are drunk have more difficulty walking in a straight line. Also, the cerebellum contributes to emotional responses, helps us discriminate between different ...
day2-morning2
... achivement and personal happiness may depend on our ability to listen efficiently. • Listening is an important method for learning at all academic levels. ...
... achivement and personal happiness may depend on our ability to listen efficiently. • Listening is an important method for learning at all academic levels. ...
The Human Body
... “Essential understandings,” or generalizations, represent ideas that are transferable to other contexts. ...
... “Essential understandings,” or generalizations, represent ideas that are transferable to other contexts. ...
File
... • Most complicated cortical region • Involved with intellect, cognition, recall, and personality • Contains working memory needed for judgment, reasoning, persistence, and conscience • Development depends on feedback from social environment ...
... • Most complicated cortical region • Involved with intellect, cognition, recall, and personality • Contains working memory needed for judgment, reasoning, persistence, and conscience • Development depends on feedback from social environment ...
Laboratory Exercise 11: Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain
... a visual reflex center; two lower ones, the inferior colliculi, an auditory reflex center. These reflex centers control movements of the eyes, head, and trunk to visual and auditory stimuli. Hindbrain Pons - lies between midbrain and medulla. Function: The pons provides a nerve tract path between ce ...
... a visual reflex center; two lower ones, the inferior colliculi, an auditory reflex center. These reflex centers control movements of the eyes, head, and trunk to visual and auditory stimuli. Hindbrain Pons - lies between midbrain and medulla. Function: The pons provides a nerve tract path between ce ...
Neuroanatomy of memory

The neuroanatomy of memory encompasses a wide variety of anatomical structures in the brain.